Abstract
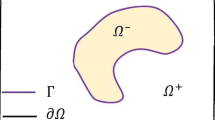
The radial basis function (RBF) collocation methods for the numerical solution of partial differential equation have been popular in recent years because of their advantage. For instance, they are inherently meshless, integration free and highly accurate. In this article we study the RBF solution of Eikonal equation using boundary knot method and analog equation method. The boundary knot method (BKM) is a meshless boundary-type radial basis function collocation technique. In contrast with the method of fundamental solution (MFS), the BKM uses the non-singular general solution instead of the singular fundamental solution to obtain the homogeneous solution. Similar to MFS, the RBF is employed to approximate the particular solution via the dual reciprocity principle. In the current paper, we applied the idea of analog equation method (AEM). According to AEM, the nonlinear governing operator is replaced by an equivalent nonhomogeneous linear one with known fundamental solution and under the same boundary conditions. Finally numerical results and discussions are presented to show the validity and efficiency of the proposed method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bardi M, Dalio F (1997) On the Bellman equation for some unbounded control problems. Nonlinear Differ Equ Appl 4: 491–510
Belytschko T, Lu YY, Gu L (1994) Element-free Galerkin methods. Int J Numer Meth Eng 37: 229–256
Boue M, Dupuis P (1992) Markov chain approximations for deterministic control problems with affine dynamics and quadratic cost in the control. SIAM J Numer Anal 36: 667–695
Bruss AR (1982) The Eikonal equation: some results applicable to computer vision. J Math Phys 23: 890–896
Bryson S, Levy D (2003) High-order central WENO schemes for multidimensional Hamilton–Jacobi equations. SIAM J Numer Anal 41: 1339–1369
Cecil T, Qian J, Osher S (2004) Numerical methods for high dimensional Hamilton–Jacobi equations using radial basis functions. J Comput Phys 196: 327–347
Cheng Y, Shu CW (2007) A discontinuous Galerkin finite element method for directly solving Hamilton–Jacobi equations. J Comput Phys 223: 398–415
Chen JS, Pan C, Wu CT, Liu WK (1996) Reproducing kernel particle methods for large deformation analysis of nonlinear structures. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 139: 195–228
Chen W, Tanaka M (2000) New insights in boundary-only and domain-type RBF methods. Int J Nonlinear Sci Numer Simulation 1: 145–152
Chen W, Tanaka M (2002) A meshfree, integration-free, and boundary-only RBF technique. Comput Math Appls 43: 379–391
Chen W, Shen LJ, Shen ZJ, Yuan GW (2005) Boundary knot method for Poisson equations. Engrg Anal Bound Elem 29: 756–760
Chen W (2002) Symmetric boundary knot method. Engrg Anal Bound Elem 26: 489–494
Crandall MG, Lions PL (1983) Viscosity solution of Hamilton–Jacobi equations. Trans Amer Math Soc 227: 1–42
Danielsson P (1980) Euclidean distance mapping. Comput Graph Image Process 14: 227–248
Deschamps T, Cohen LD (2002) Fast extraction of tubular and tree 3D surfaces with front propagation methods. Proc Intl Conf Pattern Recognition 731–734
Dehghan M (2006) Finite difference procedures for solving a problem arising in modeling and design of certain optoelectronic devices. Math Comput Simul 71: 16–30
Dehghan M, Hosseinzadeh H (2010) Development of circular arc boundary elements method. Eng Anal Bound Elem. doi:10.1016/j.enganabound.2010.08.014
Dehghan M, Shokri A (2008) A numerical method for solution of the two-dimensional sine-Gordon equation using the radial basis functions. Math Comput Simul 79: 700–715
Dehghan M, Salehi R (2010) A seminumeric approach for solution of the Eikonal partial differential equation and its applications. Numer Meth Partial Diff Equ 26: 702–722
Dehghan M, Salehi R (2009) The use of variational iteration method and Adomian decomposition method to solve the Eikonal equation and its application in the reconstruction problem. Commun Numer Meth Eng. doi:10.1002/cnm.1315A
Duarte CA, Oden JT (1996) H-p clouds–an hp meshless method. Numer Method Partial Diff Eq 12: 673–705
Engquist B, Runborg O (1996) Multi-phase computations in geometric optics. J Comput Appl Math 74: 175–192
Hon YC, Chen W (2003) Boundary knot method for 2D and 3D Helmholtz and convection–diffusion problems under complicated geometry. Int J Numer Meth Engrg 56: 1931–1948
Hu C, Shu CW (1999) A discontinuous Galerkin finite element method for Hamilton–Jacobi equations. SIAM J Sci Comput 21: 666–690
Jiang GS, Peng DP (2000) Weighted ENO schemes for Hamilton–Jacobi equations. SIAM J Sci Comput 21: 2126–2143
Jin S, Xin Z (1998) Numerical passage from systems of conservation laws to Hamilton–Jacobi equations and relaxation schemes. SIAM J Numer Anal 35: 2385–2404
Jin B, Zheng Y (2005) Boundary knot method for the Cauchy problem associated with the inhomogeneous Helmholtz equation. Eng Anal Bound Elem 29: 925–935
Jin B, Chen W (2006) Boundary knot method based on geodesic distance for anisotropic problems. J Comput Phys 215: 614–629
Katsikadelis JT (1994) The analog equation method–a powerful BEM-based solution technique for solving linear and nonlinear engineering problems. In: Brebbia CA (eds) Boundary Element Method XVI. CLM Publications, Southampton, p 167
