Abstract
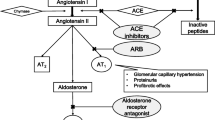
Patients with chronic proteinuric nephropathies are at high risk of developing progressive renal insufficiency. There are limited controlled data on the efficacy of potentially toxic immunosuppressive therapies for many of these diseases such as immunoglobulin A nephropathy and idiopathic membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis. This limitation has not deterred healthcare providers from using such agents based on anecdotal experience. We report our experience taking care of three children with heavy proteinuria from chronic glomerular diseases. All were treated with a combination of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers without concomitant immunosuppression. All went into complete remission soon after starting therapy, allowing corticosteroid avoidance. The purpose of this report is to make healthcare professionals more aware of the potential success that can be achieved with this relatively nontoxic drug regimen. Larger controlled clinical trials using this strategy are needed to better evaluate the efficacy and safety of this approach in children with glomerular diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Giri S, Mahajan SK, Sen R, Sharma A (2002) Effects of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor on renal function in patients of membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis with mild to moderate renal insufficiency. J Assoc Physicians India 50:1245–1249
Praga M, Gutierrez E, Gonzalez E, Morales E, Hernandez E (2003) Treatment of IgA nephropathy with ACE inhibitors: a randomized and controlled trial. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:1578–1583
Russo D, Minutolo R, Pisani A, Esposito R, Signoriello G, Andreucci M, Balletta MM (2001) Coadministration of losartan and enalapril exerts additive antiproteinuric effect in IgA nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis 38:18–25
Nakao N, Yoshimura A, Morita H, Takada M, Kayano T, Ideura T (2003) Combination treatment of angiotensin-II receptor blocker and angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor in non-diabetic renal disease (COOPERATE): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 361:117–124
Tanaka H, Suzuki K, Nakahata T, Tsugawa K, Konno Y, Tsuruga K, Ito E, Waga S (2004) Combined therapy of enalapril and losartan attenuates histologic progression in immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Pediatr Int 46:576–579
Bhattacharjee R, Filler G (2002) Additive antiproteinuric effect of ACE inhibitor and losartan in IgA nephropathy. Pediatr Nephrol 17:302–304
Butani L (2003) Remission of membranoproliferative nephritis with angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition and receptor blockade. Pediatr Nephrol 18:1199
Tarshish P, Bernstein J, Tobin JN, Edelmann CM, Jr. (1992) Treatment of mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis with alternate-day prednisone—a report of the International Study of Kidney Disease in Children. Pediatr Nephrol 6:123–130
Schieppati A, Remuzzi G (2003) The June 2003 Barry M. Brenner Comgan lecture. The future of renoprotection: frustration and promises. Kidney Int 64:1947–1955
Klahr S, Morrissey J (2002) Comparative effects of ACE inhibition and angiotensin II receptor blockade in the prevention of renal damage. Kidney Int Suppl 23–26
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Butani, L. Angiotensin blockade in children with chronic glomerulonephritis and heavy proteinuria. Pediatr Nephrol 20, 1651–1654 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-005-2031-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-005-2031-5