Abstract
Background
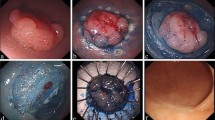
Owing to the rising number of screening endoscopies and instrumental advances in endoscopic ultrasound (EUS), colorectal subepithelial tumors (SETs) are being increasingly detected. We aimed to determine the feasibility of endoscopic resection (ER) and the impact of EUS-based surveillance on colorectal SETs.
Methods
The medical records of 984 patients with incidentally detected colorectal SETs between 2010 and 2019 were retrospectively reviewed. Overall, 577 colorectal SETs underwent ER, and 71 colorectal SETs underwent serial colonoscopy for > 12 months.
Results
The mean tumor size (± standard deviation) of 577 colorectal SETs for which ER was performed was 7.0 ± 5.7 (median, 55; range, 1–50) mm; 475 tumors were located in the rectum and 102, in the colon. En bloc resection was achieved in 560/577 treated lesions (97.1%), and complete resection was achieved in 516/577 (89.4%). ER-related adverse events occurred in 15/577 (2.6%) patients. SETs originating from the muscularis propria showed a higher risk of ER-related adverse events and perforation than SETs arising from the mucosal or submucosal layer (odds ratio [OR] 19.786, 95% confidence interval [CI] 4.556–85.919; P = 0.002 and OR 141.250, 95% CI 11.596–1720.492; P = 0.046, respectively). Seventy-one patients were followed up after EUS without any treatment for > 12 months, during which three showed progression; eight, regression; and sixty, no changes.
Conclusions
ER for colorectal SETs showed excellent efficacy and safety. Additionally, colorectal SETs without high-risk features in surveillance with colonoscopy showed an excellent prognosis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hedenbro JL, Ekelund M, Wetterberg P (1991) Endoscopic diagnosis of submucosal gastric lesions. The results after routine endoscopy. Surg Endosc 5:20–23
Lim YJ, Son HJ, Lee JS, Byun YH, Suh HJ, Rhee PL, Kim JJ, Rhee JC (2010) Clinical course of subepithelial lesions detected on upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. World J Gastroenterol 16:439–444
Hwang JH, Rulyak SD, Kimmey MB, American Gastroenterological Association I (2006) American Gastroenterological Association Institute technical review on the management of gastric subepithelial masses. Gastroenterology 130:2217–2228
Humphris JL, Jones DB (2008) Subepithelial mass lesions in the upper gastrointestinal tract. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 23:556–566
Park EY, Kim GH (2019) Diagnosis of gastric subepithelial tumors using endoscopic ultrasonography or abdominopelvic computed tomography: which is better? Clin Endosc 52:519–520
Sakamoto H, Kitano M, Kudo M (2010) Diagnosis of subepithelial tumors in the upper gastrointestinal tract by endoscopic ultrasonography. World J Radiol 2:289–297
Aso A, Yoshinaga S (2016) Future potential means of diagnosing gastric subepithelial lesions: Beyond conventional endoscopic ultrasound and endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration. Dig Endosc 28(Suppl 1):32–33
Chu YY, Lien JM, Tsai MH, Chiu CT, Chen TC, Yang KC, Ng SC (2012) Modified endoscopic submucosal dissection with enucleation for treatment of gastric subepithelial tumors originating from the muscularis propria layer. BMC Gastroenterol 12:124
Chun SY, Kim KO, Park DS, Lee IJ, Park JW, Moon SH, Baek IH, Kim JH, Park CK, Kwon MJ (2013) Endoscopic submucosal dissection as a treatment for gastric subepithelial tumors that originate from the muscularis propria layer: a preliminary analysis of appropriate indications. Surg Endosc 27:3271–3279
Ye LP, Zhang Y, Luo DH, Mao XL, Zheng HH, Zhou XB, Zhu LH (2016) Safety of endoscopic resection for upper gastrointestinal subepithelial tumors originating from the muscularis propria layer: an analysis of 733 tumors. Am J Gastroenterol 111:788–796
Soh JS, Kim JK, Lim H, Kang HS, Park JW, Kim SE, Moon SH, Kim JH, Park CK, Cho JW, Lim MS, Kim KO (2016) Comparison of endoscopic submucosal dissection and surgical resection for treating gastric subepithelial tumours. Scand J Gastroenterol 51:633–638
Song JH, Kim SG, Chung SJ, Kang HY, Yang SY, Kim YS (2015) Risk of progression for incidental small subepithelial tumors in the upper gastrointestinal tract. Endoscopy 47:675–679
Kushnir VM, Keswani RN, Hollander TG, Kohlmeier C, Mullady DK, Azar RR, Murad FM, Komanduri S, Edmundowicz SA, Early DS (2015) Compliance with surveillance recommendations for foregut subepithelial tumors is poor: results of a prospective multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc 81:1378–1384
Ye LS, Li Y, Liu W, Yao MH, Khan N, Hu B (2020) Clinical course of suspected small gastrointestinal stromal tumors in the stomach. World J Gastrointest Surg 12:171–177
Kim J, Ryu S, Kim YJ (2020) Endoscopic submucosal dissection of a colonic calcifying fibrous tumor. Clin Endosc 53:487–490
