Abstract
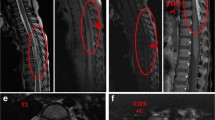
Spinal epidural lipomatosis (SEL) in patients on steroid therapy may be explained by two hypotheses: (1) steroids induce SEL and (2) steroids cause the growth of a pre-existing SEL, especially in obese children. Steroid-induced SEL (SSEL) is rarely described in children, with only six cases reported elsewhere. However, we have already reported four nephrotic children with SSEL, including one child in another hospital, in addition to the six cases. We investigated the frequency of SSEL in 125 children with renal diseases treated with glucocorticoids in a single hospital over 16 years, and examined the risk factors in 62 patients with SSEL reported in the literature. When patients complained of symptoms at the early stage of SSEL, i.e., back pain or numbness, and patients were obese, we performed spinal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). SSEL was detected in 5 of 125 children (4.0%). Of the 5 patients with SSEL, 3 had vertebral compression fractures, and all 5 patients were on methylprednisolone pulse therapy. Our study suggests that many more patients can be detected at the early stage of SSEL by performing spinal MRI for patients with early symptoms, obesity, and those who have received methylprednisolone pulse therapy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Munoz A, Barkovich JA, Mateos F, Simon R (2002) Symptomatic epidural lipomatosis of the spinal cord in a child: MR demonstration of spinal cord injury. Pediatr Radiol 32:865–868
George WE Jr, Wilmot M, Greenhouse R, Hammeke M (1983) Medical management of steroid induced epidural lipomatosis. N Engl J Med 308:316–319
Quint DJ, Boulou RS, Sanders WP, Mehta BA, Petel SC, Tiel RL (1988) Epidural lipomatosis. Radiology 169:485–490
Arroyo IL, Barron KS, Brewer EJ Jr (1988) Spinal cord compression by epidural lipomatosis in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31:447–451
Shirai I, Ando K (1990) Spinal epidural lipomatosis during steroid therapy (in Japanese). Shoni Naika 22:795–799
Miller DL, Blaser S, Laxer RM (2002) Clinical images: epidural lipomatosis in a 14-year-old boy with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 46:1291
Kano K, Kuwashima S, Kyo K, Ando T, Ichimura T (1996) Steroid-induced epidural lipomatosis in nephritic children: early recognition with MR imaging. Dokkyo J Med Sci 23:185–191
Hierholzer J, Benndorf G, Lehmann T, Schneider GH, Podrabsky P, Sander B, Soerensen R, Siekman R, Stoltenburg G, Felix R (1996) Epidural lipomatosis; case report and literature review. Neuroradiography 38:343–348
Pennisi AK, Meisler WJ, Dina TS (1985) Lymphomatous meningitis and steroid-induced epidural lipomatosis: CT evaluation. J Comput Assist Tomogr 9:595–598
Healy ME, Hesselink JR, Ostrup RC, Alksne JF (1987) Demonstration by magnetic resonance of symptomatic spinal epidural lipomatosis. Neurosurgery 21:414–415
Vazquez L, Ellis A, Saint-Genez D (1988) Epidural lipomatosis after renal transplantation—complete recovery without surgery. Transplantation 46:773–774
Buthiau D, Piette JT, Ducerveau MN, Robert G, Godeau P, Heitz F (1988) Steroid-induced spinal epidural lipomatosis: CT survey. J Comput Assist Tomogr 12:501–503
Maehara T, Tanohata K, Noda M, Nakayama D (1988) Medically treated steroid-induced epidural lipomatosis. Neuroradiology 30:281
Kaplan JG, Barasch E, Hirschfeld A, Ross L, Einberg K, Gordon M (1989) Spinal epidural lipomatosis: a serious complication of iatrogenic Cushing’s syndrome. Neurology 39:1031–1034
Soloniuk DS, Pecoraro SR, Munshauer FE (1989) Myelopathy secondary to spinal epidural lipomatosis: a case report. 14:119–122
Crayton HE, Partington CR, Bell CL (1992) Spinal cord compression by epidural lipomatosis in a patient with lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 35:482–484
Laroche F, Chemouilli P, Carlier R, Lebras P, Doyon D, Said G (1993) Efficacite du traitement medical dans une compression medullaire par lipomatose epidurale compliquant une corticotherapie prolongee (in French). Rev Rhum 60:846–849
Lemaire M, Maldague P, Noel P (1998) Corticosteroid-induced epidural lipomatosis: efficacy of medical treatment. Ann Med Intrene 149:459–463
Akiyama N, Takeuchi M, Shibagaki Y, Uchiyama S, Iwata M (1999) Two cases of spinal epidural lipomatosis. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 39:634–638
Andress H-J, Schuermann M, Heuck A, Schmand J, Lob G (2000) A rare case of osteoporotic spine fractures associated with epidural lipomatosis causing paraplegia following long-term cortisone therapy. Arth Orthop Trauma Surg 120:484–486
Jalladeau E, Carpentier AF, Napolitano M, Delattre J-Y (2000) Corticosteroid induced epidural lipomatosis. Rev Neurol (Paris) 156:517–519
Walchli B, Benini A (2001) Spinal epidural lipomatosis. Swiss Med Wkly 131:359
Ebright JR, Stellini MA, Tselis AC (2001) Spinal epidural lipomatosis in a human immunodeficiency virus-positive patient receiving steroids and protease inhibitor therapy. Clin Infect Dis 32:e90–91
Chen C-C, Lee W-Y, Cho D-Y (2002) Spinal epidural lipomatosis. Chinese Med J (Taipei) 65:86–89
Miyakoshi N, Shimada Y, Murai H, Suzuki T, Hongo M, Itoi E (2002) Combination of lumbar kyphosis, epidural lipomatosis, and perineural cyst as a cause of neurological deficit: a case report. J Orthop Sci 7:717–720
Sato M, Yamashita K, Aoki Y, Hiroshima K (1995) Idiopathic spinal epidural lipomatosis; case report and review of literature. Clin Orthop 320:129–134
Beges C, Rousselin B, Chevrot A, Godefroy D, Vallee C, Berenbaum F, Deshays C, Amor B (1994) Epidural lipomatosis: interest of magnetic resonance imaging in a weight-reduction treated case. Spine 19:251–254
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. S. Tomita (Department of Surgical and Molecular Pathology, Dokkyo University School of Medicine) and Dr. Y. Ueda (Department of Pathology, Koshigaya Hospital, Dokkyo University School of Medicine) for their valuable advice on renal histology, Dr. S. Kuwashima (Department Radiology, Dokkyo University School of Medicine) for her radiological diagnosis, and Dr. K. Kimura (the Medical Engineering Laboratory, Dokkyo University School of Medicine) for his advice on statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kano, K., Kyo, K., Ito, S. et al. Spinal epidural lipomatosis in children with renal diseases receiving steroid therapy. Pediatr Nephrol 20, 184–189 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-004-1723-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-004-1723-6