Abstract
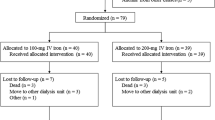
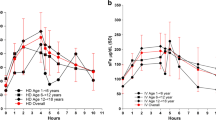
Pediatric patients with end-stage renal disease undergoing hemodialysis (HD) frequently develop anemia. Administration of recombinant human erythropoietin (rHuEPO) is effective in managing this anemia, although the additional demand for iron often results in iron deficiency. In adult patients undergoing HD, intravenous (IV) iron administration is known to replenish iron stores more effectively than oral iron administration. Nevertheless, IV iron supplementation is underutilized in pediatric patients, possibly because of unproved safety in this population. This international, multicenter study investigated the safety and efficacy of two dosing regimens (1.5 mg kg−1 and 3.0 mg kg−1) of sodium ferric gluconate complex (SFGC) therapy, during eight consecutive HD sessions, in iron-deficient pediatric HD patients receiving concomitant rHuEPO therapy. Safety was evaluated in 66 patients and efficacy was evaluated in 56 patients. Significant increases from baseline were observed in both treatment groups 2 and 4 weeks after cessation of SFGC dosing for mean hemoglobin, hematocrit, transferrin saturation, serum ferritin, and reticulocyte hemoglobin content. Efficacy and safety profiles were comparable for 1.5 mg kg−1 and 3.0 mg kg−1 SFGC with no unexpected adverse events with either dose. Administration of SFGC was safe and efficacious in the pediatric HD population. Given the equivalent efficacy of the two doses, an initial dosing regimen of 1.5 mg kg−1 is recommended for pediatric HD patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
National Kidney Foundation-K/DOQI (2001) National Kidney Foundation-K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for anemia of chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis 37(Suppl 1):S182–S238
Chavers BM, Roberts TL, Herzog CA, Collins AJ, St Peter WL (2004) Prevalence of anemia in erythropoietin-treated pediatric as compared to adult chronic dialysis patients. Kidney Int 65:266–273
Gillespie RS, Wolf FM (2004) Intravenous iron therapy in pediatric hemodialysis patients: a meta-analysis. Pediatr Nephrol 19:662–666
Nissenson AR (1989) Recombinant human erythropoietin: impact on brain and cognitive function, exercise tolerance, sexual potency, and quality of life. Semin Nephrol 9(1 Suppl 2):25–31
Kausz AT, Obrador GT, Pereira BJ (2000) Anemia management in patients with chronic renal insufficiency. Am J Kidney Dis 36(Suppl 3):S39–S51
Mitsnefes MM, Daniels SR, Schwartz SM, Meyer RA, Khoury P, Strife CF (2000) Severe left ventricular hypertrophy in pediatric dialysis: prevalence and predictors. Pediatr Nephrol 14:898–902
Warady BA, Ho M (2003) Morbidity and mortality in children with anemia at initiation of dialysis. Pediatr Nephrol 18:1055–1062
U.S. Renal Data System (2004) USRDS 2004 Annual data report: atlas of end-stage renal disease in the United States. National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Bethesda, Md
Bruner AB, Joffe A, Duggan AK, Casella JF, Brandt J (1996) Randomised study of cognitive effects of iron supplementation in non-anaemic iron-deficient adolescent girls. Lancet 348:992–996
Finch CA, Miller LR, Inamdar AR, Person R, Seiler K, Mackler B (1976) Iron deficiency in the rat. Physiological and biochemical studies of muscle dysfunction. J Clin Invest 58:447–453
Levin NW, Lazarus M, Nissenson AR (1993) Maximizing patient benefits with epoetin alfa therapy. National Cooperative rHu Erythropoietin Study in patients with chronic renal failure—an interim report. Am J Kidney Dis 22(Suppl 1):3–12
Coladonato JA, Frankenfield DL, Reddan DN, Klassen PS, Szczech LA, Johnson CA, Owen WF Jr (2002) Trends in anemia management among US hemodialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:1288–1295
Richardson D, Bartlett C, Will EJ (2001) Optimizing erythropoietin therapy in hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 38:109–117
