Abstract
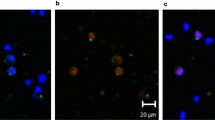
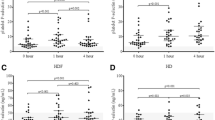
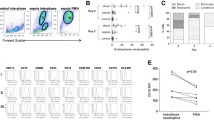
Experimental and clinical evidence suggest that activated neutrophils (PMN) could contribute to endothelial damage in Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (D+HUS). Additionally, while PMN-activating cytokines and PMN-derived products have been found in D+HUS sera, we have demonstrated phenotypic alterations in D+HUS PMN compatible with a deactivation state. Here, we investigated whether D+HUS PMN were actually hyporesponsive, and explored some of the mechanisms probably involved in their derangement. Twenty-two D+HUS children were bled in the acute period, and blood samples from healthy, acute uremic and neutrophilic children were obtained as controls. We evaluated degranulation markers in response to cytokines, intracellular granule content, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation in circulating D+HUS and control PMN. The influence of D+HUS-derived plasma and the direct effects of Stx in vitro were evaluated on healthy donors’ PMN. We found that D+HUS PMN presented reduced degranulatory capacity in response to cytokines and intracellular granule content, and decreased ROS generation. D+HUS plasma or Stx did not affect the phenotype and function of healthy donors’ PMN. These results suggest that upon hospitalization D+HUS PMN are functionally impaired and show features of previous degranulation, indicating a preceding process of activation with release of ROS and proteases involved in endothelial damage.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karmali MA, Petric M, Lim C, Fleming PC, Arbus GS, Lior H (1985) The association between idiopathic hemolytic uremic syndrome and infection by verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis 151:775–782
Remuzzi G, Ruggenenti P (1995) The hemolytic uremic syndrome. Kidney Int 48:2–19
Paton JC, Paton AW (1998) Pathogenesis and diagnosis of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli infections. Clin Microbiol Rev 11:450–479
Keusch GT, Acheson DW (1997) Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura associated with Shiga toxins. Semin Hematol 34:106–116
Milford D, Taylor CM, Rafaat F, Halloran E, Dawes J (1989) Neutrophil elastases and haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Lancet 2:1153
Fitzpatrick MM, Shah V, Filler G, Dillon MJ, Barratt TM (1992) Neutrophil activation in the haemolytic uraemic syndrome: free and complexed elastase in plasma. Pediatr Nephrol 6:50–53
Weiss SJ (1989) Tissue destruction by neutrophils. N Engl J Med 320:365–376
Lentsch AB, Ward PA (2000) Regulation of inflammatory vascular damage. J Pathol 190:343–348
Sengelov H, Kjeldsen L, Borregaard N (1993) Control of exocytosis in early neutrophil activation. J Immunol 150:1535–1543
Borregaard N, Cowland JB (1997) Granules of the human neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocyte. Blood 89:3503–3521
Fernandez GC, Rubel C, Barrionuevo P, Lopez L, Ramirez F, Diaz M, Isturiz MA, Palermo MS (2002) Phenotype markers and function of neutrophils in children with hemolytic uremic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 17:337–344
Gianantonio CA, Vitacco M, Mendilaharzu F, Gallo GE, Sojo ET (1973) The hemolytic-uremic syndrome. Nephron 11:174–192
Knapp W, Strobl H, Majdic O (1994) Flow cytometric analysis of cell-surface and intracellular antigens in leukemia diagnosis. Cytometry 18:187–198
Rubel C, Fernandez GC, Rosa FA, Gomez S, Bompadre MB, Coso OA, Isturiz MA, Palermo MS (2002) Soluble fibrinogen modulates neutrophil functionality through the activation of an extracellular signal-regulated kinase-dependent pathway. J Immunol 168:3527–3535
Duner KI (1993) A new kinetic single-stage Limulus amoebocyte lysate method for the detection of endotoxin in water and plasma. J Biochem Biophys Methods 26:131–142
