Abstract
Background
Laparoscopic surgery provides many benefits to the patients. The purpose of this study was to evaluate cerebral blood flow changes and the possibility of ischemia-reperfusion injury occurring during carbon dioxide (CO2) pneumoperitoneum.
Methods
Forty-eight New Zealand white rabbits were divided into four experimental and two control groups. Rabbits were subjected to CO2 pneumoperitoneum with an intraabdominal pressure of 8 and 15 mmHg for 60 or 180 min as designed for experimental groups. We then assessed the changes in physiological and transcranial Doppler ultrasonographic parameters, as well as brain malondialdehyde levels.
Results
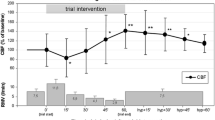
Transcranial Doppler sonography of the basilar artery revealed elevated mean velocity and decreased resistance index and pulsatility index values with the longer-duration and higher-pressure CO2 pneumoperitoneum. However, there were no statistically significant difference in malondialdehyde values.
Conclusion
Elevated intraabdominal pressure by CO2-pneumoperitoneum, which does not lead to ischemia-reperfusion injury of the brain tissue, results in increased cerebral blood flow and reduced cerebrovascular resistance as an autoregulatory cerebral answer for CO2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaslid R, Lindegaard KF, Sorteberg W, Nornes H (1989) Cerebral autoregulation dynamics in humans. Stroke 20: 45–52
Bonatsos G, Leandros E, Dourakis N, Birbas C, Delibaltadakis G, Golematis B (1995) Laparoscopic cholecystectomy: intraoperative findings and postoperative complications. Surg Endosc 9: 889–893
Bouma GJ, Muizelaar JP (1990) Relationship between cardiac output and cerebral blood flow in patients with intact and with impaired autoregulation. J Neurosurg 73: 368–774
Czosnyka M, Hugh KR, Helen EW, Pickard J (1996) Relationship between transcranial Doppler-determined pulsatility index and cerebrovascular resistance: an experimental study. J Neurosurg 84: 79–84
Fujii Y, Tanaka H, Tsuruoka S, Toyooka H, Amaha K (1994) Middle cerebral arterial blood flow velocity increases during laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Anesth Analg 78: 80–83
Grishman MB, Granger DN (1989) Free radicals: reactive metabolites of oxygen as mediators of postischemic reperfusion injury. In: Martson A, Bulkley GB, Fidian-Green RG, Haglund U (eds) Splanchnic ischemia and multiple organ failure. Mosby, St. Louis, pp 135–144
Hansen N, Stonestreet B, Rosenkrantz T (1983) Validity of Doppler measurements of anterior cerebral artery blood flow velocity: correlation with brain blood flow in piglets. Pediatrics 72: 526–531
Harper HM (1965) Inter-relationship between PaCO2 and blood pressure in the regulation of blood flow through the cerebral cortex. Acta Neurol Scand (Suppl 14) 41: 94–103
Kety SS, Schmidt CF (1948b) The effects of altered arterial tensions of carbon dioxide and oxygen on cerebral blood flow and cerebral oxygen consumption of normal young men. J Clin Invest 27: 484–489
Kirkinen P, Hirvonen E, Kauko M, Purhonen S, Nuutinen L (1995) Intracranial blood flow during laparoscopic hysterectomy. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 74: 71–74
Kotzampassi K, Kapanidis N, Kazamias P, Eleftheriadia E (1993) Hemodynamic events in the peritoneal environment during pneumoperitoneum in dogs. Surg Endosc 7: 494–499
Kubota K, Kajiura N, Teruya M, Ishihara T, Tsusima H, Ohta S, Nakao K, Arizono S (1993) Alterations in respiratory function and hemodynamics during laparoscopic cholecystectomy under pneumoperitoneum. Surg Endocs 7: 500–504
Kuroda Y, Murakami M, Tsuruta J, Murakawa T, Sakabe T (1997) Blood flow velocity of middle cerebral artery during prolonged anesthesia with halothane, isoflurane and sevoflurane in humans. Anesthesiology 87: 527–532
Muller K, Meier-Peter A, Piscol C (1967) Localized cerebral circulatory disorder as an unusual complication following laparoscopy. Med Klin Nov 62: 1790–1795
Obrist WD, Thompson HK, King CH, HS, Wang (1967) Determination of regional cerebral blood flow by inhalation of 133-xenon. Circ Res 20: 124–135
Rasmussen IB, Berggren U, Arvidsson D, Ljungdahl M, Haglund U (1995) Effects of pneumoperitoneum on splanchnic hemodynamics: an experimental study in pigs. Eur J Surg 161: 819–826
Sechzer PH, Egbert LD, Linde HW, Cooper DY, Dripps RD, Price HL (1960) Effect of CO2 inhalation on arterial pressure, ECG and plasma catecholamines and 17-OH corticosteroids in normal man. J Appl Physiol 15: 454–458
Sharma KC, Kabinoff G, Ducheine Y, Tierney J, Brandstetter RD (1997) Laparoscopic surgery and its potential for medical complications. Heart Lung 26: 52–67
Sorteberg W, Langmoen IA, Lindegaard KF, H, Nornes (1990) Side to side differences and day to day variations of transcranial Doppler parameters in normal subjects. J Ultrasound Med 9: 403–409
Tranquart F, Berson M, Bodard S, Roncin A, Pourcelot L (1991) Evaluation of cerebral blood flow in rabbits with transcranial Doppler sonography: first results. Ultrasound Med Biol 17: 815–818
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Online publication: 11 May 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erkan, N., Gokmen, N., Goktay, A.Y. et al. Effects of CO2 pneumoperitoneum on the basilar artery. Surg Endosc 15, 806–811 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004640090007
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004640090007