Qi ZP, Shi Q, Liu JZ, Yao LQ, Xu MD, Cai SL, Li B, Take I, Zhang YQ, Chen WF, Zhong YS, Zhou PH (2018) Efficacy and safety of endoscopic submucosal dissection for submucosal tumors of the colon and rectum. Gastrointest Endosc 87(540–548):e541
Bruno M, Carucci P, Repici A, Pellicano R, Mezzabotta L, Goss M, Magnolia MR, Saracco GM, Rizzetto M, De Angelis C (2009) The natural history of gastrointestinal subepithelial tumors arising from muscularis propria: an endoscopic ultrasound survey. J Clin Gastroenterol 43:821–825
Kim MY, Jung HY, Choi KD, Song HJ, Lee JH, Kim DH, Choi KS, Lee GH, Kim JH (2011) Natural history of asymptomatic small gastric subepithelial tumors. J Clin Gastroenterol 45:330–336
Lok KH, Lai L, Yiu HL, Szeto ML, Leung SK (2009) Endosonographic surveillance of small gastrointestinal tumors originating from muscularis propria. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis 18:177–180
Park EY, Baek DH, Song GA, Kim GH, Lee BE, Park DY (2020) Long-term outcomes of endoscopically resected laterally spreading tumors with a positive histological lateral margin. Surg Endosc 34:3999–4010
Landi B, Palazzo L (2009) The role of endosonography in submucosal tumours. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 23:679–701
Cho JW, Korean ESDSG (2016) Current guidelines in the management of upper gastrointestinal subepithelial tumors. Clin Endosc 49:235–240
Ye LP, Zhang Y, Mao XL, Zhu LH, Zhou X, Chen JY (2014) Submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection for small upper gastrointestinal subepithelial tumors originating from the muscularis propria layer. Surg Endosc 28:524–530
Zhang Y, Ye LP, Zhou XB, Mao XL, Zhu LH, He BL, Huang Q (2013) Safety and efficacy of endoscopic excavation for gastric subepithelial tumors originating from the muscularis propria layer: results from a large study in China. J Clin Gastroenterol 47:689–694
Oda I, Suzuki H, Nonaka S, Yoshinaga S (2013) Complications of gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection. Dig Endosc 25(Suppl 1):71–78
Li R, Cai S, Sun D, Shi Q, Ren Z, Qi Z, Li B, Yao L, Xu M, Zhou P, Zhong Y (2021) Risk factors for delayed bleeding after endoscopic submucosal dissection of colorectal tumors. Surg Endosc 35:6583–6590
Lee EJ, Lee JB, Choi YS, Lee SH, Lee DH, Kim DS, Youk EG (2012) Clinical risk factors for perforation during endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for large-sized, nonpedunculated colorectal tumors. Surg Endosc 26:1587–1594
Yang SC, Wu CK, Tai WC, Liang CM, Li YC, Yeh WS, Lee CH, Yang YH, Tsai TH, Hsu CN, Chuah SK (2020) Incidence and risk factors of colonoscopic post-polypectomy bleeding and perforation in patients with end-stage renal disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 35:1704–1711
Dumonceau JM, Deprez PH, Jenssen C, Iglesias-Garcia J, Larghi A, Vanbiervliet G, Aithal GP, Arcidiacono PG, Bastos P, Carrara S, Czako L, Fernandez-Esparrach G, Fockens P, Gines A, Havre RF, Hassan C, Vilmann P, van Hooft JE, Polkowski M (2017) Indications, results, and clinical impact of endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided sampling in gastroenterology: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Clinical Guideline—updated January 2017. Endoscopy 49:695–714
Menon L, Buscaglia JM (2014) Endoscopic approach to subepithelial lesions. Therap Adv Gastroenterol 7:123–130
Akahoshi K, Oya M, Koga T, Shiratsuchi Y (2018) Current clinical management of gastrointestinal stromal tumor. World J Gastroenterol 24:2806–2817
Acknowledgements
We thank the Department of Biostatistics, Clinical Trial Center, Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital for their excellent assistance in the statistical analysis, and Editage (www.editage.co.kr) for their English language editing.
Funding
This study was supported by a Biomedical Research Institute Grant (grant number: 20220031), Pusan National University Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EYP: Study concept, design, statistical analysis, interpretation of data, and manuscript drafting. DHB: Study concept, design, statistical analysis and interpretation of data, manuscript drafting and editing, supervision, and funding. SMH, BEL, MWL, and GHK: interpretation of data and supervision. DHB and EYP: Statistical analysis and interpretation of data, manuscript drafting, and editing. DHB: data acquisition, statistical analysis, and interpretation. GAS: supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
Eun Young Park, Dong Hoon Baek, Seung Min Hong, Bong Eun Lee, Moon Won Lee, Gwang Ha Kim, and Geun Am Song have no conflict of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Park, E.Y., Baek, D.H., Hong, S.M. et al. Feasibility of endoscopic resection and impact of endoscopic ultrasound-based surveillance on colorectal subepithelial tumors. Surg Endosc 37, 6867–6876 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-023-10195-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-023-10195-7