Abstract
Background
Anti-reflux mucosal intervention (ARMI), including anti-reflux mucosectomy (ARMS) and anti-reflux mucosal ablation (ARMA), is a promising endoscopic treatment for gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Few studies reported a detailed analysis of the objective reflux parameters.
Methods
Patients with chronic PPI-dependent GERD and receiving ARMI were prospectively enrolled. Comprehensive clinical symptom profiles, endoscopy results, and 24-h multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH (MII-pH) monitoring were collected and analyzed before and 3 months after ARMI.
Results
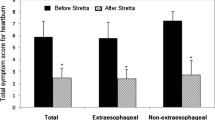
Twenty-three patients undergoing ARMI (11 ARMS and 12 ARMA) were enrolled. The median (IQR) operative time and post-procedure stays were 50 (46–56) min and 2 (2–2) days without major complications. 73.9% of patients reported subjective global improvement. A significant decrease in the total reflux symptom index score was noted from 12 (5–19) to 8 (4–12) (P = 0.010). The esophageal acid exposure time (AET) significantly decreased from 4.6 (2.8–6.9) to 2.1 (1.1–5.6) (P = 0.013), and the number of acid refluxes and DeMeester score were significantly reduced. Three patients (13%) had increased AET (3.4% to 6.1%, 6.3% to 15.4%, and 3.2% to 5.6%); however, all reported global improvement and two patients could discontinue PPI subjectively. One patient (4.3%) had worsened erosive esophagitis and reflux symptoms. 56.5% of patients stopped PPI.
Conclusions
ARMI is generally effective and safe in PPI-dependent patients. However, possible negative effects of ARMI exist in some patients; further application of MII-pH is necessitated to evaluate the treatment response after ARMI and avoid the detrimental effect of PPI discontinuation.
Graph.
Graphical abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gyawali CP, Kahrilas PJ, Savarino E, Zerbib F, Mion F, Smout A, Vaezi M, Sifrim D, Fox MR, Vela MF, Tutuian R, Tack J, Bredenoord AJ, Pandolfino J, Roman S (2018) Modern diagnosis of GERD: the lyon consensus. Gut 67:1351–1362
Katz PO, Dunbar KB, Schnoll-Sussman FH, Greer KB, Yadlapati R, Spechler SJ (2022) ACG Clinical Guideline for the diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol 117:27–56
Hung LJ, Hsu PI, Yang CY, Wang EM, Lai KH (2011) Prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux disease in a general population in Taiwan. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 26:1164–1168
Zerbib F, Bredenoord AJ, Fass R, Kahrilas PJ, Roman S, Savarino E, Sifrim D, Vaezi M, Yadlapati R, Gyawali CP (2021) ESNM/ANMS consensus paper: diagnosis and management of refractory gastro-esophageal reflux disease. Neurogastroenterol Motil 33:e14075
Pauwels A, Boecxstaens V, Andrews CN, Attwood SE, Berrisford R, Bisschops R, Boeckxstaens GE, Bor S, Bredenoord AJ, Cicala M, Corsetti M, Fornari F, Gyawali CP, Hatlebakk J, Johnson SB, Lerut T, Lundell L, Mattioli S, Miwa H, Nafteux P, Omari T, Pandolfino J, Penagini R, Rice TW, Roelandt P, Rommel N, Savarino V, Sifrim D, Suzuki H, Tutuian R, Vanuytsel T, Vela MF, Watson DI, Zerbib F, Tack J (2019) How to select patients for antireflux surgery? The ICARUS guidelines (international consensus regarding preoperative examinations and clinical characteristics assessment to select adult patients for antireflux surgery). Gut 68:1928–1941
Sumi K, Inoue H, Kobayashi Y, Iwaya Y, Abad MRA, Fujiyoshi Y, Shimamura Y, Ikeda H, Onimaru M (2021) Endoscopic treatment of proton pump inhibitor-refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease with anti-reflux mucosectomy: experience of 109 cases. Dig Endosc 33:347–354
