Abstract
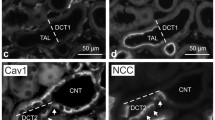
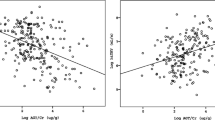
Caveolae are plasma membrane invaginations that contain a variety of signal transduction molecules and receptors for growth factors and cytokines. This study was performed to examine the in vivo expression and localization of caveolin-1 in kidneys from 19 children who underwent surgery release of ureteropelvic junction obstruction (UPJO) in relation to renal function and degree of tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Renal biopsies were carried out at the time of surgery for obstruction release. Kidney tissue from children of similar age removed because of carcinoma was used as control. Expression of caveolin-1 at the protein level in renal tissue and urine was demonstrated in patients with technetium 99 m labeled diethylene triamine pentaacetate (99Tc DTPA) renal scan 28.8±2% and increased tubular interstitial fibrosis in seven patients at the time of obstruction release. Colocalization staining of AT1 angiotensin II receptor with caveolin-1 in basolateral membrane of epithelial tubule cells, enhanced AT1 messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) and decreased endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), were shown in these patients. In contrast, absence of association of caveolin-1 with AT1 receptor expression in proximal and collecting tubule membranes with AT1 receptor mRNA and eNOS mRNA expression near control were demonstrated in 12 patients, with 99Tc DTPA renal scan 39.7+2.1% and no evidence of tubulointerstitial fibrosis. From our results, the role of caveolin-1 as a factor contributing to the severity of the tubulointerstitial process resulting from obstructive nephropathy could be suggested.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Warady BA (1997) Renal transplantation, chronic dialysis, and chronic renal insufficiency in children and adolescents. The 1995 annual report of the North American pediatric renal transplantation cooperative study. Pediatr Nephrol 11:49–64
Chevalier RL (1998) Effects of ureteral obstruction on renal growth. Semin Nephrol 15:353–360
Klahr S (1998) Obstructive nephropathy. Kidney Int 54:286–300
Klahr S, Morrissey J (1998) Angiotensin II and gene expression in the kidney. Am J Kidney Dis 31:171–176
Pueyo ME, Arnal JF, Rami J, Michel JB (1998) Angiotensin II stimulates the production of NO and peroxynitrite in endothelial cells. Am J Physiol 274(Cell Physiol 43):C214–C220
Ricardo SO, Diamond JD (1998) The role of macrophages and reactive oxygen species in experimental hydronephrosis. Semin Nephrol 18:612–621
Miyajina A, Chen J, Kirman I, Poppas DP, Darracott Vaughan E Jr, Felsen D (2000) Interaction of nitric oxide and transforming growth factor-[beta] induced by angiotensin II and mechanical stretch in rat renal tubular epithelial cells. J Urol 164:1729–1734
Vallés P, Pascual L, Manucha W, Carrizo L, Rüttler M (2003) Role of endogenous nitric oxide in unilateral ureteropelvic junction(UPJ) obstruction in children. Kidney Int 63:1104–1111
Huang A, Palmer LS, Hom D, Vaderrama E, Trachtman H (2000) The role of nitric oxide in obstructive nephropathy. J Urol 163:1276–1281
Thomas SE, Anderson S, Gordon KL (1998) Tubulointerstitial disease in aging: evidence for underlying peritubular capillary damage, a potential role for renal ischemia. J Am Soc Nephrol 9:231–242
Ishizaka N, Griendling KK, Lassegue B, Alexander RW (1998) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor: relationship with caveolae and caveolin after initial agonist stimulation. Hypertension 32:459–466
Li D, Tomson K, Yang B, Mehta P, Croker BP, Mehta JL (1999) Modulation of constitutive nitric oxide synthase, bcl-2 and Fas expression in cultured human coronary endothelial cell exposed to anoxia-reoxygenation and angiotensin II: role of AT1 receptor activation. Cardiovasc Res 41:109–115
Rothberg KG, Heuser JE, Donzell WC, Ying Y, Glenney JR, Anderson RGW (1992) Caveolin, a protein component of caveolae membrane coats. Cell 68:673–682
Fra AM, Williamson E, Simons K, Parton RG (1995) De novo formation of caveolae in lymphocytes by expression of VIP21-caveolin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:8655–8659
Zhao YY, Liu Y, Stan RV, Fan L, Gu Y, Dalton N, Chu PH, Peterson K, Ross J Jr, Chien KR (2002) Defects in caveolin-1 cause dilated cardiomyopathy and pulmonary hypertension in knockout mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:11375–11380
Cohen AW (2004) Role of caveolae and caveolins in health and disease. Physiol Rev 84:1341–1379
Okamoto T, Schlegel A, Scherer PE, Lisanti MP (1998) Caveolins, a family of scaffolding proteins for organizing “preassembled signaling complexes” at the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem 273:5419–5422
Goligorsky MS, Li H, Brodsky H, Chen J (2002) Relationships between caveolae and eNOS: everything in proximity and the proximity of everything. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 283:F1–F10
Drab M, Verkade P, Elger M, Kasper M, Lohn M, Lauterbach B, Menne J, Lindschau C, Mende F, Luft FC, Schedl A, Haller H, Kurzchalia TV (2001) Loss of caveolae, vascular dysfunction, and pulmonary defects in caveolin-1 gene-disrupted mice. Science 293:2449–2452
Chun M, Liyanage UK, Lisanti MP, Lodish HF (1994) Signal transduction of a G protein-coupled receptor in caveolae: colocalization of endothelin and its receptor with caveolin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:11728–11732