te Loo DM, Monnens LA, van Der Velden TJ, Vermeer MA, Preyers F, Demacker PN, van Den Heuvel LP, van Hinsbergh VW (2000) Binding and transfer of verocytotoxin by polymorphonuclear leukocytes in hemolytic uremic syndrome. Blood 95:3396–3402
Palermo MS, Alves Rosa MF, Van Rooijen N, Isturiz MA (1999) Depletion of liver and splenic macrophages reduces the lethality of Shiga toxin-2 in a mouse model. Clin Exp Immunol 116:462–467
Rosenbloom AJ, Pinsky MR, Napolitano C, Nguyen TS, Levann D, Pencosky N, Dorrance A, Ray BK, Whiteside T (1999) Suppression of cytokine-mediated beta2-integrin activation on circulating neutrophils in critically ill patients. J Leukoc Biol 66:83–89
Rodeberg DA, Bass RC, Alexander JW, Warden GD, Babcock GF (1997) Neutrophils from burn patients are unable to increase the expression of CD11b/CD18 in response to inflammatory stimuli. J Leukoc Biol 61:575–582
Vaissiere C, Le Cabec V, Maridonneau-Parini I (1999) NADPH oxidase is functionally assembled in specific granules during activation of human neutrophils. J Leukoc Biol 65:629–634
Borregaard N, Heiple JM, Simons ER, Clark RA (1983) Subcellular localization of the b-cytochrome component of the human neutrophil microbicidal oxidase: translocation during activation. J Cell Biol 97:52–61
Karlsson A, Dahlgren C (2002) Assembly and activation of the neutrophil NADPH oxidase in granule membranes. Antioxid Redox Signal 4:49–60
Sassetti B, Vizcarguenaga MI, Zanaro NL, Silva MV, Kordich L, Florentini L, Diaz M, Vitacco M, Sanchez Avalos JC (1999) Hemolytic uremic syndrome in children: platelet aggregation and membrane glycoproteins. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 21:123–128
Cohen G, Haag-Weber M, Horl WH (1997) Immune dysfunction in uremia. Kidney Int Suppl 62:S79–82
Cohen G, Rudnicki M, Walter F, Niwa T, Horl WH (2001) Glucose-modified proteins modulate essential functions and apoptosis of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:1264–1271
Wagner JG, Roth RA (1999) Neutrophil migration during endotoxemia. J Leukoc Biol 66:10–24
Burtnick LD (1984) Modification of actin with fluorescein isothiocyanate. Biochim Biophys Acta 791:57–62
Miller L, Phillips M, Reisler E (1988) Polymerization of actin modified with fluorescein isothiocyanate. Eur J Biochem 174:23–29
Favazza M, Lerho M, Houssier C (1990) Labelling of histone H5 and its interaction with DNA. 1. Histone H5 labelling with fluorescein isothiocyanate. J Biomol Struct Dyn 7:1291–1300
Johnson DA, Taylor P (1982) Site-specific fluorescein-labeled cobra alpha-toxin. Biochemical and spectroscopic characterization. J Biol Chem 257:5632–5636
Hentz NG, Richardson JM, Sportsman JR, Daijo J, Sittampalam GS (1997) Synthesis and characterization of insulin-fluorescein derivatives for bioanalytical applications. Anal Chem 69:4994–5000
Fong JS, Kaplan BS (1982) Impairment of platelet aggregation in hemolytic uremic syndrome: evidence for platelet “exhaustion”. Blood 60:564–570
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a “R. Carrillo-A. Oñativia” award from Ministerio de Salud de la Nación, by Fundación Alberto J. Roemmers, and Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica, Argentina. The authors thank Marta Felippo, Nora Galassi and Norma Riera for their excellent technical assistance. The authors also thank Fundación de la Hemofilia and Academia Nacional de Medicina for the use of the FACScan flow cytometer, and the Departamento de Hemoterapia of CEMIC for healthy adult blood samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernández, G.C., Gómez, S.A., Rubel, C.J. et al. Impaired neutrophils in children with the typical form of hemolytic uremic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 20, 1306–1314 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-005-1906-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-005-1906-9