Abstract
Background and aims
The main limitation of plastic stents is the relatively short stent patency due to occlusion. We designed enteral extended biliary stents with lengths of 26 cm (EEBS-26 cm) and 30 cm (EEBS-30 cm) to prolong stent patency. This study aimed to compare patency among EEBS-26 cm, EEBS-30 cm, and conventional plastic biliary stent (CPBS).
Methods
A single-center prospective randomized controlled study was conducted. Eligible patients were randomized into the EEBS-26 cm, EEBS-30 cm, and CPBS groups, respectively. All patients were followed up every 3 months until stent occlusion, patient death, or at 12-month follow-up. The primary outcome was stent patency. The secondary outcomes included stent occlusion rate, patient survival, mortality, the rate of technical success, and adverse events.
Results
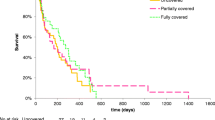
Totally 117 patients were randomized into the three groups. There were no significant differences among the three groups in technical success rate, hospital stay, mortality, patient survival, and adverse events (P = 1.000, 0.553, 0.965, 0.302, and 0.427, respectively). Median stent patency durations in the EEBS-26 cm, EEBS-30 cm, and CPBS groups were 156.0 (95% CI 81.6–230.4) days, 81.0 (95% CI 67.9–94.1) days, and 68.0 (95% CI 20.0–116.0) days, respectively (P = 0.002). The EEBS-26 cm group had longer stent patency compared with the CPBS (P = 0.007) and EEBS-30 cm (P < 0.001) groups. The EEBS-26 cm group had lower stent occlusion rates compared with the other groups at 6 months (48.1% vs. 90.5% vs. 82.8%, P = 0.001) and 9 months (75.0% vs. 100.0% vs. 92.9%, P = 0.022).
Conclusion
EEBS-26 cm has prolonged stent patency and is safe and effective for the alleviation of unresectable extrahepatic malignant biliary obstruction.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dumonceau JM, Tringali A, Papanikolaou IS, Blero D, Mangiavillano B, Schmidt A, Vanbiervliet G, Costamagna G, Deviere J, Garcia-Cano J, Gyokeres T, Hassan C, Prat F, Siersema PD, van Hooft JE (2018) Endoscopic biliary stenting: indications, choice of stents, and results: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Clinical Guideline - Updated October 2017. Endoscopy 50:910–930
Pedersen FM, Lassen AT, Schaffalitzky DMO (1998) Randomized trial of stent placed above and across the sphincter of Oddi in malignant bile duct obstruction. Gastrointest Endosc 48:574–579
van Berkel AM, Boland C, Redekop WK, Bergman JJ, Groen AK, Tytgat GN, Huibregtse K (1998) A prospective randomized trial of Teflon versus polyethylene stents for distal malignant biliary obstruction. Endoscopy 30:681–686
van Berkel AM, Bruno MJ, Bergman JJ, van Deventer SJ, Tytgat GN, Huibregtse K (2003) A prospective randomized study of hydrophilic polymer-coated polyurethane versus polyethylene stents in distal malignant biliary obstruction. Endoscopy 35:478–482
Bernon MM, Shaw J, Burmeister S, Chinnery G, Hofmeyr S, Kloppers JC, Jonas E, Krige JE (2018) Distal malignant biliary obstruction: a prospective randomised trial comparing plastic and uncovered self-expanding metal stents in the palliation of symptomatic jaundice. S Afr J Surg 56:30–34
Boulay BR, Birg A (2016) Malignant biliary obstruction: from palliation to treatment. World J Gastrointest Oncol 8:498–508
Bill JG, Mullady DK (2019) Stenting for benign and malignant biliary strictures. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 29:215–235
Hong WD, Chen XW, Wu WZ, Zhu QH, Chen XR (2013) Metal versus plastic stents for malignant biliary obstruction: an update meta-analysis. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 37:496–500
Sawas T, Al HS, Parsi MA, Vargo JJ (2015) Self-expandable metal stents versus plastic stents for malignant biliary obstruction: a meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc 82:256–267