Rigden SPA, Montini G, Morris M, Clark KGA, Haycock GB, Chantler C, Hill RC (1990) Recombinant human erythropoietin therapy in children maintained by haemodialysis. Pediatric Nephrol 4:618–622
De Palo T, Giordano M, Palumbo F, Bellantuono R, Messina G, Colella V, Caringella AD (2004) Clinical experience with darbepoietin alfa (NESP) in children undergoing hemodialysis. Pediatr Nephrol 19:337–340
Warady BA, Sabath RJ, Smith CA, Alon U, Hellerstein S (1991) Recombinant human erythropoietin therapy in pediatric patients receiving long-term peritoneal dialysis. Pediatr Nephrol 5:718–723
Eschbach JW (1989) The anemia of chronic renal failure: pathophysiology and the effects of recombinant erythropoietin. Kidney Int 35:134–148
Müller-Wiefel DE, Sinn H, Gilli G, Scharer K (1977) Hemolysis and blood loss in children with chronic renal failure. Clin Nephrol 8:481–486
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (2004) 2003 Annual Report: End Stage Renal Disease Clinical Performance Measures Project. Am J Kidney Dis 44(Suppl 1):S1-S92
Neu A, Ho P, McDonald R, Warady A (2002) Chronic dialysis in children and adolescents. The 2001 NAPRTCS Annual Report. Pediatr Nephrol 17:656–663
Fishbane S, Ungureanu V-D, Maesaka JK, Kaupke CJ, Lim V, Wish J (1996) The safety of intravenous iron dextran in hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 28:529–534
Michael B, Coyne DW, Fishbane S, Folkert V, Lynn R, Nissenson AR, Agarwal R, Eschbach JW, Fadem SZ, Trout JR, Strobos J, Warnock DG (2002) Sodium ferric gluconate complex in hemodialysis patients: adverse reactions compared to placebo and iron dextran. Kidney Int 61:1830–1839
Bastani B, Rahman S, Gellens M (2002) Lack of reaction to ferric gluconate in hemodialysis patients with a history of severe reaction to iron dextran. ASAIO J 48:404–406
Nissenson AR, Lindsay RM, Swan S, Seligman P, Strobos J (1999) Sodium ferric gluconate complex in sucrose is safe and effective in hemodialysis patients: North American clinical trial. Am J Kidney Dis 33:471–482
Fishbane S, Wagner J (2001) Sodium ferric gluconate complex in the treatment of iron deficiency for patients on dialysis. Am J Kidney Dis 37:879–883
Tenbrock K, Muller-Berghaus J, Michalk D, Querfeld U (1999) Intravenous iron treatment of renal anemia in children on hemodialysis. Pediatr Nephrol 13:580–582
Yorgin P, Belson A, Sarwal M, Alexander SR (2000) Sodium ferric gluconate therapy in renal transplant and renal failure patients. Pediatr Nephrol 171–175
Jabs K, Alexander S, McCabe D, Lerner G, Harmon W (1994) Primary results from the U.S. multicenter pediatric recombinant erythropoietin study [abstract]. J Am Soc Nephrol 5:456A
Morgan HE, Gautam M, Geary DF (2001) Maintenance intravenous iron therapy in pediatric hemodialysis patients. Pediatr Nephrol 16:779–783
Greenbaum LA, Pan CG, Caley C, Nelson T, Sheth KJ (2000) Intravenous iron dextran and erythropoietin use in pediatric hemodialysis patients. Pediatr Nephrol 14:908–911
Warady BA, Kausz A, Lerner G, Brewer ED, Chadha V, Brugnara C, Dahl NV, Watkins SL (2004) Iron therapy in the pediatric hemodialysis population. Pediatr Nephrol 19:655–661
Ruiz-Jaramillo ML, Guizar-Mendoza JM, Gutierrez-Navarro MJ, Dubey-Ortega LA, Amador-Licona N (2004) Intermittent versus maintenance iron therapy in children on hemodialysis: a randomized study. Pediatr Nephrol 19:77–81
Macdougall IC (1995) Poor response to erythropoietin: practical guidelines on investigation and management. Nephrol Dial Transplant 10:607–614
Brugnara C, Zurakowski D, DiCanzio J, Boyd T, Platt O (1999) Reticulocyte hemoglobin content to diagnose iron deficiency in children. JAMA 281:2225–2230
Kalantar-Zadeh K, Rodriguez RA, Humphreys MH (2004) Association between serum ferritin and measures of inflammation, nutrition and iron in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 19:141–149
Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kleiner M, Dunne E, Ahern K, Nelson M, Koslowe R, Luft FC (1998) Total iron-binding capacity-estimated transferrin correlates with the nutritional subjective global assessment in hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 31:263–272
Fishbane S, Galgano C, Langley RC Jr, Canfield W, Maesaka JK (1997) Reticulocyte hemoglobin content in the evaluation of iron status of hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 52:217–222
Tsuchiya K, Okano H, Teramura M, Iwamoto Y, Yamashita N, Suda A, Shimada K, Nihei H, Ando M (2003) Content of reticulocyte hemoglobin is a reliable tool for determining iron deficiency in dialysis patients. Clin Nephrol 59:115–123
Fishbane S, Shapiro W, Dutka P, Valenzuela OF, Faubert J (2001) A randomized trial of iron deficiency testing strategies in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 60:2406–2411
Mitsuiki K, Harada A, Miyata Y (2003) Assessment of iron deficiency in chronic hemodialysis patients: investigation of cutoff values for reticulocyte hemoglobin content. Clin Exp Nephrol 7:52–57
Van Wyck DB, Cavallo G, Spinowitz BS, Adhikarla R, Gagnon S, Charytan C, Levin N (2000) Safety and efficacy of iron sucrose in patients sensitive to iron dextran: North American clinical trial. Am J Kidney Dis 36:88–97
Faich G, Strobos J (1999) Sodium ferric gluconate complex in sucrose: safer intravenous iron therapy than iron dextrans. Am J Kidney Dis 33:464–470
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the contributions of Wendy Arnone, PhD, from Watson Laboratories, Inc., the North American Pediatric Renal Transplant Cooperative Study (NAPRTCS)* organization, and Pharm-Olam International (UK), Ltd. Ferrlecit Pediatric Study Group: Amira Peco-Antic, University Children’s Hospital, Tirsova, Serbia; Nadine M. Benador,* University of California, San Diego, USA; Mark R. Benfield,* University of Alabama at Birmingham, USA; Igor V. Diatchenko, Russian Children’s Clinical Hospital, Moscow, Russia; Tomasz Jarmolinski, Children’s and Teenager’s Hospital, Szczecin, Poland; Rasim K. Kuanshkaliev, Children’s Municipal Hospital #1, St. Petersburg, Russia; Vladimir I. Kudinov, Republic Children’s Clinical Hospital of Ministry of Health, Bashkortostan, Russia; Gary R. Lerner,* Children’s Hospital—Los Angeles, USA; Ewa Marczak, Children Nephrology Clinic of Independent Public Children Hospital No. 1 of Academic Clinical Centre Medical Academy, Gdansk, Poland; Georgy K. Nazarov, Children’s Municipal Hospital #13, Moscow, Russia; Michal Nowicki, Polish Mother’s Memorial Hospital Research Institute, Lodz, Poland; ll’dar D. Shakirov, Children’s Republic Clinical Hospital of Ministry of Health, Tartarstan, Russia; Roman Stankiewicz, Hemodialysis Station of Department Children Hospital, Torun, Poland; Krystyna Szprynger, Childhood Independent Public Clinic Hospital, Zabrze, Poland; Alfredo Chew-Wong, Hospital Miguel Hidalgo, Aguascalientes, Mexico; Peter D. Yorgin,* Stanford University Medical Center, USA; Maria Malgorzata Zajaczkowska, Clinical Children’s Hospital Pediatry and Nephrology Clinic, Lublin, Poland; Dmitriy V. Zverev, Saint Vladimir Children’s Municipal Clinical Hospital, Moscow, Russia; Walentyna Zoch-Zwierz, 1st Children’s Disease Clinic of Medical Academy, Independent Public Clinic Hospital, Bialystok, Poland; Danuta Zwolinska, Medical Academy, Wroclaw, Poland. This work has been submitted in part to the American Society of Nephrology for presentation at the 2004 Annual meeting of the Society. This trial was supported by a grant from Watson Pharmaceuticals, to each of the participating centers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00467-005-2134-z
The Ferrlecit Pediatric Study Group is a co-author of this paper
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Warady, B.A., Zobrist, R.H., Wu, J. et al. Sodium ferric gluconate complex therapy in anemic children on hemodialysis. Pediatr Nephrol 20, 1320–1327 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-005-1904-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-005-1904-y