Katsikadelis JT, Nerantzaki MS (1999) The boundary element method for nonlinear problems. Eng Anal Bound Elem 23: 365–373
Katsikadelis JT, Nerantzaki MS (2001) A Boundary element solution to the soap bubble problem. Comput Mech 27: 154–159
Katsikadelis JT (2002) The analog equation method. A boundary-only integral equation method for nonlinear static and dynamic problems in general bodies. Int J Theor Appl Mech 27: 13–38
Katsikadelis JT, Tsiatas GC (2003) Nonlinear dynamic analysis of heterogeneous orthotropic membranesby the analog equation method. Eng Anal Bound Elem 27: 115–124
Katsikadelis JT (2008) The 2D elastostatic problem in inhomogeneous anisotropic bodies by the meshless analog equation method(MAEM). Eng Anal Bound Elem 32: 997–1005
Katsikadelis JT (2009) The meshless analog equation method. I. Solutionvof elliptic partial differential equations. Arch Appl Mech 79: 557–578
Kimmel R, Sethian JA (2001) Optimal algorithm for shape from shading and path planning. J Math Imaging Vis 14: 237–244
Kimmel R, Bruckstein AM (1993) Shape offsets via level sets. Comput Aided Des 25: 154–162
Kimmel R, Shaked D, Kiryati N, Bruckstein A (1995) Skeletonization via distance maps and level sets. Comput Vis Image Unders 62: 382–391
Kim DW, Liu WK (2006) Maximum principle and convergence analysis for the meshfree point collocation method. SIAM J Numer Anal 44: 515–539
Kim DW, Yoon YC, Liu WK, Belytschko T (2007) Extrinsic meshfree approximation using asymptotic expansion for interfacial discontinuity of derivative. J Comput Phys 221: 370–394
Kim DW, Liu WK, Yoon YC, Belytschko T, Lee SH (2007) Meshfree point collocation method with intrinsic enrichment for interface problems. Comput Mech 40: 1037–1052
Li F, Shu CW, Zhao YT, Zhao H (2008) A second order discontinuous Galerkin fast sweeping method for Eikonal equations. J Comput Phys 227: 8191–8208
Liu WK, Jun S, Zhang Y (2005) Reproducing kernel particle method. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 20: 1081–1106
Liu WK, Jun S, Li S, Adee J, Belytschko T (1995) Reproducing kernel particle methods for structural dynamics. Int J Numer Methods Eng 38: 1655–1679
Li S, Liu WK (2004) Meshfree particle methods. Springer, Berlin
Liu WK, Li S, Belytschko T (1997) Moving least squares reproducing kernelm ethods, Part I. methodology and convergence. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 143: 113–154
Li G, Aluru NR (2002) Boundary cloud method: a combined scattered point/boundary integral approach for boundary-only analysis. Comput Meth Appl Mech Engrg 191: 2337–2370
Liu GR, Gu YT (2001) A point interpolation method for two dimensional solid. Int J Numer Meth Engrg 50: 937–951
Lucy LB (1977) A numerical approach to the testing of the fission hypothesis. Astron J 82(12): 1013–1024
Melenk JM, Babuska I (1996) The partition of unity finite element method: basic theory and applications. Comput Methods Appl Mech Engrg 139: 289–314
Mirzaei D, Dehghan M (2010) A meshless based method for solution of integral equations. Appl Numer Math 60: 245–262
Mitchell IM, Sastry S (2003) Continuous path planning with multiple constraint. IEEE 5: 5502–5507
Mukherjee YX, Mukherjee S (1997) The boundary node method for potential problems. Int J Numer Meth Engrg 40: 797–815
Nayroles B, Touzot G, Villon P (1992) Generalizing the finite element method: Diffuse approximation and diffuse elements. Comput Mech 10: 307–318
Osher S (1993) A level set formulation for the solution of the Dirichlet problem for Hamilton–Jacobi equations. SIAM J Math Anal 24: 1145–1152
Osher S, Sethian J (1988) Fronts propagating with curvature dependent speed: algorithms based on Hamilton–Jacobi formulations. J Comput Phys 79: 12–49
Osher S, Shu CW (1991) High-order essentially nonoscillatory schemes for Hamilton–Jacobi equations. SIAM J Numer Anal 28: 907–922
Rouy E, Tourin A (1992) A viscosity solutions approach to shape-from-shading. SIAM J Numer Anal 29: 867–884
Rawlinson N, Sambridge M (2005) The fast marching method: an effective tool for tomographics imaging and tracking multiple phases in complex layered media. Explor Geophys 36: 341–350
Shu C-W (2004) High order numerical methods for time dependent Hamilton–Jacobi equations. WSPC/Lecture Notes Series
Sukumar N, Moran B, Belytschko T (1998) The natural element method in solid mechanics. Int J Numer Meth Eng 43: 839–887
Tatari M, Dehghan M (2009) On the solution of the non-local parabolic partial differential equations via radial basis functions. Appl Math Modell 33: 1729–1738
Wang F, Chen W, Jiang X (2009) Investigation of regularized techniques for boundary knot method. Commun Numer Method Eng doi:10.1002/cnm.1275
Zhu T, Zhang JD, Atluri SN (1998) A local boundary integral equation (LBIE) method in computational mechanics, and a meshless discretization approaches. Comput Mech 21: 223–235
Zhang YT, Zhao HK, Qian J (2006) High order fast sweeping methods for static Hamilton–Jacobi equations. J Sci Comput 29: 25–56
Zhang YT, Shu CW (2003) High order WENO schemes for Hamilton–Jacobi equations on triangular meshes. SIAM J Sci Comput 24: 1005–1030
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dehghan, M., Salehi, R. A boundary-only meshless method for numerical solution of the Eikonal equation. Comput Mech 47, 283–294 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-010-0547-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-010-0547-4