Prat F, Chapat O, Ducot B, Ponchon T, Pelletier G, Fritsch J, Choury AD, Buffet C (1998) A randomized trial of endoscopic drainage methods for inoperable malignant strictures of the common bile duct. Gastrointest Endosc 47:1–7
Chen MY, Lin JW, Zhu HP, Zhang B, Jiang GY, Yan PJ, Cai XJ (2016) Covered stents versus uncovered stents for unresectable malignant biliary strictures: a meta-analysis. Biomed Res Int 2016:6408067
Saleem A, Leggett CL, Murad MH, Baron TH (2011) Meta-analysis of randomized trials comparing the patency of covered and uncovered self-expandable metal stents for palliation of distal malignant bile duct obstruction. Gastrointest Endosc 74:321–327
Reddy DN, Banerjee R, Choung OW (2006) Antireflux biliary stents: are they the solution to stent occlusions? Curr Gastroenterol Rep 8:156–160
Kwon CI, Lehman GA (2016) Mechanisms of biliary plastic stent occlusion and efforts at prevention. Clin Endosc 49:139–146
Dua KS, Reddy ND, Rao VG, Banerjee R, Medda B, Lang I (2007) Impact of reducing duodenobiliary reflux on biliary stent patency: an in vitro evaluation and a prospective randomized clinical trial that used a biliary stent with an antireflux valve. Gastrointest Endosc 65:819–828
Leong QW, Shen ML, Au KW, Luo D, Lau JY, Wu JC, Chan FK, Sung JJ (2016) A prospective, randomized study of the patency period of the plastic antireflux biliary stent: an interim analysis. Gastrointest Endosc 83:387–393
Vihervaara H, Gronroos JM, Hurme S, Gullichsen R, Salminen P (2017) Antireflux versus conventional plastic stent in malignant biliary obstruction: a prospective randomized study. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 27:53–57
Yuan XL, Wei B, Ye LS, Wu CC, Tan QH, Yao MH, Zhang YH, Zeng XH, Li Y, Zhang YY, Hu B (2019) New antireflux plastic stent for patients with distal malignant biliary obstruction. World J Gastroenterol 25:2373–2382
Arhan M, Odemis B, Parlak E, Ertug˘rul I, Bas¸ar O (2009) Migration of biliary plastic stents: experience of a tertiary center. Surg Endosc 23:769–775
Groen AK, Out T, Huibregtse K, Delzenne B, Hoek FJ, Tytgat GN (1987) Characterization of the content of occluded biliary endoprostheses. Endoscopy 19:57–59
Leung JW, Ling TK, Kung JL, Vallance-Owen J (1988) The role of bacteria in the blockage of biliary stents. Gastrointest Endosc 34:19–22
Speer AG, Cotton PB, Rode J, Seddon AM, Neal CR, Holton J, Costerton JW (1988) Biliary stent blockage with bacterial biofilm. A light and electron microscopy study. Ann Intern Med 108:546–553
Donelli G, Guaglianone E, Di Rosa R, Fiocca F, Basoli A (2007) Plastic biliary stent occlusion: factors involved and possible preventive approaches. Clin Med Res 5:53–60
Weickert U, Venzke T, Konig J, Janssen J, Remberger K, Greiner L (2001) Why do bilioduodenal plastic stents become occluded? A clinical and pathological investigation on 100 consecutive patients. Endoscopy 33:786–790
van Berkel AM, van Marle J, Groen AK, Bruno MJ (2005) Mechanisms of biliary stent clogging: confocal laser scanning and scanning electron microscopy. Endoscopy 37:729–734
Afghani E, Lo SK, Covington PS, Cash BD, Pandol SJ (2017) Sphincter of oddi function and risk factors for dysfunction. Front Nutr 4:1
Sung JY, Costerton JW, Shaffer EA (1992) Defense system in the biliary tract against bacterial infection. Dig Dis Sci 37:689–696
Rerknimitr R, Fogel EL, Kalayci C, Esber E, Lehman GA, Sherman S (2002) Microbiology of bile in patients with cholangitis or cholestasis with and without plastic biliary endoprosthesis. Gastrointest Endosc 56:885–889
Wagh MS, de Bellis M, Fogel EL, Frakes JT, Johanson JF, Qaseem T, Howell DA, Lehman GA, Sherman S (2013) Multicenter randomized trial of 10-french versus 11.5-french plastic stents for malignant biliary obstruction. Diagn Ther Endosc 2013:891915
