Abstract
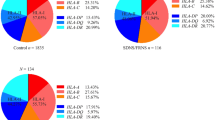
The association between HLA class II antigens and childhood primary nephrotic syndrome has been reported in different populations. To investigate this association in Egyptian children, DRB1 alleles were typed by DNA polymerase chain reverse hybridization in 20 frequent relapsers/steroid-dependent and 14 steroid-resistant children with minimal change nephrotic syndrome (MCNS) and 121 unrelated healthy controls from the northern part of Egypt. The strength of the association was expressed as the relative risk (RR) estimated by the odds ratio. The DRBI *07011 allele frequency was significantly higher among patients than controls (78.9% vs. 16%, Pc <0.001). The etiological fraction (EF) was high at 0.75 [RR=20.1, confidence interval (CI)=6.0–66.7]. Similarly, patients with steroid-resistant MCNS had a higher frequency of the DRBI *07011 allele than controls (64.3% vs. 16.5%, P c<0.001). The EF was high at 0.57 (RR=9.6, CI 2.9–31.7). In the whole group of patients the frequency of DRBI *11 alleles was low compared with controls (11.4% vs. 32.2%, P =0.02), but was not significant when P was corrected. In conclusion, the DRBI *07011 allele confers susceptibility to a frequently relapsing and steroid-dependent or steroid-resistant course of childhood MCNS. These patterns of the disease seem to have the same immunogenetic components.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
International Study of Kidney Disease in Children (1978) Nephrotic syndrome in children. Prediction of histopathology from clinical and laboratory characteristics at time of diagnosis. Kidney Int 13:159–165
Bouissou F, Meissner I, Konrad M, Sommer E, Mytilimeos J, Ohayon E, Sierp G, Barthe B, Opelz G, Cambon-Thomsen A, et al (1995) Clinical implications from studies of HLA antigens in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in children. Clin Nephrol 44:279–283
Lagueruela CC, Buettner TL, Cole BR, Kissane JM, Robson AM (1990) HLA extended haplotypes in steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome of childhood. Kidney Int 38:145–150
Karabay-Bayazit A, Noyan A, Bayazit Y, Ozel A, Anarat A (2001) HLAs in children with minimal change disease and other types of nephrotic syndrome in the southern part of Turkey. Turk J Pediatr 43:24–28
Adhikari M, Coovadia HM, Hammond MG (1985) Associations between HLA antigens and nephrotic syndrome in African and Indian children in South Africa. Nephron 41:289–292
Unanue ER, Allen PM (1987) The basis for the immunoregulatory role and other accessory cells. Science 235:551–557
Marsh SG (1997) Nomenclature for factors of HLA system, update January/February. WHO Nomenclature Committee for factors of HLA system. Hum Immunol 53:224
Odmer WF (1997) HLA: what′s the name commentary on HLA nomenclature development over the years. Tissue Antigens 49:293–296
Buyse I, Decorte R, Beans M, Cuppens H, Semana G, Emonds MP, Marynen P, Cassiman JJ (1993) Rapid DNA typing of class II HLA antigens using the polymerase chain reaction and reverse dot blot hybridization. Tissue Antigens 41:1–14
Thonnard J, Deldime F, Heusterpreute M, Delepaut B, Hanon F, De Bruyaere M, Philip M (1995) HLA class II genotyping: two assay systems compared. Clin Chem 41:553–556
Vaughan RW (1991) PCR-SSO typing for HLA-DRB alleles. Eur J Immunogenet 18:69–80
Emery AEH (1976) Methodology in medical generics, 1st edn. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, p 98
Bevgtsson BO, Thomson G (1981) Measuring the strength of association between HLA antigens and diseases. Tissue Antigens, 18:356–363
Tomlinson IP, Bodmer WF (1995). The HLA system and the analysis of multifactorial disease. Trends Genet 11:493–498
Bakr AM, El-Chenawi F (1998) HLA-DQB1 and DRB1 alleles in Egyptian children with steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 12:234–237
Al-Eisa AA, Haider MZ, Srivasta BS (2000) HLA-DRB1 alleles in Kuwaiti children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 15:79–81
Konrad M, Mytilineos J, Bouissou F, Scherer S, Gulli MP, Meissner I, Cambon-Thomsen A, Oplez G, Scharer K (1994) HLA class II associations with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in children. Tissue Antigens 43:275–280
Krasowska-Kwiecien A, Sancewicz-Pach K, Pogan A (2001) Class II human leukocyte antigens in minimal change nephrotic syndrome and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis—preliminary study. Pol Merkuriusz Lek 10:256–258
Cambon-Thomsen A, Bouissou F, Abbel M, Duprat MP, Barthe P, Calot M, Ohayon E (1986) HLA and Bf in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in children: differences between corticosensitive and corticoresistant forms. Pathol Biol (Paris) 34:725–730
Clark AG, Vaughan RW, Stephens HA, Chantler C, Williams DG, Welsh KI (1990) Genes encoding the beta-chains of HLA-DR7 and HLA-DQw2 define major susceptibility determinants for idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Clin Sci 78:391–397
Ruder H, Scharer K, Opelz G, Lenhard V, Waldherr R, Muller-Wiefel DE, Wingen AM, Dippell J (1990) Human leucocyte antigens in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in children. Pediatr Nephrol 4:478–481
Haeffner A, Abbal M, Mytilineos J, Konrad M, Krammer I, Bouissou F, Opelz G, Scharer K, Cambon-Thomsen A (1997) Oligotyping for HLA-DQA, -DQB and -DPB in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 11:291–295
Kobayashi T, Ogawa A, Takahashi K, Uchiyama M (1995) HLA-DQB1 allele associates with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in Japanese children. Acta Paediatr Jpn 37:293–296
Konrad M, Mytilineos J, Ruder H, Opelz G, Scharer K (1997) HLA-DR7 predicts the response to alkylating agents in steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 11:16–19
McEnery PT, Welch TR (1989) Major histocompatibility complex antigens in steroid-responsive nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 3:33–36
Zaki M, Daoud AS, AI-Saleh QA, AI-Najedi AI–Najedi AK, White AG (1994) HLA antigens in Arab children with steroid-responsive nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 8:74–75
Abe KK, Michinage I, Hiratsuka T, Ogahara S, Natio S, Arakawa K, Tsuru N, Tokieda K (1995) Association of DQBI *0302 alloantigens in Japanese pediatric patients with steroid sensitive nephrotic syndrome Nephron 70:28–34
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bakr, A.M., El-Chenawi, F. & Al-Husseni, F. HLA alleles in frequently relapsing steroid-dependent and -resistant nephrotic syndrome in Egyptian children. Pediatr Nephrol 20, 159–162 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-004-1730-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-004-1730-7