Liu P, Ying Y, Ko Y, Anderson RGW (1996) Localization of platelet-derived growth factor-stimulated phosphorylation cascade to caveolae. J Biol Chem 271:10299–10303
Mineo C, James GL, Smart EJ, Anderson RGW (1996) Localization of epidermal growth factor-stimulated Ras/Raf-1 interaction to caveolae membrane. J Biol Chem 271:11930–11935
Wyse BD, Prior IA, Qian H, Morrow IC, Nixon S, Muncke C, Kurzchalia TV, Thomas WG, Parton RG, Hancock JF (2003) Caveolin interacts with the angiotensin II type 1 receptor during exocytic transport but not at the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem 278:23738–23746
Li S, Couet J, Lisanti MP (1996) Src tyrosine kinases, G alpha subunits and H-Ras share a common membrane-anchored scaffolding protein, caveolin. Caveolin binding negatively regulates the auto-activation of Src tyrosine kinases. J Biol Chem 271:29182–29190
Peterson Ma E, Guicciardi R, Gulati LS, Kleppe CS, Mueske M, Mookadam G, Sowa GJ, Gores WC, Sessa RD, Simari RD (2003) Caveolin-1 can regulate vascular smooth muscle cell fate by switching platelet-derived growth. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23:1521–1527
Maizels M, Reisman ME, Nelson J, Fernbach S, Firlit CF, Conway JJ (1992) Grading nephroureteral dilatation detected in the first year of life. Correlation with obstruction. J Urol Part 2 148:609–614
Majd M (1992) Nuclear medicine in pediatric urology. In: Kelalis P, King LR, Belman AB (eds) Clinical pediatric urology, Chapt 4, 3rd edn. W.B. Saunders Co, Philadelphia, pp 117–165
Chung S, Majd M, Gil Rushton H, Belman B (1993) Diuretic renography in the evaluation of neonatal hydronephrosis: is it reliable? J Urol 150:765–768
(1987) Report of the Second Task Force on blood pressure control in children—1987. Task Force on blood pressure control in children. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, Maryland. Pediatrics 79:1–25
Schwartz GJ, Haycock GB, Spitzer A (1976) Plasma creatinine and urea concentration in children. J Pediatr 88:828–832
Hruska KA, Guo G, Wozniak M, Martin D, Miller S, Liapis H, Loveday K, Klahr S, Sampath TK, Morrissey J (2000) Osteogenic protein-1 prevents renal fibrogenesis associated with ureteral obstruction. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 279:F130–F143
Morrissey J, Hruska K, Guo G, Wang S, Chen Q, Klahr S (2002) Bone morphometric protein-7 improves renal fibrosis and accelerates the return of renal function. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:S14–S21
William T, Lisanti M (2004) The Caveolin genes: from cell biology to medicine. Ann Med 36:584–595
Pimentel JL, Martinez Maldonado M, Wilcox JN, Wang S, Luo C(1993) Regulation of renin-angiotensin system in unilateral ureteral obstruction. Kidney Int 44:390–400
Klahr S, Morrissey J (1998) The role of growth factors, cytokines, and vasoactive compounds in obstructive nephropathy. Semin Nephrol 18:622–632
Mahmoudi M, Willgoss D, Cuttle L, Yang T, Pat B, Winterford C, Endre Z, Johnson DW, Gobe GC (2003) In vivo and in vitro models demonstrate a role for caveolin-1 in the pathogenesis of ischaemic acute renal failure. J Pathol 200:396–404
Zager RA, Johnson A, Hanson S, De La Rosa V (2002) Altered colesterol localization and caveolin expression during the evolution of acute renal failure. Kidney Int 61:1674–1683
Cachat F, Lange-Sperandio B, Chang AY, Kiley S, Thornhill BA, Forbes M, Chevalier RL (2003) Ureteral obstruction in neonatal mice elicits segment-specific tubular cell responses leading to nephron loss. Kidney Int 63:564–575
Truong LD, Sheikh-Hamad D, Chakaborty S, Suki WN (1998) Cell apoptosis and proliferation in obstructive uropathy. Semin Nephrol 18:641–651
Gobe GC, Axelsen RA (1987) Genesis of renal tubular atrophy in experimental hydronephrosis in the rat. Lab Invest 56:273–281
Schumer M, Colombel MC, Sawczuk IS, Gobe G, Connor J, O’Toole KM, Olsson CA, Wise GJ, Buttyan R (1992) Morphologic, biochemical and molecular evidence of apoptosis during the reperfusion phase after brief periods of renal ischemia. Am J Pathol 140:831–838
Michel JB, Feron O, Sacks D, Michel T (1997) Reciprocal regulation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase by Ca2+-calmodulin and caveolin. J Biol Chem 272:15583–15586
Sindhu RK, Ehdaie A, Vaziri ND, Ohashi R, Shimizu A, Masuda Y, Kitamura H, Ishizaki M, Sugisaki Y, Yamanaka N (2002) Peritubular capillary regression during the progression of experimental obstructive nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:1795–1805
Roberts CK (2004) Effects of chronic renal failure on caveolin-1, guanylate cyclase and AKT protein expression. Biochim Biophys Acta 1690:231–237
Acknowledgments
This work was performed with financial support from CONICET, PICT/2002 N 05-12620, and the Research and Technology Council of Cuyo University (CIUNC) Mendoza, Argentina / N: 1143 / 04 to P. G. Vallés. Part of this work was presented as an abstract at the 3rd Argentine Pediatric Nephrology Congress, Argentina, 23–25 May, 2006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vallés, P.G., Manucha, W., Carrizo, L. et al. Renal caveolin-1 expression in children with unilateral ureteropelvic junction obstruction. Pediatr Nephrol 22, 237–248 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-006-0290-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-006-0290-4