Abstract
Background
Sphincter-saving operation is the treatment of choice in patients with lower rectal cancer, although abdominoperineal resection (APR) is necessary in some cases for adequate oncological outcomes. This study compared the oncologic outcomes of patients with low rectal cancer undergoing APR and intersphincteric resection (ISR) after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT).
Methods
We compared 104 patients who underwent ISR for lower rectal cancer between 2008 and 2014 with 79 patients who underwent APR during the same period. Cases in which tumors involved the levator ani muscle or the external anal sphincter, as well as those in which surgeons were unable to obtain a negative distal margin via sphincter-saving operation were excluded. Fifty-two patients who underwent ISR were matched via propensity scoring with 52 patients who underwent APR. The analyzed variables included patient and tumor characteristics and long-term outcomes before and after 1:1 propensity score matching (PSM).
Results
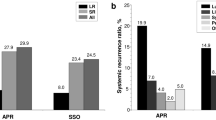
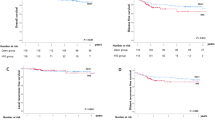
After matching, there were no significant differences between the two groups in clinical stage and tumor distance from anal verge. Short- and long-term outcomes were similar between the two groups. The 5-year disease-free survival rate was 76.3% in the ISR group and 57.8% in the APR group (p = 0.080). The 5-year cancer-specific survival rate was 89.5% in the ISR group and 85.4% in the APR group (p = 0.383).
Conclusions
This reveals that ISR and APR have similar oncologic outcomes following nCRT in patients with advanced low rectal cancer adjusted for background variables.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martin ST, Heneghan HM, Winter DC (2012) Systematic review of outcomes after intersphincteric resection for low rectal cancer. Br J Surg 99:603–612
Benson AB, Venook AP, Al-Hawary MM, Cederquist L, Chen YJ, Ciombor KK, Cohen S, Cooper HS, Deming D, Engstrom PF, Grem JL, Grothey A, Hochster HS, Hoffe S, Hunt S, Kamel A, Kirilcuk N, Krishnamurthi S, Messersmith WA, Meyerhardt J, Mulcahy MF, Murphy JD, Nurkin S, Saltz L, Sharma S, Shibata D, Skibber JM, Sofocleous CT, Stoffel EM, Stotsky-Himelfarb E, Willett CG, Wuthrick E, Gregory KM, Gurski L, Freedman-Cass DA (2018) Rectal cancer, version 2.2018, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 16:874–901
Rouanet P, Fabre JM, Dubois JB, Dravet F, Saint Aubert B, Pradel J, Ychou M, Solassol C, Pujol H (1995) Conservative surgery for low rectal carcinoma after high-dose radiation. Functional and oncologic results. Ann Surg 221:67–73
Wagman R, Minsky BD, Cohen AM, Guillem JG, Paty PP (1998) Sphincter preservation in rectal cancer with preoperative radiation therapy and coloanal anastomosis: long term follow-up. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 42:51–57
Rullier E, Laurent C, Bretagnol F, Rullier A, Vendrely V, Zerbib F (2005) Sphincter-saving resection for all rectal carcinomas: the end of the 2-cm distal rule. Ann Surg 241:465–469
Schiessel R, Karner-Hanusch J, Herbst F, Teleky B, Wunderlich M (1994) Intersphincteric resection for low rectal tumours. Br J Surg 81:1376–1378
West NP, Anderin C, Smith KJ, Holm T, Quirke P, European Extralevator Abdominoperineal Excision Study Group (2010) Multicentre experience with extralevator abdominoperineal excision for low rectal cancer. Br J Surg 97:588–599
van Leersum N, Martijnse I, den Dulk M, Kolfschoten N, Le Cessie S, van de Velde C, Tollenaar R, Wouters M, Rutten HJ (2014) Differences in circumferential resection margin involvement after abdominoperineal excision and low anterior resection no longer significant. Ann Surg 259:1150–1155