Shimamura Y, Inoue H (2020) Anti-reflux mucosectomy: can we do better? Dig Endosc 32:736–738
Inoue H, Tanabe M, de Santiago ER, Abad MRA, Shimamura Y, Fujiyoshi Y, Ueno A, Sumi K, Tomida H, Iwaya Y, Ikeda H, Onimaru M (2020) Anti-reflux mucosal ablation (ARMA) as a new treatment for gastroesophageal reflux refractory to proton pump inhibitors: a pilot study. Endosc Int Open 8:E133–E138
Inoue H, Ito H, Ikeda H, Sato C, Sato H, Phalanusitthepha C, Hayee B, Eleftheriadis N, Kudo SE (2014) Anti-reflux mucosectomy for gastroesophageal reflux disease in the absence of hiatus hernia: a pilot study. Ann Gastroenterol 27:346–351
Wong HJ, Su B, Attaar M, Kuchta K, Stearns S, Linn JG, Haggerty SP, Denham W, Ujiki MB (2021) Anti-reflux mucosectomy (ARMS) results in improved recovery and similar reflux quality of life outcomes compared to laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Surg Endosc 35:7174–7182
Debourdeau A, Vitton V, Monino L, Barthet M, Gonzalez JM (2020) Antireflux Mucosectomy Band (ARM-b) in treatment of refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease after bariatric surgery. Obes Surg 30:4654–4658
Yoo IK, Ko WJ, Kim HS, Kim HK, Kim JH, Kim WH, Hong SP, Yeniova AO, Cho JY (2020) Anti-reflux mucosectomy using a cap-assisted endoscopic mucosal resection method for refractory gastroesophageal disease: a prospective feasibility study. Surg Endosc 34:1124–1131
Weusten B, Barret M, Bredenoord AJ, Familiari P, Gonzalez JM, van Hooft JE, Lorenzo-Zuniga V, Louis H, Martinek J, van Meer S, Neumann H, Pohl D, Prat F, von Renteln D, Savarino E, Sweis R, Tack J, Tutuian R, Ishaq S (2020) Endoscopic management of gastrointestinal motility disorders—part 2: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline. Endoscopy 52:600–614
Rodriguez de Santiago E, Sanchez-Vegazo CT, Penas B, Shimamura Y, Tanabe M, Alvarez-Diaz N, Parejo S, Kazuya S, Marcos-Carrasco N, Vazquez-Sequeiros E, Inoue H, Albillos A (2021) Antireflux mucosectomy (ARMS) and antireflux mucosal ablation (ARMA) for gastroesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endosc Int Open 9:E1740–E1751
Ghisa M, Barberio B, Savarino V, Marabotto E, Ribolsi M, Bodini G, Zingone F, Frazzoni M, Savarino E (2020) The lyon consensus: does it differ from the previous ones? J Neurogastroenterol Motil 26:311–321
Jonasson C, Wernersson B, Hoff DA, Hatlebakk JG (2013) Validation of the GerdQ questionnaire for the diagnosis of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 37:564–572
Farahat M, Malki KH, Mesallam TA (2012) Development of the arabic version of reflux symptom index. J Voice 26(814):e815-819
Taft TH, Carlson DA, Triggs J, Craft J, Starkey K, Yadlapati R, Gregory D, Pandolfino JE (2018) Evaluating the reliability and construct validity of the eckardt symptom score as a measure of achalasia severity. Neurogastroenterol Motil 30:e13287
Eckardt VF, Aignherr C, Bernhard G (1992) Predictors of outcome in patients with achalasia treated by pneumatic dilation. Gastroenterology 103:1732–1738
Tseng PH, Wong RKM, Wu JF, Chen CC, Tu CH, Lee YC, Lee HC, Wang HP, Wu MS (2018) Normative values and factors affecting water-perfused esophageal high-resolution impedance manometry for a Chinese population. Neurogastroenterol Motil 30:e13265
Kahrilas PJ, Bredenoord AJ, Fox M, Gyawali CP, Roman S, Smout AJ, Pandolfino JE, International High Resolution Manometry Working Group (2015) The Chicago classification of esophageal motility disorders, v3.0. Neurogastroenterol Motil 27:160–174
