Abstract
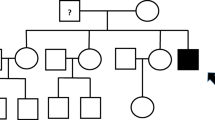
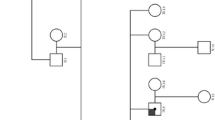
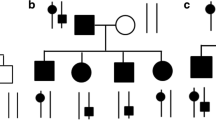
Alport syndrome is an important hereditary disorder characterized by nephritis and sometimes accompanied by impairment or loss of vision and hearing. The most common form of Alport syndrome is an X-linked dominant trait that has been associated with the gene COL4A5, one of the six types of IV collagen genes. More than 300 different mutations have been identified in the COL4A5 gene, and appear randomly along the whole gene. Three novel mutations, G198E, G3189D and G669R, were found in 5 young patients from 3 different Slovenian families. On the basis of the results of our study and the existing national register of Alport syndrome patients, we demonstrated that non-invasive methods, such as the genetic analysis of collagen genes, particularly in the case of young patients with undefined clinical features, may be of great importance and could diminish the need for invasive skin and renal biopsy. Our study showed the importance of molecular genetic data for the purpose of providing quick and precise diagnoses for affected family members and their offspring, particularly small children.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kashtan CE (1999) Alport sydrome. Medicine 78:338–360
Flinter F (1997) Alport’s syndrome. J Med Genet 34:326–330
Rumpelt HJ (1980) Hereditary nephropathy (Alport syndrome): correlation of clinical data with glomerular basement membrane alternations. Clin Nephrol 13:203–207
Barker DF, Hostikka SL, Zhou J, Chow LT, Oliphant AR, Gerken SC, Gregory MC, Skolnick MH, Atkin CL, Tryggvason K (1990) Identification of mutations in the COL4A5 gene in Alport syndrome. Science 248:1224–1227
Gross O, Netzer K-O, Lambrecht R, Seibold S, Weber M (2002) Meta-analysis of genotype-phenotype correlation in X-linked Alport syndrome: impact on clinical counseling. Nephrol Dial Transplant 17:1218–1227
Mochizuki T, Lemmink HH, Mariyama M, Antignac C, Gubler M-C, Pirson Y, Verelen-Dumoulin C, Chan B, Schröder CH, Smeets HJM, Reeders ST (1994) Identification of mutations in the alpha3(IV) and alpha4(IV) collagen genes in autosomal recessive Alport syndrome. Nat Genet 8:77–81
Renieri A, Bruttini M, Galli L, Zanelli P, Neri T, Rosseti S, Turco A, Heiskari N, Zhou J, Gusmano R, Masella L, Banfi G, Scolari F, Sessa A, Rizzoni G, Tryggvason K, Pignati PF, Savi M, Ballabio A, De Marchi M. (1996) X-linked Alport syndrome: an SSCP-based mutation survey over all 51 exons of the COL4A5 gene. Am J Hum Genet 58:1192–1204
Lemmink HH, Nillesen WN, Mochizuki T, Schröder H, Brunner HG, van Oost BA, Monnens LAH, Smeets HJM (1996) Benign familial hematuria due to mutation of the type IV collagen α4 gene. J Clin Invest 98:1114–1118
Martin P, Heiskari N, Zhou J, Leinonen A, Tumelius T, Hertz JM, Barker D, Gregory M, Atkin C, Styrkarsdottir U, Neumann H, Springate J, Shows T, Pettersson E, Trygvason K (1998) High mutation detection rate in the COL4A5 collagen gene in suspected Alport syndrome using PCR and direct DNA sequencing. J Am Nephrol 9:2291–2301
Jais JP, Knebelmann B, Giatras I, De Marhi M, Rizzoni G, Renieri A, Weber M, Gross O, Netzer KO, Flinter F, Pirson Y, Verellen C, Wieslander J, Persson U, Tryggvason K, Martin P, Hertz JM, Schröder H, Sanak M, Krejcova S, Carvalho MF, Saus J, Antignac C, Smeets H, Gubler MC (2000) X-linked Alport syndrome: Natural history in 195 families and genotype-phenotype correlations in males. J Am Soc Nephrol 11:649–657
Hertz JM, Juncker I, Persson U, Matthijs G, Schmidtke J, Peterson MB, Kjeldsen M, Gregersen N (2001) Detection of mutations in the COL4A5 gene by SSCP in X-linked Alport syndrome. Hum Mutat 18:141–148
Jais JP, Knebelmann B, Giatras I, De Marchi M, Rizzoni G, Renieri A, Weber M, Gross O, Netzer KO, Flinter F, Pirson Y, Dahan K, Wieslander J, Persson U, Tryggvason K, Martin P, Hertz JM, Schröder H, Sanak M, Carvalho MF, Saus J, Antignac C, Smeets H, Gubler MC (2003) X-linked Alport syndrome: Natural history and genotype-phenotype correlations in girls and women belonging to 195 families: a ‘‘European Community Alport Syndrome concerted Action’’ study. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:2603–2610
Meglic A, Kuman D, Jazbec J, Japelj Pavesic B, Kenda R (2003) Erythrocyte deformability and microhematuria in children and adolescents. Pediatr Nephrol 18:127–132
Meleg-Smith S (2001) Alport disease: a review of the diagnostic difficulties. Ultrastruc Pathol 25:193–200
Grünfeld JP (2000) Contemporary diagnostic approach in Alport’s syndrome. Renal Failure 22:759–763
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
M. Šlajpah and A. Meglič contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Šlajpah, M., Meglič, A., Furlan, P. et al. The importance of non-invasive genetic analysis in the initial diagnostics of Alport syndrome in young patients. Pediatr Nephrol 20, 1260–1264 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-005-1975-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-005-1975-9