Abstract
Background: Laparoscopic cholecystectomy (LC) has become the reference treatment for biliary lithiasis, but the management strategy for common bile duct stones (CBDS) remains a subject of controversy in the absence of an established consensus. While conventional surgery remains the reference treatment for CBDS, minimally invasive techniques are becoming more and more popular. These methods consist of the extraction of the common bile duct stones either exclusively by laparoscopy or by sequential treatment with endoscopic sphincterotomy (ES) followed by LC. The aim of this study was to evaluate the treatment of CBDS in a one-stage operation by laparoscopic cholecystectomy (LC) and perioperative endoscopic sphincterotomy.
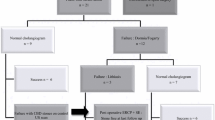
Patients and methods: Between January 1994 and March 1998, 44 patients, 20 male and 24 female, (sex ratio 1.2) with a median age of 57 years (range 28–84 years) were treated for suspected or confirmed CBDS. The CBDS were uncomplicated in 39 cases (88%) and associated with a complication in 5 cases (12%), namely, cholangitis (2 cases) or acute pancreatitis (3 cases).
The perioperative ES was performed immediately after the LC during the same operative time, with perioperative cholangiography being systematically performed (1 failure). In 6 cases, a transcystic drain was left in place (to ensure complete evacuation of the CBDS postoperatively) when there were more than three stones and/or when they were larger than 6 mm. The patient was positioned in the left lateral position in order to perform the ES.
Results: Mean operative time for LC was 60 min, range 40–90 min. The general anesthesia was prolonged by 40 min in order to perform an ES (range 30–60 min).The perioperative ES was unsuccessful in one case (2%), due to the impossibility of catheterizing the papilla, the preoperative MR cholangiogram being normal. Immediate clearance of the CBD was achieved in 95% of the cases (42 p). In 2 cases, residual stone was found in the sixth day after cholangiography and was spontaneously evacuated as shown by 21st-day control. There was no mortality or postoperative complications. The duration of the postoperative hospitalization was 4.6 days (range 3–6).
Conclusions: We believe that LC combined with perioperative ES is a quick, reliable, and safe technique for the treatment of CBDS during a single operative procedure, although this approach is limited by the proximity and availability of an endoscopic team.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 6 July 1998/Accepted: 12 February 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meyer, C., Vo Huu Le, J., Rohr, S. et al. Management of common bile duct stones in a single operation combining laparoscopic cholecystectomy and perioperative endoscopic sphincterotomy. Surg Endosc 13, 874–877 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004649901123
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004649901123



