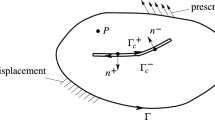
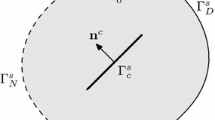
Abstract
Taking into account arbitrary crack geometries, crack closure generally occurs independently of the load case. As the standard eXtended Finite Element Method (XFEM) does not prevent unphysical crack face penetration in this case, a formulation allowing for crack face contact is proposed in terms of a penalty formulation for normal contact. The discretization is developed for non-planar cracks intersecting hexahedral elements in an arbitrary manner. Typical problems of many crack face contact implementations within the XFEM, like locking or the introduction of additional degrees of freedom, are avoided by projecting the contact contribution onto the hexahedral element nodes. The method is tested by means of suitable numerical examples, finally presenting an application in form of a multiscale setup with arbitrarily arranged micro cracks in the vicinity of a macro crack front.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dolbow J, Moës N, Belytschko T (2001) An extended finite element method for modeling crack growth with frictional contact. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 190: 6825–6846
Elguedj T, Gravouil A, Combescure A (2007) A mixed augmented Lagrangian-extended finite element method for modelling elastic-plastic fatigue crack growth with unilateral contact. Int J Numer Methods Eng 71: 1569–1597
Fischer KA, Wriggers P (2005) Frictionless 2D contact formulations for finite deformations based on the mortar method. Comput Mech 36: 226–244
Fischer KA, Wriggers P (2006) Mortar based frictional contact formulation for higher order interpolations using the moving friction cone. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 195: 5020–5036
Fries T-P (2008) A corrected XFEM approximation without problems in blending elements. Int J Numer Methods Eng 75: 503–532
Géniaut S, Massin P, Moës N (2007) A stable 3D contact formulation using X-FEM. Eur J Comput Mech 16: 259–275
Giner E, Tur M, Tarancón JE, Fuenmayor FJ (2010) Crack face contact in X-FEM using a segment-to-segment approach. Int J Numer Methods Eng 82: 1424–1449
Hüeber S, Matei A, Wohlmuth BI (2007) Efficient algorithms for problems with friction. SIAM J Sci Comput 29: 70–92
Krstulović-Opara L, Wriggers P, Korelc J (2002) A C 1-continuous formulation for 3D finite deformation frictional contact. Comput Mech 29: 27–42
Liu F, Borja RI (2008) A contact algorithm for frictional crack propagation with the extended finite element method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 76: 1489–1512
Liu F, Borja RI (2009) An extended finite element framework for slow-rate frictional faulting with bulk plasticity and variable friction. Int J Numer Analyt Methods Geomech 33: 1535–1560
Liu F, Borja RI (2010) Finite deformation formulation for embedded frictional crack with the extended finite element method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 82: 773–804
Loehnert S, Belytschko T (2007) A multiscale projection method for macro/microcrack simulations. Int J Numer Methods Eng 71: 1466–1482
Loehnert S, Mueller-Hoeppe DS (2008) Multiscale methods for fracturing solids. In: IUTAM symposium on theoretical, computational and modelling aspects of inelastic media, Adelaide, pp 79–87
Loehnert S, Mueller-Hoeppe DS, Wriggers P (2011) 3D corrected XFEM approach and extension to finite deformation theory. Int J Numer Methods Eng 86: 431–452
McDevitt TW, Laursen TA (2000) A mortar-finite element formulation for frictional contact problems. Int J Numer Methods Eng 48: 1525–1547
Moës N, Béchet E, Tourbier M (2006) Imposing Dirichlet boundary conditions in the extended finite element method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 67: 1641–1669
Moës N, Dolbow J, Belytschko T (1999) A finite element method for crack growth without remeshing. Int J Numer Methods Eng 46: 131–150
Mueller-Hoeppe DS, Loehnert S, Clasen H, Krstulovic-Opara L, Vesenjak M (2012) Numerical aspects of the comparison of metal foams with and without filler material computed using the XFEM. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng (submitted)
Nistor I, Guiton MLE, Massin P, Moës N, Géniaut S (2009) An X-FEM approach for large sliding contact along discontinuities. Int J Numer Methods Eng 78: 1407–1435
Osher S, Sethian JA (1988) Fronts propagating with curvature-dependent speed: algorithms based on Hamilton-Jacobi formulations. J Comput Phys 79: 12–49
Parisch H (1989) A consistent tangent stiffness matrix for three-dimensional non-linear contact analysis. Int J Numer Methods Eng 28: 1803–1812
Pierres E, Baietto MC, Gravouil A, Morales-Espejel G (2010) 3D two scale X-FEM crack model with interfacial frictional contact: application to fretting fatigue. Tribol Int 43: 1831–1841
Ribeaucourt R, Baietto-Dubourg M-C, Gravouil A (2007) A new fatigue frictional contact crack propagation model with the coupled X-FEM / LATIN method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 196: 3230–3247
Siavelis M, Massin P, Guiton MLE, Mazet S, Moës N (2010) Robust implementation of contact under friction and large sliding with the eXtended finite element method. Eur J Comput Mech 19: 189–203
Simo JC, Wriggers P, Taylor RL (1985) A perturbed Langrangian formulation for the finite element solution of contact problems. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 50: 163–180
Song J-H, Belytschko T (2009) Dynamic fracture of shells subjected to impulsive loads. ASME J Appl Mech 76: 051301
Sukumar N, Moës N, Moran B, Belytschko T (2000) Extended finite element method for three-dimensional crack modelling. Int J Numer Methods Eng 48: 1549–1570
Wriggers P (2006) Computational contact mechanics. Springer, Heidelberg
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mueller-Hoeppe, D.S., Wriggers, P. & Loehnert, S. Crack face contact for a hexahedral-based XFEM formulation. Comput Mech 49, 725–734 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-012-0701-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-012-0701-2