Coene PP, Groen AK, Cheng J, Out MM, Tytgat GN, Huibregtse K (1990) Clogging of biliary endoprostheses: a new perspective. Gut 31:913–917
Catalano MF, Geenen JE, Lehman GA, Siegel JH, Jacob L, McKinley MJ, Raijman I, Meier P, Jacobson I, Kozarek R, Al-Kawas FH, Lo SK, Dua KS, Baille J, Ginsberg GG, Parsons W, Meyerson SM, Cohen S, Nelson DB, McHattie JD, Carr-Locke DL (2002) “Tannenbaum” Teflon stents versus traditional polyethylene stents for treatment of malignant biliary stricture. Gastrointest Endosc 55:354–358
Kwon CI, Kim G, Jeong S, Lee WS, Lee DH, Ko KH, Hong SP, Hahm KB (2016) Bile flow phantom model and animal bile duct dilation model for evaluating biliary plastic stents with advanced hydrophilic coating. Gut Liver 10:632–641
Costamagna G, Mutignani M, Rotondano G, Cipolletta L, Ghezzo L, Foco A, Zambelli A (2000) Hydrophilic hydromer-coated polyurethane stents versus uncoated stents in malignant biliary obstruction: a randomized trial. Gastrointest Endosc 51:8–11
Yang F, Ren Z, Chai Q, Cui G, Jiang L, Chen H, Feng Z, Chen X, Ji J, Zhou L, Wang W, Zheng S (2016) A novel biliary stent coated with silver nanoparticles prolongs the unobstructed period and survival via anti-bacterial activity. Sci Rep 6:21714
Yan X, Huang Y, Chang H, Zhang Y, Yao W, Li K (2018) Suspended over length biliary stents versus conventional plastic biliary stents for the treatment of biliary stricture: a retrospective single-center study. Medicine 97:e13312
Kwon CI, Gromski MA, Sherman S, Easler JJ, El HI, Watkins J, Fogel EL, McHenry L, Lehman GA (2016) Time sequence evaluation of biliary stent occlusion by dissection analysis of retrieved stents. Dig Dis Sci 61:2426–2435
Sung JJ, Chung SC, Tsui CP, Co AL, Li AK (1994) Omitting side-holes in biliary stents does not improve drainage of the obstructed biliary system: a prospective randomized trial. Gastrointest Endosc 40:321–325
Binmoeller KF, Seitz U, Seifert H, Thonke F, Sikka S, Soehendra N (1995) The Tannenbaum stent: a new plastic biliary stent without side holes. Am J Gastroenterol 90:1764–1768
Budzyńska A, Nowakowska-Duława E, Marek T, Hartleb M (2016) Comparison of patency and cost-effectiveness of self-expandable metal and plastic stents used for malignant biliary strictures: a Polish single-center study. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 28:1223–1228
Soderlund C, Linder S (2006) Covered metal versus plastic stents for malignant common bile duct stenosis: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc 63:986–995
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Award Number: 82070653), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (Number: 7222207) and Capital's Funds for Health Improvement and Research (Number: 2022-2Z-40914).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YH designed the EEBSs. XX, XY, HC, and YH conceived and designed the study. XX carried out the initial analysis and prepared the first draft of manuscript. YH, XY, and HC critically reviewed and revised the manuscript. XX, YZ, WZ, and YW completed the work of follow-up. WY and KL conducted the research and collected the data.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Xiaofen Xu, Yaopeng Zhang, Wei Zheng, Yingchun Wang, Wei Yao, Ke Li, Xiue Yan, Hong Chang, Yonghui Huang have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Zhang, Y., Zheng, W. et al. Enteral extended biliary stents versus conventional plastic biliary stents for the treatment of extrahepatic malignant biliary obstruction: a single-center prospective randomized controlled study. Surg Endosc 36, 8202–8213 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-022-09265-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-022-09265-z