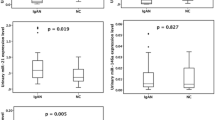
Abstract
Recent studies have suggested that gene expression studies using urinary sediment might be a non-invasive approach to assessing activity and pathogenesis in glomerulonephritis. However, little information is available regarding the mRNA expression patterns of functional molecules, such as T-bet, GATA-3, FOXP3, and retinoic acid-inducible gene-I (RIG-I), in urinary sediment, from patients with immunocomplex-mediated glomerulonephritis. Fourteen lupus nephritis (LN) patients, 13 IgA nephropathy (IgAN) patients, and 12 healthy controls were enrolled in the study. The mRNA expressions of T-bet, GATA-3, FOXP3 and RIG-I in urinary sediment were measured using real time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. We also studied the expression of RIG-I in kidney tissue specimens obtained from LN and IgAN patients. Significant differences in the expression patterns of GATA-3, FOXP3 and RIG-I, and marginal differences in T-bet expression, were observed between the three study groups. Immunofluorescent staining for RIG-I was observed in the tissue specimens from the LN patients, but not in those from the IgAN patients. The mRNA expression patterns of T-bet, GATA-3, FOXP3 and RIG-I in urinary sediment differ according to diagnostic category. These results suggest that the measurement of these target gene expressions might be a useful, non-invasive method for clinical monitoring and studying of pathogenesis in glomerulonephritis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anders HJ, Vielhauer V, Kretzler M (2001) Chemokine and chemokine receptor expression during initiation and resolution of immune complex glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:919–931
Holdsworth SR, Kitching AR, Tipping PG (1999) Th1 and Th2 T helper cell subsets affect patterns of injury and outcomes in glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int 55:1198–1216
Sakatsume M, Xie Y, Ueno M, Obayashi H, Goto S, Narita I, Homma N, Tasaki K, Suzuki Y, Gejyo F (2001) Human glomerulonephritis accompanied by active cellular infiltrates shows effector T cells in urine. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:2634–2644
Lim CS, Zheng S, Kim YS, Ahn C, Kim S, Lee JS, Chae DW, Koo JR, Chun RW, Noh JW (2001) Th1/Th2 predominance and proinflammatory cytokines determine the clinicopathological severity of IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 16:269–275
Chan RW, Lai FM, Li EK, Tam L, Chow K, Li PK, Szeto C (2006) Imbalance of Th1/Th2 transcription factors in patients with lupus nephritis. Rheumatology 45:951–957
Chien JW, Chen WL, Tsui YG, Lee MC, Lin AY, Lin CY (2006) Daily urinary interleukin-11 excretion correlated with proteinuria in IgA nephropathy and lupus nephritis. Pediatr Nephrol 21:490–496
Rengarajan J, Szabo SJ, Glimcher LH (2000) Transcriptional regulation of Th1/Th2 polarization. Immunol Today 21:479–483
Hori S, Nomura T, Sakaguchi S (2003) Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science 299:1057–1061
Fontenot JD, Gavin MA, Rudensky AY (2003) Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol 4:330–336
von Boehmer H (2005) Mechanisms of suppression by suppressor T cells. Nat Immunol 6:338–344
Suzuki K, Imaizumi T, Tsugawa K, Ito E, Tanaka H (2007) Expression of retinoic acid-inducible gene-I in lupus nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 22:2407–2409
Yoneyama M, Kikuchi M, Natsukawa T, Shinobu N, Imaizumi T, Miyagishi M (2004) The RNA helicase RIG-I has an essential function in double-stranded RNA-induced innate antiviral responses. Nat Immunol 5:730–737
Heim MH (2005) RIG-I: an essential regulator of virus-induced interferon production. J Hepatol 42:431–433
Imaizumi T, Yagihashi N, Hatakeyama M, Yamashita K, Ishikawa A, Taima K, Yoshida H, Yagihashi S, Satoh K (2004) Upregulation of retinoic acid-inducible gene-I in T24 urinary bladder carcinoma cells stimulated with interferon-γ. Tohoku J Exp Med 203:313–318
Kitamura H, Matsuzaki Y, Kimura K, Nakano H, Imaizumi T, Satoh K, Hanada K (2007) Cytokine modulation of retinoic acid-inducible gene-I (RIG-I) expression in human epidermal keratinocytes. J Dermatol Sci 45:127–134
