Abstract
Background
Transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF) with Medigus Ultrasonic Surgical Endostapler (MUSE) is a new intervention for treatment of gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD). We aimed at assessing the clinical, functional, and endoscopic effects of TIF by MUSE.
Methods
Forty-six patients underwent TIF. Proton pump inhibitor (PPI) consumption, GERD-health-related quality of life (HRQL) and reflux symptom index (RSI) questionnaires, upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy, esophageal 24-h pH-impedance recording, and high-resolution manometry (HRM) were done before TIF and scheduled 6 and 12 months later (HRM only at 6-month). PPI consumption and symptoms were then assessed yearly. Data up to 3 years are reported in this study (PP- and ITT-analysis).
Results
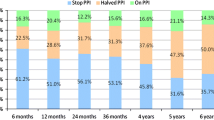
TIF was successfully performed in 45/46 patients; in one patient esophageal intubation was impossible. Perforation occurred in two cases. One patient required surgery within 6 months. Clinical follow-up was available for 42 patients at 6 months and 1 year, 35 patients at 2 years, and 31 patients at 3 years. At 1, 2, and 3 years, PPI consumption was stopped, respectively, in 64.3%, 62.9%, and 74.2% of cases (ITT-analysis: 58.7%, 56.4%, and 65.7%). GERD-HRQL and RSI scores decreased at least 50%, respectively, in 71.5% and 76.2%, 71.4% and 68.6%, and 67.7% of cases (ITT-analysis: 65.2% and 69.6%, 64.1% and 61.5%, and 60%). A significant improvement of both scores was observed up to 3 years. 6-month and 1-year functional follow-up were possible in 31 and 20 patients. HRM showed significant increase of the median lower esophageal sphincter length and rate of peristaltic waves. Esophageal pH-impedance recording found significantly fewer acid, proximal and total refluxes, and percentage of esophageal pH < 4 total time at 6 months, but not at 1 year.
Conclusion
TIF by MUSE significantly improved symptoms and PPIs consumption up to 3 years. However, esophagitis still persisted in one-third of cases at 1 year and functional improvement at 6 months was not confirmed at 1 year. Severe complications requiring surgery occurred in two cases.
ClinicalTrials.Gov
ID: NCT03669874.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CI:
-
Confidence intervals
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- DCI:
-
Distal contractile integral
- GERD:
-
Gastro-esophageal reflux disease
- GI:
-
Gastrointestinal
- HRM:
-
High-resolution manometry
- HRQL:
-
Health-related quality of life
- ITT:
-
Intention to treat
- LES:
-
Lower esophageal sphincter
- MUSE:
-
Medigus ultrasonic surgical endostapler
- NERD:
-
Non-erosive reflux disease
- PEEP:
-
Positive end-expiratory pressure
- PP:
-
Per protocol
- PPI:
-
Proton pump inhibitor
- RSI:
-
Reflux symptom index
- TIF:
-
Transoral incisionless fundoplication
References
Huang X, Chen S, Zhao H, Zeng X, Lian J, Tseng Y, Chen J (2017) Efficacy of transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF) for the treatment of GERD: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Surg Endosc 31:1032–1044. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-5111-7
McCarty TR, Itidiare M, Njei B, Rustagi T (2018) Efficacy of transoral incisionless fundoplication for refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy 50:708–725. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-0576-6589
Muls V, Eckardt AJ, Marchese M, Bastens B, Buset M, Devière J, Louis H, Rajan A, Daniel MA, Costamagna G (2013) Three-year results of a multicenter prospective study of transoral incisionless fundoplication. Surg Innov 20:321–330. https://doi.org/10.1177/1553350612459275
Witteman PBL, Strijkers R, de Vries E, Toemen L, Conchillo JM, Hameeteman W, Dagnelie PC, Koek GH, Bouvy ND (2012) Transoral incisionless fundoplication for treatment of gastroesophageal reflux diseases in clinical practice. Surg Endosc 26:3307–3315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-012-2324-2
Roy-Shapira A, Bapaye A, Date S, Pujari R, Dorwat S (2015) Trans-oral anterior fundoplication: 5-year follow-up of pilot study. Surg Endosc 29:3717–3721. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4142-9
Kim HJ, Kwon CI, Kessler WR, Selzer DJ, McNulty G, Bapaye A, Bonavina L, Lehman GA (2016) Long-term follow-up results of endoscopic treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease with the MUSETM endoscopic stapling device. Surg Endosc 30:3402–3408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4622-y
Trad KS, Barnes WE, Prevou ER, Simoni G, Steffen JA, Shughoury AB, Raza M, Heise JA, Fox MA, Mavrelis PG (2018) The TEMPO trial at 5 years: transoral fundoplication (TIF 2.0) is safe, durable, and cost-effective. Surg Innov 25:149–157. https://doi.org/10.1177/1553350618755214
Stefanidis G, Viazis N, Kotsikoros N, Tsoukalas N, Lala E, Theocharis L, Fassaris A, Manolakopoulos S (2017) Long-term benefit of transoral incisionless fundoplication using the Esophyx device for the management of gastroesophageal reflux disease responsive to medical therapy. Dis Esophagus 30:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/dote.12525
