Abstract.
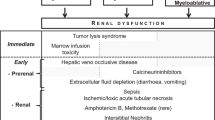
Since more and more children survive allogeneic bone marrow transplantation (BMT), knowledge of acute and late complications becomes increasingly important. Besides the major complications [(opportunistic) infections, veno-occlusive disease, graft versus host disease, and recurrence of primary disease], acute and chronic renal insufficiency are significant post-transplant complications that may contribute to transplant-related mortality. To elucidate risk factors for acute and chronic renal insufficiency post BMT, we performed a prospective study of all 66 children who received a BMT in a 2-year period at our institution; 21% had acute renal insufficiency post BMT. Risk factors for acute renal insufficiency were veno-occlusive disease, high cyclosporin serum levels, and foscarnet therapy. Of surviving patients, 11% developed chronic renal insufficiency 1 year post BMT. Acute renal insufficiency was the sole predictor of chronic renal insufficiency. In contrast to studies in adults, we did not find total body irradiation to be a risk factor for chronic renal insufficiency. Future long-term studies are needed to assess incidence and morbidity of chronic renal insufficiency in children following allogeneic BMT.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kist-van Holthe, J.E., Goedvolk, C.A., Brand, R. et al. Prospective study of renal insufficiency after bone marrow transplantation. Pediatr Nephrol 17, 1032–1037 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-002-0989-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-002-0989-9