Williams NS, Dixon MF, Johnston D (1983) Reappraisal of the 5 centimetre rule of distal excision for carcinoma of the rectum: a study of distal intramural spread and of patients’ survival. Br J Surg 70:150–154
Hohenberger W, Merkel S, Matzel K, Bittorf B, Papadopoulos T, Gohl J (2006) The influence of abdomino-peranal (intersphincteric) resection of lower third rectal carcinoma on the rates of sphincter preservation and locoregional recurrence. Colorectal Dis 8:23–33
Portier G, Ghouti L, Kirzin S, Guimbaud R, Rives M, Lazorthes F (2007) Oncological outcome of ultra-low coloanal anastomosis with and without intersphincteric resection for low rectal adenocarcinoma. Br J Surg 94:341–345
Schiessel R, Novi G, Holzer B, Rosen HR, Renner K, Holbling N, Feil W, Urban M (2005) Technique and long-term results of intersphincteric resection for low rectal cancer. Dis Colon Rectum 48:1858–1865
Birbeck KF, Macklin CP, Tiffin NJ, Parsons W, Dixon MF, Mapstone NP, Abbott CR, Scott N, Finan PJ, Johnston D, Quirke P (2002) Rates of circumferential resection margin involvement vary between surgeons and predict outcomes in rectal cancer surgery. Ann Surg 235:449–457
Adam IJ, Mohamdee MO, Martin IG, Scott N, Finan PJ, Johnston D, Dixon MF, Quirke P (1994) Role of circumferential margin involvement in the local recurrence of rectal cancer. Lancet 344:707–711
Quirke P, Durdey P, Dixon MF, Williams NS (1986) Local recurrence of rectal adenocarcinoma due to inadequate surgical resection. histopathological study of lateral tumour spread and surgical excision. Lancet 2:996–999
Saito N, Ito M, Kobayashi A, Nishizawa Y, Kojima M, Nishizawa Y, Sugito M (2014) Long-term outcomes after intersphincteric resection for low-lying rectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 21:3608–3615
Koyama M, Murata A, Sakamoto Y, Morohashi H, Takahashi S, Yoshida E, Hakamada K (2014) Long-term clinical and functional results of intersphincteric resection for lower rectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 21(Suppl 3):S422-428
Camma C, Giunta M, Fiorica F, Pagliaro L, Craxi A, Cottone M (2000) Preoperative radiotherapy for resectable rectal cancer: a meta-analysis. JAMA 284:1008–1015
Guillem JG, Chessin DB, Cohen AM, Shia J, Mazumdar M, Enker W, Paty PB, Weiser MR, Klimstra D, Saltz L, Minsky BD, Wong WD (2005) Long-term oncologic outcome following preoperative combined modality therapy and total mesorectal excision of locally advanced rectal cancer. Ann Surg 241:829–836
Trial SRC, Cedermark B, Dahlberg M, Glimelius B, Pahlman L, Rutqvist LE, Wilking N (1997) Improved survival with preoperative radiotherapy in resectable rectal cancer. N Engl J Med 336:980–987
Bosset JF, Collette L, Calais G, Mineur L, Maingon P, Radosevic-Jelic L, Daban A, Bardet E, Beny A, Ollier JC, EORTC Radiotherapy Group Trial 22921 (2006) Chemotherapy with preoperative radiotherapy in rectal cancer. N Engl J Med 355:1114–1123
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by a grant from the Korea Health Technology R&D project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (Grant Number : HI 17C1888).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Drs. Jung Kyong Shin, Hee Cheol Kim, Woo Yong Lee, Seong Hyeon Yun, Yong Beom Cho, Jung Wook Huh, Yoon Ah Park have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, J.K., Kim, H.C., Lee, W.Y. et al. Sphincter-saving surgery versus abdominoperineal resection in low rectal cancer following neoadjuvant treatment with propensity score analysis. Surg Endosc 36, 2623–2630 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-021-08558-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-021-08558-z