Abstract
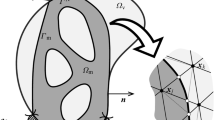
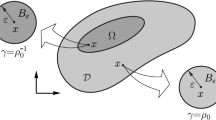
A new topology optimization method for free-form surfaces is developed, significantly reducing the dimensions of the design problem, providing smooth structural boundary descriptions and inherently avoiding checkerboard patterns. First, the basic idea is to represent the topology of free-form surfaces with a manifold-based material field function with the predefined spatial correlation. Then we employ a series expansion and truncation technique on the material field function to reduce the control coefficients of the topology description down to a small set. The spatial correlation of the manifold-based material field is formulated in an exponential form expressed with the geodesic distance. Herein, the geodesic distance is evaluated based on the heat method, which is convenient to implement and can achieve high computational efficiency and accuracy. The sensitivity analysis procedures are provided, and the gradient-based optimization algorithm is utilized to solve the proposed optimization model without requiring special filtering techniques. Several numerical examples are presented to illustrate the validity and applicability of the present topology optimization method on free-form surface structures and its potential for gradient-free topology optimization.






























Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data and code will be made available on request. The MATLAB code for the original MFSE method can also be downloaded from the website https://journal.hep.com.cn/fme/EN/10.1007/s11465-021-0637-3.
References
Desbrun M, Kanso E, Tong Y. (2008) Discrete differential forms for computational modeling. Discrete Differential Geometry. Birkhäuser Basel, 287–324
Seo YD, Youn SK, Yeon JH, Chang SY, Yoo JT. (2004) Topology optimization of inner-wall stiffener for critical buckling loads of cylindrical containers. In: 10th AIAA/ISSMO Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization Conference. p 4418
Zhu JH, Zhang WH, Xia L (2016) Topology optimization in aircraft and aerospace structures design. Arch Comput Methods Eng 23(4):595–622
Zhu JH, Li Y, Zhang WH. Topology optimization with shape preserving design. In: Proceedings of 5th international conference on computational methods, Cambridge, UK, 2014
Sigmund O, Maute K (2013) Topology optimization approaches. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48(6):1031–1055
Eschenauer HA, Olhoff N (2001) Topology optimization of continuum structures: a review. Appl Mech Rev 54(4):331–390
Rozvany GIN (2009) A critical review of established methods of structural topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 37(3):217–237
van Dijk NP, Maute K, Langelaar M, van Keulen F (2013) Level-set methods for structural topology optimization: a review. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48(3):437–472
Munk DJ, Vio GA, Steven GP (2015) Topology and shape optimization methods using evolutionary algorithms: a review. Struct Multidiscip Optim 52(3):613–631
Bendsøe MP, Kikuchi N (1988) Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 71(2):197–224
Ansola R, Canales J, Tarrago JA, Rasmussen J (2002) On simultaneous shape and material layout optimization of shell structures. Struct Multidiscip Optim 24(3):175–184
Bendsøe MP (1989) Optimal shape design as a material distribution problem. Struct Optim 1(4):193–202
Zhou M, Rozvany GIN (1991) The COC algorithm, part II: topological, geometrical and generalized shape optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 89(1–3):309–336
Hassani B, Tavakkoli SM, Ghasemnejad H (2013) Simultaneous shape and topology optimization of shell structures. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48(1):221–233
Deng Y, Liu Z, Korvink JG (2020) Topology optimization on two-dimensional manifolds. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 364:112937
Gu XD, Wang S, Kim J, Zeng Y, Wang Y, Qin H, Samaras D. (2007) Ricci flow for 3D shape analysis. In: 11th International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE, pp 1–8
Gu XD, Wang Y, Chan TF, Thompson PM, Yau ST (2004) Genus zero surface conformal mapping and its application to brain surface mapping. IEEE Trans Med Imag 23(8):949–958
Ye Q, Guo Y, Chen S, Lei N, Gu XD (2019) Topology optimization of conformal structures on manifolds using extended level set methods (X-LSM) and conformal geometry theory. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 344:164–185
