Abstract
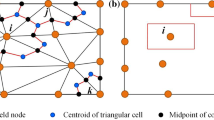
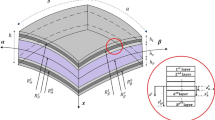
In this paper, the static and free vibration analysis of laminated shells is performed by radial basis functions (RBFs) collocation, according to a layerwise deformation theory (LW). The present LW theory accounts for through-the-thickness deformation, by considering an Mindlin-like evolution of all displacements in each layer. The equations of motion and the boundary conditions are obtained by Carrera’s unified formulation, and further interpolated by collocation with RBFs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koiter WT (1970) On the foundations of the linear theory of thin elastic shell. Proc Kon Nederl Akad Wetensch 73: 169–195
Naghdi PM (1956) A survey of recent progress in the theory of elastic shells. Appl Mech Rev 9: 365–368
Ren JG (1987) Exact solutions for laminated cylindrical shells in cylindrical bending. Compos Sci Technol 29: 169–187
Varadan TK, Bhaskar K (1991) Bending of laminated orthotropic cylindrical shells—an elasticity approach. Compos Struct 17: 141–156
Noor AK, Rarig PL (1974) Three-dimensional solutions of laminated cylinders. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 3: 319–334
Noor AK, Peters WS (1989) Stress, vibration and buckling of multilayered cylinders. J Struct Eng ASCE 115: 69–89
Noor AK, Peters WS (1989) A posteriori estimates for shear correction factors in multilayered composite cylinders. J Eng Mech ASCE 115: 1225–1245
Ye JQ, Soldatos KP (1994) Three-dimensional vibration of laminated cylinders and cylindrical panels with symmetric or antisymmetric cross-ply lay-up. Compos Eng 4: 429–444
Grigolyuk EI, Kulikov GM (1988) General direction of the development of the theory of shells. Mekhanica Kompozitnykh Materialov 2: 287–298
Kapania RK, Raciti S (1989) Recent advances in analysis of laminated beams and plates. AIAA J 27: 923–946
Kapania RK (1989) A review on the analysis of laminated shells. J Press Vessel Technol 111: 88–96
Noor AK, Burton WS (1989) Assessment of shear deformation theories for multilayered composite plates. Appl Mech Rev 41: 1–18
Noor AK, Burton WS (1990) Assessment of computational models for multilayered composite shells. Appl Mech Rev 43: 67–97
Noor AK, Burton WS, Bert CW (1996) Computational model for sandwich panels and shells. Appl Mech Rev 49: 155–199
Soldatos KP, Timarci T (1993) A unified formulation of laminated composites, shear deformable, five-degrees-of-freedom cylindrical shell theories. Compos Struct 25: 165–171
Reddy JN (1997) Mechanics of laminated composite plates, theory and analysis. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Hsu T, Wang JT (1970) A theory of laminated cylindrical shells consisting of layers of orthotropic laminae. AIAA J 8: 2141–2146
Cheung YK, Wu CI (1972) Free vibrations of thick, layered cylinders having finite length with various boundary conditions. J Sound Vib 24: 189–200
Srinivas S (1973) A refined analysis of composite laminates. J Sound Vib 30: 495–550
Sun CT, Whitney JM (1973) On the theories for the dynamic response of laminated plates. AIAA J 11: 372–398
Barbero EJ, Reddy JN, Teply JL (1990) General two-dimensional theory of laminated cylindrical shells. AIAA J 28: 544–553
Cho KN, Bert CW, Striz AG (1991) Free vibrations of laminated rectangular plates analyzed by higher order individual-layer theory. J Sound Vib 145: 429–442
Nosier A, Kapania RK, Reddy JN (1993) Free vibration analysis of laminated plates using a layer-wise theory. AIAA J 31: 2335–2346
Gaudenzi P, Barboni R, Mannini A (1995) A finite element evaluation of single-layer and multi-layer theories for the analysis of laminated plates. Compos Struct 30: 427–440
Carrera E (1998) Evaluation of layer-wise mixed theories for laminated plates analysis. AIAA J 36: 830–839
Carrera E (1998) Layer-wise mixed models for accurate vibration analysis of multilayered plates. J Appl Mech 65: 820–828
Carrera E (2003) Theories and finite elements for multilayered plates and shells: a unified compact formulation with numerical assessment and benchmarking. Arch Comput Methods Eng 97: 10–215
Carrera E (1999) Multilayered shell theories accounting for layerwise mixed description. Part 1: governing equations. AIAA J 37(9): 1107–1116
Carrera E (1999) Multilayered shell theories accounting for layerwise mixed description. Part 2: numerical evaluations. AIAA J 37(9): 1117–1124
Carrera E (1999) A study of transverse normal stress effect on vibration of multilayered plates and shells. J Sound Vib 225(5): 803–829
Carrera E (1998) A Reissner’s mixed variational theorem applied to vibrational analysis of multilayered shell. J Appl Mech 66: 63–78
Dennis ST, Palazotto AN (1989) Transverse shear deformation in orthotropic cylindrical pressure vessels using a higher-order shear theory. AIAA J 27(10): 1441–1447
Merk J (1995) Hierarchische, Kontinuumbasiert Shalenelemente höhere Ordnung. PhD Dissertation, Institute for Statics and Dynamics, Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany
Di S, Ramm E (1993) Hybrid stress formulation for higher-order theory of laminated shell analysis. Comput Method Appl Mech Eng 109: 359–376
