Abstract
Background
Omental wrapping (OW) is the leading cause of obstruction of the peritoneal dialysis (PD) catheter, which interferes with dialysis treatment. Routinely or selectively performing omentopexy during laparoscopic PD catheter placement has been suggested to prevent OW. However, most of the published techniques for performing this adjunctive procedure require additional incisions and suturing. Herein, we aimed to report our experience in performing omentopexy with a sutureless technique during dual-incision PD catheter insertion. We also performed a comparative analysis to assess the benefit/risk profile of routine omentopexy in these patients.
Methods
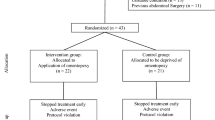
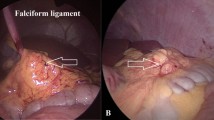
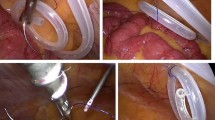
This retrospective study enrolled 469 patients who underwent laparoscopic PD catheter insertion. Their demographic characteristics and operative details were collected from the database of our institution. Omentopexy was performed by fixing the inferior edge of the omentum to the round ligament of the liver using titanium clips. For analysis, the patients were divided into the omentopexy group and the non-omentopexy group. We also reviewed the salvage management and outcomes of patients who experienced OW.
Results
The patients were categorized into the omentopexy (n = 81) and non-omentopexy (n = 388) groups. The patients in the non-omentopexy group had a higher incidence of OW, whereas no patient in the omentopexy group experienced this complication (5.2% vs. 0.0%, p = 0.033). The median operative time was 27 min longer in patients who underwent omentopexy than in those who did not [100 (82–118) min vs. 73 (63–84) min, p < 0.001]. One patient had an intra-abdominal hematoma after omentopexy and required salvage surgery to restore catheter function. The complication rate of omentopexy was 1.2% (1/81).
Conclusion
Sutureless omentopexy during laparoscopic PD catheter insertion is a safe and reliable technique that does not require additional incisions and suturing. Routinely performing omentopexy provides clinical benefits by reducing the risk of catheter dysfunction due to OW.
Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mujais S, Story K (2006) Peritoneal dialysis in the US: evaluation of outcomes in contemporary cohorts. Kidney Int 70:S21–S26
Shahbazi N, McCormick BB (2011) Peritoneal dialysis catheter insertion strategies and maintenance of catheter function. Semin Nephrol 31:138–151
Ogünç G (2002) Malfunctioning peritoneal dialysis catheter and accompanying surgical pathology repaired by laparoscopic surgery. Perit Dial Int 22:454–462
Ogunc G (2016) Malfunctioning peritoneal dialysis catheter and current treatment. Progress in peritoneal dialysis. SMGroup, Dover, pp 1–7
Yang PJ, Lee CY, Yeh CC, Nien HC, Tsai TJ, Tsai MK (2010) Mini-laparotomy implantation of peritoneal dialysis catheters: outcome and rescue. Perit Dial Int 30:513–518
Ogunc G (2017) Diagnosis and management of catheter dysfunction. In: Haggerty S (ed) Surgical aspects of peritoneal dialysis, 1st edn. Springer, Cham, pp 131–136
Oğünç G, Tuncer M, Oğünç D, Yardimsever M, Ersoy F (2003) Laparoscopic omental fixation technique versus open surgical placement of peritoneal dialysis catheters. Surg Endosc 17:1749–1755
Haggerty S, Roth S, Walsh D, Stefanidis D, Price R, Fanelli RD, Penner T, Richardson W (2014) Guidelines for laparoscopic peritoneal dialysis access surgery. Surg Endosc 28:3016–3045
Attaluri V, Lebeis C, Brethauer S, Rosenblatt S (2010) Advanced laparoscopic techniques significantly improve function of peritoneal dialysis catheters. J Am Coll Surg 211:699–704
Crabtree JH (2006) Selected best demonstrated practices in peritoneal dialysis access. Kidney Int 70:S27–S37
Haskins IN, Schreiber M Jr, Prabhu AS, Krpata DM, Perez AJ, Tastaldi L, Tu C, Rosen MJ, Rosenblatt S (2017) Peritoneal dialysis catheter placement as a mode of renal replacement therapy: long-term results from a tertiary academic institution. Surgery 162:1112–1120
Ogunc G (2005) Minilaparoscopic extraperitoneal tunneling with omentopexy: a new technique for CAPD catheter placement. Perit Dial Int 25:551–555
Cao W, Tu C, Jia T, Liu C, Zhang L, Zhao B, Liu J, Zhang L (2019) Prophylactic laparoscopic omentopexy: a new technique for peritoneal dialysis catheter placement. Ren Fail 41(1):113–117
Zhang L, Liu J, Shu J, Hu J, Yu X, Mao H, Ren H, Hong H, Xing C (2011) Low-site peritoneal catheter implantation decreases tip migration and omental wrapping. Perit Dial Int 31:202–204
Krezalek MA, Bonamici N, Lapin B, Carbray J, Velasco J, Denham W, Linn J, Ujiki M, Haggerty SP (2016) Laparoscopic peritoneal dialysis catheter insertion using rectus sheath tunnel and selective omentopexy significantly reduces catheter dysfunction and increases peritoneal dialysis longevity. Surgery 160:924–935
Kaya M, Boleken M, Soran M, Yucesan S (2012) Laparoscopic omental folding: a new procedure to prevent omental wraps of continuous peritoneal dialysis catheters. Eur Surg 44:345–348
Ogünç G (2001) Videolaparoscopy with omentopexy: a new technique to allow placement of a catheter for continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Surg Today 31:942–944
Crabtree JH, Fishman A (2003) Selective performance of prophylactic omentopexy during laparoscopic implantation of peritoneal dialysis catheters. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 13:180–184
Crabtree JH, Burchette RJ (2009) Effective use of laparoscopy for long-term peritoneal dialysis access. Am J Surg 198:135–141
Yeh CN, Liao CH, Liu YY, Cheng CT, Wang SY, Chiang KC, Tian YC, Chiu CC, Weng SM, Hwang TL (2013) Dual-incision laparoscopic surgery for peritoneal dialysis catheter implantation and fixation: a novel, simple, and safe procedure. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 23:673–678
Zhao L, Yang J, Bai M, Dong F, Sun S, Xu G (2021) Risk factors and management of catheter malfunction during urgent-start peritoneal dialysis. Front Med 8:741312
Harvey EA (2001) Peritoneal access in children. Perit Dial Int 21:S218–S222
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely appreciated the assistance of all the PD nurses.
Funding
There are no funds associated with this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Hao-Wei Kou, Chun-Nan Yeh, Chun-Yi Tsai, Jun-Te Hsu, Chao-Wei Lee, Shang-Yu Wang, Ming-Chin Yu, Wen-Hsin Chen, Chien-Chih Chiu, and Tsann-Long Hwang have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kou, HW., Yeh, CN., Tsai, CY. et al. A novel technique of sutureless omentopexy during dual-incision laparoscopic peritoneal dialysis catheter insertion to prevent catheter dysfunction due to omental wrapping. Surg Endosc 37, 148–155 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-022-09449-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-022-09449-7