Abstract
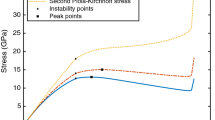
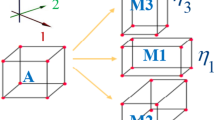
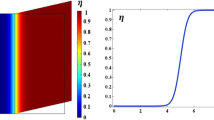
A finite element framework of a phase field model for nanoscale martensitic transformation is proposed on the basis of time-dependent Ginzburg–Landau kinetic equations. The bulk total free energy consists of the chemical driving energy, the interfacial energy, the elastic energy, the inertial energy (for a dynamic case), the energy due to applied field and the effects of surface energy which need to be considered at the nanoscale. Single-variant and multi-variant martensitic phase transformations in a nano-sized NiAl plate are considered. The numerical results show the effects of each energy item on the phase transformation and the self-accommodating twinned morphologies as the result of strain energy minimization.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen L-Q, Wang Y (1996) The continuum field approach to modeling microstructural evolution. JOM 48:13–18
Barrales-Mora LA, Mohles V, Konijnenberg PJ, Molodov DA (2007) A novel implementation for the simulation of 2-D grain growth with consideration to external energetic fields. Comput Mater Sci 39(1):160–165
Boettinger WJ, Warren JA, Beckermann C, Karma A (2002) Phase-field simulation of solidification. Annu Rev Mater Res 32:163–194
Wang YU, Jin YM, Cuitino AM, Khachaturyan AG (2001) Phase field microelasticity theory and modeling of multiple dislocation dynamics. Appl Phys Lett 78(16):2324–2326
Patoor E, Lagoudas DC, Entchev PB, Brinson LC, Gao X (2006) Shape memory alloys, Part I: general properties and modeling of single crystals. Mech Mater 38:391–429
Olson GB, Hartman H (1982) Martensite and life : displacive transformations as biological processes. J Phys Colloques 43(C4):855–865
Bhattacharya K (2003) Why it forms and how it gives rise to the shape-memory effect. Oxford University Press, New York
James RD, Hane KF (2000) Martensitic transformations and shape-memory materials. Acta Mater 48(1):197–222
Artemev A, Jin Y, Khachaturyan AG (2001) Three-dimensional phase field model of proper martensitic transformation. Acta Mater 49(7):1165–1177
Khachaturyan AG (1983) Theory of structural transformation in solids. Wiley, New York
Wang Y, Khachaturyan AG (1997) Three-dimensional field model and computer modeling of martensitic transformations. Acta Mater 45(2):759–773
Chen L-Q (2002) Phase-field models for microstructure evolution. Annu Rev Mater Res 32(1):113–140
Moelans N, Blanpain B, Wollants P (2008) An introduction to phase-field modeling of microstructure evolution. CALPHAD 32(2):268–294
Lei CH, Li LJ, Shu YC, Li JY (2010) Austenite–martensite interface in shape memory alloys. Appl Phys Lett 96(14):141910
Li LJ, Yang Y, Shu YC, Li JY (2010) Continuum theory and phase-field simulation of magnetoelectric effects in multiferroic bismuth ferrite. J Mech Phys Solids 58(10):1613–1627
Shu YC, Yen JH (2008) Multivariant model of martensitic microstructure in thin films. Acta Mater 56(15):3969–3981
Levitas VI, Preston DL (2002) Three-dimensional Landau theory for multivariant stress-induced martensitic phase transformations. I. Austenite to martensite. Phys Rev B 66(13):134206
Levitas VI, Preston DL (2002) Three-dimensional Landau theory for multivariant stress-induced martensitic phase transformations. II. Multivariant phase transformations and stress space analysis. Phys Rev B 66(13):134207
Chen LQ, Shen J (1998) Applications of semi-implicit Fourier-spectral method to phase field equations. Comput Phys Commun 108:147–158
Yamanaka A, Takaki T, Tomita Y (2008) Elastoplastic phase-field simulation of self- and plastic accommodations in martensitic transformation. Mater Sci Eng A 491:378–384
Mahapatra DR, Melnik RVN (2006) Finite element analysis of phase transformation dynamics in shape memory alloys with a consistent Landau–Ginzburg free energy model. Mech Adv Mater Struct 13(6):443–455
Alexander VI, Joon-Yeoun C, Valery IL (2008) Finite element modeling of dynamics of martensitic phase transitions. Appl Phys Lett 93(4):043102
Cho JY (2009) Finite element model of martensitic phase transformation. Ph.D. thesis, Texas Tech. University
Cho JY, Idesman AV, Levitas VI, Park T (2012) Finite element simulations of dynamics of multivariant martensitic phase transitions based on Ginzburg–Landau theory. Int J Solids Struct 49(14):1973–1992
She H, Liu Y, Wang B (2013) Phase field simulation of heterogeneous cubic to tetragonal martensite nucleation. Int J Solids Struct 50:1187–1191
Finel A, Le Bouar Y, Gaubert A, Salman U (2010) Phase field methods: microstructures, mechanical properties and complexity. Comptes Rendus Physique 11:245–256
She H, Wang B (2009) A geometrically nonlinear finite element model of nanomaterials with consideration of surface effects. Finite Elem Anal Des 45:463–467
Gao W, Yu S, Huang G (2006) Finite element characterization of the size-dependent mechanical behaviour in nanosystems. Nanotechnology 17(4):1118–1122
Park HS, Klein PA, Wagner GJ (2006) A surface Cauchy–Born model for nanoscale materials. Int J Numer Methods Eng 68(10):1072–1095
Dingreville R, Qu J, Mohammed C (2005) Surface free energy and its effect on the elastic behavior of nano-sized particles, wires and films. J Mech Phys Solids 53(8):1827–1854
Miller RE, Shenoy VB (2000) Size-dependent elastic properties of nanosized structural elements. Nanotechnology 11(3):139–147
Shenoy VB (2005) Atomistic calculations of elastic properties of metallic fcc crystal surfaces. Phys Rev B 71(9):094104
Levitas VI, Levin VA, Zingerman KM, Freiman EI (2009) Displacive phase transitions at large strains: phase-field theory and simulations. Phys Rev Lett 103(2):025702
Levitas VI, Lee D-W, Preston DL (2010) Interface propagation and microstructure evolution in phase field models of stress-induced martensitic phase transformations. Int J Plast 26(3):395–422
Bando Y (1964) Characteristics of phase transformation in metallic fine particles (martensitic transformation of FeNi alloys and ordering of CuAu and Cu3Au alloys). T Jpn I Met 5:135–141
Acknowledgments
This project is grateful for support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 10902128, 10732100, 50802026, 10972239, 11072271), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities. Hui She wishes to thank Dr. Wang Gang for instructions and help on COMSOL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
She, H., Liu, Y., Wang, B. et al. Finite element simulation of phase field model for nanoscale martensitic transformation. Comput Mech 52, 949–958 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-013-0856-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-013-0856-5