Sifrim D, Castell D, Dent J, Kahrilas PJ (2004) Gastro-oesophageal reflux monitoring: review and consensus report on detection and definitions of acid, non-acid, and gas reflux. Gut 53:1024–1031
Armstrong D, Bennett JR, Blum AL, Dent J, De Dombal FT, Galmiche JP, Lundell L, Margulies M, Richter JE, Spechler SJ, Tytgat GN, Wallin L (1996) The endoscopic assessment of esophagitis: a progress report on observer agreement. Gastroenterology 111:85–92
Hill LD, Kozarek RA, Kraemer SJ, Aye RW, Mercer CD, Low DE, Pope CE (1996) The gastroesophageal flap valve: in vitro and in vivo observations. Gastrointest Endosc 44:541–547
Hernandez Mondragon OV, Zamarripa Mottu RA, Garcia Contreras LF, Gutierrez Aguilar RA, Solorzano Pineda OM, Blanco Velasco G, Murcio Perez E (2020) Clinical feasibility of a new antireflux ablation therapy on gastroesophageal reflux disease (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 92:1190–1201
Li ZT, Ji F, Han XW, Zhang R, Chen LD, Li CX, Yuan LL, Wang ZG, Liu KD (2021) Endoscopic cardial constriction with band ligation in the treatment of refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease: a preliminary feasibility study. Surg Endosc 35:4035–4041
Monino L, Gonzalez JM, Vitton V, Barthet M (2020) Antireflux mucosectomy band in treatment of refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease: a pilot study for safety, feasibility and symptom control. Endosc Int Open 8:E147–E154
Patil G, Dalal A, Maydeo A (2020) Feasibility and outcomes of anti-reflux mucosectomy for proton pump inhibitor dependent gastroesophageal reflux disease: first Indian study (with video). Dig Endosc 32:745–752
Yang X, Tan J, Liu Y, Feng Y, Shi R (2022) Comparison of 180 degrees anti-reflux mucosectomy versus 270 degrees anti-reflux mucosectomy for treatment of refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease: a retrospective study. Surg Endosc 36:5002–5010
Sifrim D, Roman S, Savarino E, Bor S, Bredenoord AJ, Castell D, Cicala M, de Bortoli N, Frazzoni M, Gonlachanvit S, Iwakiri K, Kawamura O, Krarup A, Lee YY, Soon Ngiu C, Ndebia E, Patcharatraku T, Pauwels A, Perez de la Serna J, Ramos R, Remes-Troche JM, Ribolsi M, Sammon A, Simren M, Tack J, Tutuian R, Valdovinos M, Xiao Y, Zerbib F, Gyawali CP (2021) Normal values and regional differences in oesophageal impedance-pH metrics: a consensus analysis of impedance-pH studies from around the world. Gut 70:1441–1449
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the staff of the Eighth Core Lab in the Department of Medical Research at the National Taiwan University Hospital for their technical support during this study.
Funding
This work received support from National Taiwan University Hospital (Grant Nos. NTUH. 110- 005025, NTUH 111-S0174). Ministry of Science and Technology (Grant Nos. MOST 108-2628-B-002-019, 109-2628-B-002-036, 110-2628-B-002-048).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Chu-Kuang Chou, Chien-Chuan Chen, Chieh-Chang Chen, Jia-Feng Wu, Wei-Chih Liao, Han-Mo Chiu, Hsiu-Po Wang, Ming-Shiang Wu, and Ping-Huei Tseng have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chou, CK., Chen, CC., Chen, CC. et al. Positive and negative impact of anti-reflux mucosal intervention on gastroesophageal reflux disease. Surg Endosc 37, 1060–1069 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-022-09605-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-022-09605-z