Testoni PA, Testoni S, Distefano G, Mazzoleni G, Fanti L, Passaretti S (2019) Transoral incisionless fundoplication with EsophyX for gastroesophageal reflux disease: clinical efficacy is maintained up to 10 years. Endosc Int Open 7:E647–E654. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-0820-2297
Chimukangara M, Jalilvand AD, Melvin WS, Perry KA (2019) Long-term reported outcomes of transoral incisionless fundoplication: an 8-year cohort study. Surg Endosc 33:1304–1309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-018-6403-x
Kauer WK, Roy-Shapira A, Watson D, Sonnenschein M, Sonnenschein E, Unger J, Voget M, Stein HJ (2009) Preclinical trial of a modified gastroscope that performs a true anterior fundoplication for the endoluminal treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Surg Endosc 23:2728–2731. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-009-0479-2
Gweon TG, Matthes K (2016) Prospective randomized ex vivo trial to assess the ideal stapling site for endoscopic fundoplication with medigus ultrasonic surgical endostapler. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2016:ID3161738. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3161738
Testoni PA, Testoni S, Mazzoleni G, Pantaleo G, Cilona MB, Distefano G, Fanti L, Antonelli M, Passaretti S (2020) Transoral incisionless fundoplication with an ultrasonic surgical endostapler for the treatment of gastro-esophageal reflux disease: 12-month outcomes. Endoscopy 52:469–473. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1124-3187
Stefanidis D, Hope WW, Kohn GP, Reardon PR, Richardson WS, Fanelli RD, SAGES Guidelines Committee (2010) Guidelines for surgical treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Surg Endosc 24(11):2647–2669. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-010-1267-8
Velanovich V (2007) The development of the GERD-HRQL symptom severity instrument. Dis Esophagus 20:130–134. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-2050.2007.00658.x
Schindler A, Mozzanica F, Ginocchio D, Peri A, Bottero A, Ottaviani F (2010) Reliability and clinical validity of the Italian reflux symptom index. J Voice 24:354–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2008.08.008
Testoni PA, Testoni S, Mazzoleni G, Vailati C, Passaretti S (2015) Long-term efficacy of transoral incisionless fundoplication with Esophyx (TIF 2.0) and factors affecting outcomes in GERD pts followed for up to 6 years: a prospective single-center study. Surg Endosc 29:2770–2780. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-4008-6
Garg SK, Gurusamy KS (2015) Laparoscopic fundoplication surgery versus medical management for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 11:CD003243. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD003243.pub3
Lundell L, Bell M, Ruth M (2014) Systematic review: laparoscopic fundoplication for gastro-esophageal reflux disease in partial responders to proton pump inhibitors. World J Gastroenterol 20:804–813. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i3.804
Kelly JJ, Watson DI, Chin KF, Devitt PG, Game PA, Jamieson GG (2007) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: clinical outcomes at 10 years. J Am Coll Surg 205:570–575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2007.05.024
Gunter RL, Shada AL, Funk LM, Wang X, Greenberg JA, Lidor AO (2017) Long-term quality of life outcomes following Nissen versus Toupet fundoplication in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 27:931–936. https://doi.org/10.1089/lap.2017.0232
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SGGT drafted the manuscript, performed statistical analysis, followed the endoscopic case series, and collected the endoscopic data; MBC clinically followed the patients and collected the clinical data; GM, ER, and SP performed functional analysis; GM clinically followed the patients and collected clinical and functional data; SP performed statistical analysis; LF and FA assisted in transoral incisionless fundoplication procedures; GMC, DE, EV, CN, and RAZ performed endoscopic controls; PAT designed the study protocol, performed transoral incisionless fundoplication procedures, provided scientific guidance, and supervised the scientific work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Sabrina Gloria Giulia Testoni, Maria Bernadette Cilona, Giorgia Mazzoleni, Lorella Fanti, Emanuela Ribichini, Giulia Martina Cavestro, Dario Esposito, Edi Viale, Chiara Notaristefano, Raffaella Alessia Zuppardo, Francesco Azzolini, Sandro Passaretti, and Pier Alberto Testoni have no conflict of interest or financial ties to disclose. All authors revised and approved the final version of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Testoni, S.G.G., Cilona, M.B., Mazzoleni, G. et al. Transoral incisionless fundoplication with Medigus ultrasonic surgical endostapler (MUSE) for the treatment of gastro-esophageal reflux disease: outcomes up to 3 years. Surg Endosc 36, 5023–5031 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-021-08860-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-021-08860-w