Abstract
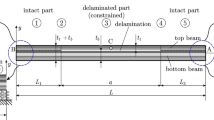
Forced oscillations of delaminated composite laminates lead to non-smooth dynamic systems due to continuously developing impact-like contacts along the delamination. The primary aim of this study is to investigate a realistic model situation for delamination problems based on experiments and numerical simulation. First, the properties of lateral impacts on beam-type structures are studied, in particular in regard to the amount of energy dissipation during contact. Taking these results into account the finite element method based on beam elements is employed to simulate the stationary state of typical oscillations observed on the delaminated structure paying special attention to the dynamically developing and strongly dissipative contact. To deal with that kind of contact arising between delaminated layers, an effective technique combining a law of impact with the classical penalty method is presented. Confronting numerical results with the experimental reference provides an insight into the accuracy and robustness of the simulation technique
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Farrar CR, Sohn H, Fugate ML, Czarnecki JJ (2001) Integrated structural health monitoring. In: Proceedings of SPIE’s 8th annual international symposium on smart structures and materials, Newport Beach, USA
Zou L, Tong L, Steven GP (2000) Vibration-based model-dependent damage (delamination) identification and health monitoring for composite structures. J Sound Vib 230(2):357–378
Zheng Y, Maev RG, Solodov IY (1999) Nonlinear acoustic applications for material characterization: a review. Can J Phys 77:927–967
Vielsack P (2002) A vibro-impacting model for the detection of delamination. J Sound Vib 253(2):347–358
Philippow E (1967) Grundlagen der Elektrotechnik. Akademische Verlagsgesellschaft Geest & Portig KG / Leipzig
Hu B, Schiehlen W, Eberhard P (2003) Comparison of analytical and experimental results for longitudinal impacts on elastic rods. J Vib Control 9:157–174
Engleder T, Vielsack P, Schweizerhof K (2002) F.E.-regularisation of non-smooth vibrations due to friction and impacts. Comput Mech 28:162–168
Zienkiewicz OC, Taylor RL (2000) The finite element method. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford
Valente AX, McClamroch NH, Mezi I (2003) Hybrid dynamics of two coupled oscillators that can impact a fixed stop. Int J Non-Linear Mech 38(5):677–689
Müller I, Vielsack P (2003) Penalty-regularisation of a dissipative vibro-impacting system. J Comput Appl Mech 4(2):173–186
Müller I, Konyukhov A, Vielsack P, Schweizerhof K (2005) Parameter estimation for finite element analyses of stationary oscillations of a vibro-impacting system. Eng Struct 27(2):191–201
Vielsack P, Hartung A (1999) An example for the orbital stability of permanently disturbed non-smooth motions. ZAMM 79(6):389–397
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müller, I. Clapping in delaminated sandwich-beams due to forced oscillations. Comput Mech 39, 113–126 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-005-0013-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-005-0013-x