Abstract
Background
Being one of the core techniques of magnetic surgery, magnetic compression technique (MCT) has been used for digestive tract anastomosis reconstruction in experimental studies. This study verified the feasibility of gastroenteric anastomosis through natural orifice using MCT in rats.
Methods
The parent and daughter magnets were designed and manufactured for oral and anal insertion in 20 Sprague‐Dawley rats. After anesthesia, the parent magnet was inserted into the colon spleen area through the anus, and the daughter magnet was inserted into the stomach through the mouth. Then the two magnets were positioned to attract each other and bind together. The position of the two magnets was monitored using X-ray. The time required for the formation of the anastomosis and expulsion of the magnets were recorded. 2 weeks later, the animal was sacrificed and the anastomotic specimen was obtained which was observed under naked eye and microscope.
Results
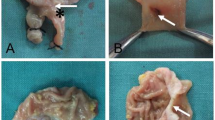
The gastroenteric anastomosis was successfully performed via natural orifices in 18 out of 20 rats. The mean time to construct the anastomosis was 3.78 ± 0.88 min. X-ray examination showed that the magnets were in the appropriate position in 17 rats. The magnets were excreted in 9.47 ± 1.62 days after surgery. The gross and microscopic examination of the specimen showed that the anastomoses were patent and the mucosa at the anastomotic was smooth. The mean bursting pressure of the anastomosis was 136.94 ± 6.79 mmHg.
Conclusion
It is feasible to perform gastroenteric anastomosis through natural orifices by MCT.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kopelman D, Hatoum OA, Kimmel B, Monassevitch L, Nir Y, Lelcuk S, Rabau M, Szold A (2007) Compression gastrointestinal anastomosis. Expert Rev Med Devices 4(6):821–828
Bai J, Huo X, Ma J, Lv Y, Yan X (2018) Magnetic compression technique for colonic anastomosis in rats. J Surg Res 231:24–29
Muensterer OJ, Sterlin A, Oetzmann von Sochaczewski C, Lindner A, Heimann A, Balus A, Dickmann J, Nuber M, Patel VH, Manfredi MA, Jennings RW, Smithers CJ, Fauza DO, Harrison MR (2020) An experimental study on magnetic esophageal compression anastomosis in piglets. J Pediatr Surg 55(3):425–432
Bruns NE, Glenn IC, Craner DR, Schomisch SJ, Harrison MR, Ponsky TA (2019) Magnetic compression anastomosis (magnamosis) in a porcine esophagus: proof of concept for potential application in esophageal atresia. J Pediatr Surg 54(3):429–433
Parlak E, Eminler AT, Koksal AS, Toka B, Uslan MI, Sokmensuer C, Guven M (2019) A new method for lumen restoration in a patient with aphagia: oro-oesophageal through-the-scope magnetic compression anastomosis. Clin Otolaryngol 44(6):1214–1217
Sterlin A, Evans L, Mahler S, Lindner A, Dickmann J, Heimann A, Sahlabadi M, Aribindi V, Harrison MR, Muensterer OJ (2021) An experimental study on long term outcomes after magnetic esophageal compression anastomosis in piglets. J Pediatr Surg S0022–3468(21):00646–00651
Ryou M, Cantillon-Murphy P, Azagury D, Shaikh SN, Ha G, Greenwalt I, Ryan MB, Lang JH, Thompson CC (2011) Smart Self-Assembling MagnetS for ENdoscopy (SAMSEN) for transoral endoscopic creation of immediate gastrojejunostomy (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 73(2):353–359
Watanabe R, Barberio M, Kanaji S, Lapergola A, Ashoka AH, Andreiuk B, Guerriero L, Pizzicannella M, Seeliger B, Saida Y, Kaneko H, Worreth M, Saadi A, Marescaux J, Klymchenko AS, Diana M (2020) Hybrid fluorescent magnetic gastrojejunostomy: an experimental feasibility study in the porcine model and human cadaver. Surg Endosc 34(3):1393–1400
An Y, Zhang Y, Liu H, Ma S, Fu S, Lv Y, Yan X (2018) Gastrojejunal anastomosis in rats using the magnetic compression technique. Sci Rep 8(1):11620
Schlottmann F, Ryou M, Lautz D, Thompson CC, Buxhoeveden R (2021) Sutureless duodeno-ileal anastomosis with self-assembling magnets: safety and feasibility of a novel metabolic procedure. Obes Surg 31(9):4195–4202