Vogiatzis P, Ma M, Chen S, Gu XD (2018) Computational design and additive manufacturing of periodic conformal metasurfaces by synthesizing topology optimization with conformal mapping. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 328:477–497
Tian J, Zhao X, Gu XD, Chen S. (2020) designing conformal ferromagnetic soft actuators using extended level set methods (X-LSM). In: International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 83990, p V010T10A012
Luo Y, Bao J (2019) A material-field series-expansion method for topology optimization of continuum structures. Comput Struct 225:106122
Liu P, Yan Y, Zhang X, Luo Y (2021) A MATLAB code for the material-field series-expansion topology optimization method. Front Mech Eng 16(3):607–622
Wang Y, Luo Y, Yan Y (2022) A multi-material topology optimization method based on the material-field series-expansion model. Struct Multidiscip Optim 65(1):1–15
Luo Y, Xing J, Kang Z (2020) Topology optimization using material-field series expansion and Kriging-based algorithm: an effective non-gradient method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 364:112966
Liu P, Yan Y, Zhang X, Luo Y, Kang Z (2021) Topological design of microstructures using periodic material-field series-expansion and gradient-free optimization algorithm. Mater Des 199:109437
Luo Y, Li Y (2022) Tunable bandgap design of soft phononic crystals using topology optimization. Adv Theor Simul 5(7):2100620
Shi S, Zhou P, Lü Z (2021) A density-based topology optimization method using radial basis function and its design variable reduction. Struct Multidiscip Optim 64(4):2149–2163
Svanberg K (1987) The method of moving asymptotes—a new method for structural optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 24(2):359–373
Schrijver A (2012) On the history of the shortest path problem. Doc Math 17(1):155–167
Surazhsky V, Surazhsky T, Kirsanov D, Gortler SJ, Hoppe H (2005) Fast exact and approximate geodesics on meshes. ACM Trans Graph (TOG) 24(3):553–560
Sethian JA, Vladimirsky A (2000) Fast methods for the Eikonal and related Hamilton-Jacobi equations on unstructured meshes. Proc Natl Acad Sci 97(11):5699–5703
Crane K, Weischedel C, Wardetzky M (2013) Geodesics in heat: a new approach to computing distance based on heat flow. ACM Trans Graph (TOG) 32(5):1–11
Tao J, Zhang J, Deng B, Fang Z, Peng Y, He Y (2019) Parallel and scalable heat methods for geodesic distance computation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 43(2):579–594
Zhang J, Ellingwood B (1994) Orthogonal series expansions of random fields in first-order reliability analysis. J Eng Mech 120(12):2660–2677
Loève M (1955) Probability theory. Van Nostrand, Princeton
Li CC, Kiureghian DA (1993) Optimal discretization of random fields. J Eng Mech 119(6):1136–1154
Luo Y, Zhan J, Xing J, Kang Z (2019) Non-probabilistic uncertainty quantification and response analysis of structures with a bounded field model. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 347:663–678
Varadhan SRS (1967) On the behavior of the fundamental solution of the heat equation with variable coefficients. Commun Pure Appl Math 20(2):431–455
Turk G, Levoy M. (1994) Zippered polygon meshes from range images. In: Proceedings of the 21st Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques. pp 311–318
Schwarz G (2006) Hodge decomposition - a method for solving boundary value problems. Springer, Newyork
Kimmel R, Sethian JA (1998) Fast marching methods on triangulated domains. Proc Nat Acad Sci 95:8431–8435
Wang SY, Tai K (2005) Structural topology design optimization using Genetic Algorithms with a bit-array representation. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 194:3749–3770
Wu CY, Tseng KY (2010) Topology optimization of structures using modified binary differential evolution. Struct Multidiscip Optim 42:939–953
Deng C, Wang Y, Qin C et al (2022) Self-directed online machine learning for topology optimization. Nat Commun 13(1):1–14
Acknowledgements
This work was supported financially by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52275237, 11902064) and the Shenzhen Stability Support Key Program of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Z., Liu, P., Sun, Z. et al. Manifold-based material field series expansion method for topology optimization on free-form surfaces. Comput Mech 71, 237–255 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-022-02233-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-022-02233-3