Kansa EJ (1990) Multiquadrics: a scattered data approximation scheme with applications to computational fluid dynamics. I: Surface approximations and partial derivative estimates. Comput Math Appl 19(8/9): 127–145
Hon YC, Lu MW, Xue WM, Zhu YM (1997) Multiquadric method for the numerical solution of byphasic mixture model. Appl Math Comput 88: 153–175
Hon YC, Cheung KF, Mao XZ, Kansa EJ (1999) A multiquadric solution for the shallow water equation. ASCE J Hydraul Eng 125(5): 524–533
Wang JG, Liu GR, Lin P (2002) Numerical analysis of biot’s consolidation process by radial point interpolation method. Int J Solids Struct 39(6): 1557–1573
Liu GR, Gu YT (2001) A local radial point interpolation method (LRPIM) for free vibration analyses of 2-d solids. J Sound Vib 246(1): 29–46
Liu GR, Wang JG (2002) A point interpolation meshless method based on radial basis functions. Int J Numer Methods Eng 54: 1623–1648
Wang JG, Liu GR (2002) On the optimal shape parameters of radial basis functions used for 2-d meshless methods. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 191: 2611–2630
Chen XL, Liu GR, Lim SP (2003) An element free galerkin method for the free vibration analysis of composite laminates of complicated shape. Compos Struct 59: 279–289
Dai KY, Liu GR, Lim SP, Chen XL (2004) An element free galerkin method for static and free vibration analysis of shear-deformable laminated composite plates. J Sound Vib 269: 633–652
Liu GR, Chen XL (2002) Buckling of symmetrically laminated composite plates using the element-free galerkin method. Int J Struct Stab Dyn 2: 281–294
Liew KM, Chen XL, Reddy JN (2004) Mesh-free radial basis function method for buckling analysis of non-uniformity loaded arbitrarily shaped shear deformable plates. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 193: 205–225
Huang YQ, Li QS (2004) Bending and buckling analysis of antisymmetric laminates using the moving least square differential quadrature method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 193: 3471–3492
Liu L, Liu GR, Tan VCB (2002) Element free method for static and free vibration analysis of spatial thin shell structures. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 191: 5923–5942
Xiang S, Wang KM, Ai YT, Sha YD, Shi H (2009) Analysis of isotropic, sandwich and laminated plates by a meshless method and various shear deformation theories. Compos Struct 91(1): 31–37
Xiang S, Shi H, Wang KM, Ai YT, Sha YD (2010) Thin plate spline radial basis functions for vibration analysis of clamped laminated composite plates. Eur J Mech A Solids 29: 844–850
Ferreira AJM, Roque CMC, Jorge RMN (2006) Analysis of composite and sandwich plate by trigonometric layer-wise deformation theory and radial basis function. J Sandwich Struct Mater 8: 497–515
Ferreira AJM (2003) A formulation of the multiquadric radial basis function method for the analysis of laminated composite plates. Compos Struct 59: 385–392
Ferreira AJM (2003) Thick composite beam analysis using a global meshless approximation based on radial basis functions. Mech Adv Mater Struct 10: 271–284
Ferreira AJM, Roque CMC, Martins PALS (2003) Analysis of composite plates using higher-order shear deformation theory and a finite point formulation based on the multiquadric radial basis function method. Compos B 34: 627–636
Carrera E (2001) Developments, ideas, and evaluations based upon reissner’s mixed variational theorem in the modelling of multilayered plates and shells. Appl Mech Rev 54: 301–329
Carrera E (1996) C0 Reissner-Mindlin multilayered plate elements including zig-zag and interlaminar stress continuity. Int J Numer Methods Eng 39: 1797–1820
Carrera E, Kroplin B (1997) Zig-zag and interlaminar equilibria effects in large deflection and post-buckling analysis of multilayered plates. Mech Compos Mater Struct 4: 69–94
Carrera E (1998) Evaluation of layer-wise mixed theories for laminated plate analysis. AIAA J 36: 830–839
Hardy RL (1971) Multiquadric equations of topography and other irregular surfaces. Geophys Res 176: 1905–1915
Ferreira AJM, Fasshauer GE (2006) Computation of natural frequencies of shear deformable beams and plates by a rbf-pseudospectral method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 196: 134–146
Reddy JN, Liu CF (1985) A higher-order shear deformation theory of laminated elastic shells. Int J Eng Sci 23: 319–330
Cinefra M, Carrera E, Nali P (2010) MITC technique extended to variable kinematic multilayered plate elements. Compos Struct 92: 1888–1895
Cinefra M, Chinosi C, Della Croce L (2011) MITC9 shell elements based on refined theories for the analysis of isotropic cylindrical structures. Mech Adv Mater Struct (in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferreira, A.J.M., Carrera, E., Cinefra, M. et al. Analysis of laminated doubly-curved shells by a layerwise theory and radial basis functions collocation, accounting for through-the-thickness deformations. Comput Mech 48, 13–25 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-011-0579-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-011-0579-4