Ryou M, Aihara H, Thompson CC (2016) Minimally invasive entero-enteral dual-path bypass using self-assembling magnets. Surg Endosc 30(10):4533–4538
Ma F, Ma J, Ma S, Fu S, Zhang Y, Liu H, Lv Y, Wu R, Yan X (2019) A novel magnetic compression technique for small intestinal end-to-side anastomosis in rats. J Pediatr Surg 54(4):744–749
Chen H, Ma T, Wang Y, Zhu HY, Feng Z, Wu RQ, Lv Y, Dong DH (2020) Fedora-type magnetic compression anastomosis device for intestinal anastomosis. World J Gastroenterol 26(42):6614–6625
Yan X, Fan C, Ma J, Li J, Dong D, Wang H, Ma F, Zheng X, Lv Y (2013) Portacaval shunt established in six dogs using magnetic compression technique. PLoS ONE 8(9):e76873
Yan XP, Liu WY, Ma J, Li JP, Lv Y (2015) Extrahepatic portacaval shunt via a magnetic compression technique: a cadaveric feasibility study. World J Gastroenterol 21(26):8073–8080
Wang HH, Ma J, Wang SP, Ma F, Lu JW, Xu XH, Lv Y, Yan XP (2019) Magnetic anastomosis rings to create portacaval shunt in a canine model of portal hypertension. J Gastrointest Surg 23(11):2184–2192
Wang SP, Yan XP, Xue F, Dong DH, Zhang XF, Ma F, Wang HH, Lv Y (2015) Fast magnetic reconstruction of the portal vein with allogeneic blood vessels in canines. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 14(3):293–299
Falk V, Walther T, Stein H, Jacobs S, Walther C, Rastan A, Wimmer-Greinecker G, Mohr FW (2003) Facilitated endoscopic beating heart coronary artery bypass grafting using a magnetic coupling device. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 126(5):1575–1579
She ZF, Yan XP, Ma F, Wang HH, Yang H, Shi AH, Wang L, Qi X, Xiao B, Zou YL, Lv Y (2017) Treatment of rectovaginal fistula by magnetic compression. Int Urogynecol J 28(2):241–247
Gao Y, Wu RQ, Lv Y, Yan XP (2019) Novel magnetic compression technique for establishment of a canine model of tracheoesophageal fistula. World J Gastroenterol 25(30):4213–4221
Ye D, Zhang MM, Shi AH, Chen WW, Gao HM, Zhang JH, Shen WC, Lyu Y, Yan XP (2021) Construction of esophagogastric anastomosis in rabbits with magnetic compression technique. J Gastrointest Surg 25(12):3033–3039
Li NN, Zhao WT, Wu XT (2016) Can a nickel-titanium memory-shape device serve as a substitute for the stapler in gastrointestinal anastomosis? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Surg Res 201(1):82–93
Fan C, Yan XP, Liu SQ, Wang CB, Li JH, Yu L, Wu Z, Lv Y (2012) Roux-en-Y choledochojejunostomy using novel magnetic compressive anastomats in canine model of obstructive jaundice. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 11(1):81–88
Zhang H, Tan K, Fan C, Du J, Li J, Yang T, Lv Y, Du X (2017) Magnetic compression anastomosis for enteroenterostomy under peritonitis conditions in dogs. J Surg Res 208:60–67
Lu G, Li J, Ren M, Ma F, Sun X, Lv Y, He S (2021) Endoscopy-assisted magnetic compression anastomosis for rectal anastomotic atresia. Endoscopy 53(12):E437–E439
Liu XM, Li Y, Zhang HK, Ma F, Wang B, Wu R, Zhang XF, Lv Y (2019) Laparoscopic magnetic compression biliojejunostomy: a preliminary clinical study. J Surg Res 236:60–67
Liu XM, Li Y, Xiang JX, Ma F, Lu Q, Guo YG, Yan XP, Wang B, Zhang XF, Lv Y (2019) Magnetic compression anastomosis for biliojejunostomy and pancreaticojejunostomy in Whipple’s procedure: an initial clinical study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 34(3):589–594
Funding
This work was supported by the Innovation Capability Support Plan of Shaanxi Province (Grant No. 2020KJXX-022) and the Key Research & Development Program-Social Development of Shaanxi Province (Grant No. 2021SF-163).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
During the conduct of this work, Miaomiao Zhang, Yixing Li, Min Pan, Shuqin Xu, Jingci Gai, Hanzhi Zhang, Yingfeng An, Aihua Shi, Yi Lyu and Xiaopeng Yan have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Li, Y., Pan, M. et al. Creation of gastroenteric anastomosis through natural orifice in rats by magnetic compression technique. Surg Endosc 36, 8170–8177 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-022-09257-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-022-09257-z