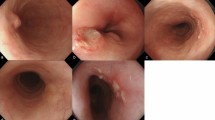
Abstract
Background
Patients with early esophageal squamous cell neoplasias (ESCNs) that are totally or nearly totally circumferential face challenges in their clinical work. Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) frequently leads to esophageal strictures. Endoscopic radiofrequency ablation (RFA), which stands out for its simplicity of use and low rate of stenosis, is a rapidly evolving therapeutic strategy for early ESCNs. We contrast ESD with RFA in order to find which method is best for the treatment of a wide range of esophageal diseases.
Methods
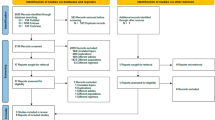
Patients who had flat-type, early, large ESCNs (extending more than 3/4 of the esophageal circumference) treated endoscopically were enrolled retrospectively. The primary outcome measurements were adverse events and local control of the neoplastic lesion.
Results
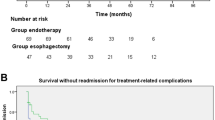
A total of 105 patients received treatment; 60 had ESD and 45 received RFA. Despite the patients receiving RFA typically having larger tumors (14.27 vs. 5.70 cm, P < 0.05), the local control of the neoplastic lesion and procedure-related complications were comparable between the ESD and RFA groups. A considerably higher risk of esophageal stenosis was observed in patients with extensive lesions in the ESD group compared to the RFA group (60% vs. 31%; P < 0.05), and the rate of refractory stricture is also higher than that of the RFA.
Conclusion
Both RFA and ESD are effective in treating large, flat, early ESCNs; however, ESD is more likely to cause side effects, such as esophageal stricture, particularly in lesions that are larger than 3/4 of the diameter. Before RFA, a more precise and thorough pretreatment examination should be performed. A more accurate pretreatment evaluation will be an important development direction for early esophageal cancer in future. After surgery, a strict routine review is crucial.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold M, Abnet CC, Neale RE et al (2020) Global burden of 5 major types of gastrointestinal cancer. Gastroenterology 159(1):335
Zeng HM, Zheng RS, Guo YM et al (2015) Cancer survival in China, 2003–2005: a population-based study. Int J Cancer 136(8):1921–1930
Ominami M, Nagami Y, Shiba M et al (2015) The five-year survival rate after endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gastrointest Endosc 81(5):AB516–AB517
Alsop BR, Sharma P (2016) Esophageal cancer. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 45(3):399–412
Haidry RJ, Dunn JM, Butt MA et al (2013) Radiofrequency ablation and endoscopic mucosal resection for dysplastic Barrett’s esophagus and early esophageal adenocarcinoma: outcomes of the UK National Halo RFA Registry. Gastroenterology 145(1):87–95
Ishihara R, Arima M, Iizuka T et al (2020) Endoscopic submucosal dissection/endoscopic mucosal resection guidelines for esophageal cancer. Dig Endosc 32(4):452–493
Li ZJ, Chai NL, Li LS et al (2018) Predictors of postoperative stricture after endoscopic submucosal dissection for large superficial esophageal squamous cell neoplasms. Am J Gastroenterol 113:S201–S202
Belghazi K, Bergman J, Pouw RE (2016) Endoscopic resection and radiofrequency ablation for early esophageal neoplasia. Dig Dis 34(5):469–475
Wang WL, Chang IW, Chang CY et al (2014) Circumferential balloon-based radiofrequency ablation for ultralong and extensive flat esophageal squamous neoplasia. Gastrointest Endosc 80(6):1185–1189
He S, Bergman J, Zhang Y et al (2015) Endoscopic radiofrequency ablation for early esophageal squamous cell neoplasia: report of safety and effectiveness from a large prospective trial. Endoscopy 47(5):398–408
Bergman JJ, Zhang YM, He S et al (2011) Outcomes from a prospective trial of endoscopic radiofrequency ablation of early squamous cell neoplasia of the esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc 74(6):1181–1190
Haidry RJ, Butt MA, Dunn J et al (2013) Radiofrequency ablation for early oesophageal squamous neoplasia: Outcomes form United Kingdom registry. World J Gastroenterol 19(36):6011–6019
Jung M, Kiesslich R (1999) Chromoendoscopy and intravital staining techniques. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 13(1):11–19
Ono H, Yao K, Fujishiro M et al (2021) Guidelines for endoscopic submucosal dissection and endoscopic mucosal resection for early gastric cancer (second edition). Dig Endosc 33(1):4–20
Draganov PV, Wang AY, Othman MO et al (2019) AGA institute clinical practice update: endoscopic submucosal dissection in the United States. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 17(1):16
Kato H, Nakajima M (2013) Treatments for esophageal cancer: a review. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 61(6):330–335
Wolf DS, Dunkin BJ, Ertan A (2012) Endoscopic radiofrequency ablation of Barrett’s esophagus. Surg Technol Int 22:83–89
Kochman ML, McClave SA, Boyce HW (2005) The refractory and the recurrent esophageal stricture: a definition. Gastrointest Endosc 62(3):474–475
Tanaka S, Kashida H, Saito Y et al (2020) Japan Gastroenterological Endoscopy Society guidelines for colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection/endoscopic mucosal resection. Dig Endosc 32(2):219–239
Ono S, Fujishiro M, Niimi K et al (2009) Predictors of postoperative stricture after esophageal endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial squamous cell neoplasms. Endoscopy 41(8):661–665
Zhang Y, Bergman JJ, Xue L et al (2015) Preliminary study on efficacy of radiofrequency ablation combined with endoscopic resection for eradicating widespread early non-flat type esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi 18(9):875–880
Lee CT, Chang CY, Tai CM et al (2012) Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early esophageal neoplasia: a single center experience in South Taiwan. J Formos Med Assoc 111(3):132–139
Fugazza A, Repici A (2021) Endoscopic management of refractory benign esophageal strictures. Dysphagia 36(3):504–516
Wang WL, Chang IW, Chen CC et al (2015) Radiofrequency ablation versus endoscopic submucosal dissection in treating large early esophageal squamous cell neoplasia. Medicine (Baltimore) 94(49):e2240
Author contributions
YD and YL contributed equally to this manuscript. YD contributed to study design, date collection, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting of the manuscript, and critical revision of manuscript for important intellectual content. YL contributed to study design, analysis and interpretation of data, and critical revision of the manuscript. SL has conducted a preliminary study, study design, analysis and interpretation of data, statistical analysis, and study supervision. WZ, QQ, and YZ contributed to data collection. RS contributed to study design, technical support, critical revision of the manuscript, fund collection, and study supervision, and revising the final manuscript. All authors have significantly contributed. All authors are in agreement with the content of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article. Yuan Ding, Yang Liu, Siyu Lei, Wanyue Zhang, Qiliu Qian, Yawen Zhao, and Ruihua Shi have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The protocol is in accordance with the ethical guidelines of the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki, as reflected by prior approval by one Chinese tertiary academic hospital (2020ZDSYLL259-P01) from Zhongda Hospital Southeast University. All participants will be informed that their anonymous data will be used for research and publication. Relevant information about this project will be provided to potential eligible participants in oral and written forms for them to make their own decisions about participation or not. Each participant will be informed that he or she can withdraw from the study at any time and that withdrawal will not affect his or her subsequent medical treatment.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, Y., Liu, Y., Lei, S. et al. Comparison between ESD and RFA in patients with total or near-total circumferential early esophageal squamous cell neoplasia. Surg Endosc 37, 6915–6921 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-023-10178-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-023-10178-8