Imaizumi T, Yagihashi N, Kubota K, Yoshida H, Sakaki H, Yagihashi S, Kimura H, Satoh K (2007) Expression of retinoic acid-inducible gene-I (RIG-I) in macrophages: possible involvement of RIG-I in atherosclerosis. J Atheroscler Thromb 14:51–55
Imaizumi T, Hatakeyama M, Yamashita K, Yoshida H, Ishikawa A, Taima K, Satoh K (2004) Interferon-γ induces retinoic acid-inducible gene-I in endothelial cells. Endothelium 11:169–173
Li B, Hartono C, Ding R, Sharma VK, Ramaswamy R, Qian B, Serur D, Mouradian J, Schwartz JE, Suthanthiran M (2001) Noninvasive diagnosis of renal-allograft rejection by measurement of messenger RNA for perforin and granzyme B in urine. N Engl J Med 344:947–954
Szeto C, Chan RW, Lai K, Szeto CY, Chow K, Li PK, Lai FM (2005) Messenger RNA expression of target genes in the urinary sediment of patients with chronic kidney diseases. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20:105–113
Szeto C, Lai K, Chow K, Szeto CY, Yip TW, Woo K, Li PK, Lai FM (2005) Messenger RNA expression of glomerular podocyte markers in the urinary sediment of acquired proteinuric diseases. Clin Chim Acta 361:182–190
Chan RW, Lai FM, Li EK, Tam L, Chow K, Li PK, Szeto C (2006) Messenger RNA expression of RANTES in the urinary sediment of patients with lupus nephritis. Nephrology 11:219–225
Avihingsanon Y, Phumesin P, Benjachat T, Akkasilpa S, Kittikowit V, Praditpornsilpa K, Wongpiyabavorn J, Eiam-Ong S, Hemachudha T, Tungsanga K, Hirankarn N (2006) Measurement of urinary chemokine and growth factor messenger RNAs: a noninvasive monitoring in lupus nephritis. Kidney Int 69:747–753
Chan RW, Tam L, Li EK, Lai FM, Chow K, Lai K, Li PK, Szto C (2003) Inflammatory cytokine gene expression in the urinary sediment of patients with lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheum 48:1326–1331
Mosca M, Bencivelli W, Vitali C, Carrai P, Neri R, Bombardieri S (2000) The validity of the ECLAM index for the retrospective evaluation of disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 9:445–450
Andreoli SP, Bergstein JM (1989) Treatment of severe IgA nephropathy in children. Pediatr Nephrol 3:248–253
Foster BJ, Bernard C, Drummond KN, Sharma AK (2000) Effective therapy for severe Henoch-Schonlein purpura nephritis with prednisone and azathioprine: a clinical and histopathologic study. J Pediatr 136:370–375
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acid Res 29:2002–2007
Chan RW, Lai FM, Li EK, Tam L, Chow K, Li PK, Szeto C (2006) The effect of immunosuppressive therapy on the messenger RNA expression of target genes in the urinary sediment of patients with active lupus nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21:1534–1540
Zanin-Zhorov A, Cahalon L, Tal G, Margalit R, Lider O, Cohen IR (2006) Heat shock protein 60 enhances CD4+CD25+regulatory T cell function via innate TLR2 signaling. J Clin Invest 116:2022–2032
Paladino P, Cummings DT, Noyce RS, Mossman KL (2006) The IFN-independent response to virus particle entry provides a first line of antiviral defense that is independent of TLRs and retinoic acid-inducible gene-I. J Immunol 177:8008–8016
Yoshida H, Imaizumi T, Lee SJ, Tanji K, Sasaki H, Matsumiya T, Ishikawa A, Taima K, Yuzawa E, Nori F, Wakabayashi K, Kimura H, Satoh K (2007) Retinoic acid-inducible gene-I mediates RANTES/CCL5 expression in U373MG human astrocytoma cells stimulated with double-strand RNA. Neurosci Res 58:199–206
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank Professor T. Miyawaki, Department of Pediatrics, Toyama University School of Medicine, and Professor T. Oite, Department of Cellular Physiology, Institute of Nephrology, Graduate School of Medical and Dental Sciences, Niigata University, for valuable discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsugawa, K., Oki, E., Suzuki, K. et al. Expression of mRNA for functional molecules in urinary sediment in glomerulonephritis. Pediatr Nephrol 23, 395–401 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-007-0683-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-007-0683-z