Abstract
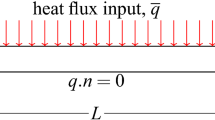
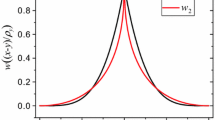
The present contribution is concerned with the macroscopic modelling of the selective electron beam melting process by using the finite element method. The modelling and simulation of the selective electron beam melting process involves various challenges: complex material behaviour, phase changes, thermomechanical coupling, high temperature gradients, different time and length scales etc. The present contribution focuses on performance considerations of solution approaches for thermomechanically coupled problems, i.e. the monolithic and the adiabatic split approach. The material model is restricted to nonlinear thermoelasticity with temperature-dependent material parameters. As a numerical example a straight scanning path is simulated, the predicted temperatures and stresses are analysed and the performance of the two algorithms is compared. The adiabatic split approach turned out to be much more efficient for linear thermomechanical problems, i.e. the solution time is three times less than with the monolithic approach. For nonlinear problems, stability issues necessitated the use of the Euler backward integration scheme, and therefore, the adiabatic split approach required small time steps for reasonable accuracy. Thus, for nonlinear problems and in combination with the Euler backward integration scheme, the monolithic solver turned out to be more efficient.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Argyris JH, Szimmat J, Willam KJ (1982) Computational aspects of welding stress analysis. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 33(1):635–665
Armero F, Simo J (1992) A new unconditionally stable fractional step method for non-linear coupled thermomechanical problems. Int J Numer Methods Eng 35(4):737–766
Bangerth W, Hartmann R, Kanschat G (2007) deal. iia general-purpose object-oriented finite element library. ACM Trans Math Softw (TOMS) 33(4):24
Čanadija M, Brnić J (2004) Associative coupled thermoplasticity at finite strain with temperature-dependent material parameters. Int J Plast 20(10):1851–1874
Chen T, Zhang Y (2006) Three-dimensional modeling of selective laser sintering of two-component metal powder layers. Trans-Am Soc Mech Eng J Manuf Sci Eng 128(1):299
Contuzzi N, Campanelli S, Ludovico A (2011) 3d finite element analysis in the selective laser melting process. Int J Simul Model 10:113–121
Dai K, Shaw L (2004) Thermal and mechanical finite element modeling of laser forming from metal and ceramic powders. Acta Mater 52(1):69–80
Dong L, Makradi A, Ahzi S, Remond Y (2009) Three-dimensional transient finite element analysis of the selective laser sintering process. J Mater Process Technol 209:700–706
Ehlers W, Zinatbakhsh S, Markert B (2013) Stability analysis of finite difference schemes revisited: A study of decoupled solution strategies for coupled multifield problems. Int J Numer Methods Eng 94(8):758–786
Felippa CA, Park K, Farhat C (2001) Partitioned analysis of coupled mechanical systems. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 190(24):3247–3270
Heinl P, Müller L, Körner C, Singer RF, Müller FA (2008) Cellular ti–6al–4v structures with interconnected macro porosity for bone implants fabricated by selective electron beam melting. Acta Biomater 4(5):1536–1544
Heinl P, Rottmair A, Körner C, Singer RF (2007) Cellular titanium by selective electron beam melting. Adv Eng Mater 9(5):360–364
Jhabvala J (2010) Study of the consolidation process under macro-and microscopic thermal effects in selective laser sintering and selective laser melting. Ph.D. Thesis, EPFL
Johansson L, Klarbring A (1993) Thermoelastic frictional contact problems: modelling, finite element approximation and numerical realization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 105(2):181–210
Kolossov S, Boillat E, Glardon R, Fischer P, Locher M (2004) 3d fe simulation for temperature evolution in the selective laser sintering process. Int J Machine Tools Manuf 44(2):117–123
Körner C, Attar E, Heinl P (2011) Mesoscopic simulation of selective beam melting processes. J Mater Process Technol 211(6):978–987
Kruth JP, Froyen L, Van Vaerenbergh J, Mercelis P, Rombouts M, Lauwers B (2004) Selective laser melting of iron-based powder. J Mater Process Technol 149(1):616–622
Kruth JP, Mercelis P, Van Vaerenbergh J, Froyen L, Rombouts M (2005) Binding mechanisms in selective laser sintering and selective laser melting. Rapid Prototyp J 11(1):26–36
Lindgren LE (2006) Numerical modelling of welding. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 195(48):6710–6736
Mercelis P, Kruth JP (2006) Residual stresses in selective laser sintering and selective laser melting. Rapid Prototyp J 12(5):254–265
Sedlak J, Piska M, Ptaekova M, Madaj M, Charvat O, Dvooaeek J, Zouhar J, Rozkosny L (2010) Properties of the biocompatible TiAl6V4 material produced by DMLS. MTM Int Virtual J 4–5:74–78
Simo J, Miehe C (1992) Associative coupled thermoplasticity at finite strains: formulation, numerical analysis and implementation. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 98(1):41–104
Williams JD, Deckard CR (1998) Advances in modeling the effects of selected parameters on the sls process. Rapid Prototyp J 4(2):90–100
Zaeh MF, Branner G (2010) Investigations on residual stresses and deformations in selective laser melting. Prod Eng 4(1):35–45
Acknowledgments
The authors want to thank the German Research Foundation (DFG) for funding the Collaborative Research Centre 814, sub-project C3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Riedlbauer, D., Steinmann, P. & Mergheim, J. Thermomechanical finite element simulations of selective electron beam melting processes: performance considerations. Comput Mech 54, 109–122 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-014-1026-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-014-1026-0