Abstract
Background
In the West, piecemeal endoscopic resection remains the primary treatment for large colon polyps (LCP), as most recurrences are believed to be benign and resectable with follow-up endoscopy. However, invasive malignancy at the site of prior piecemeal endoscopic mucosal resection has been reported in the Asian literature. This study aims to identify the incidence of and the risk factors for local recurrence with malignancy after endoscopic resection of LCP with high-grade dysplasia (HGD).
Methods
In this retrospective cohort study, we identified patients undergoing complete endoscopic resection of LCPs (≥ 20 mm) with HGD at the Cleveland Clinic between January 2000 and December 2016. Demographic, endoscopic, and pathologic data were collected. All subsequent endoscopic and pathology reports were reviewed to identify recurrence. The cumulative incidence of malignancy at the polypectomy site was determined and univariate analysis was performed to assess risk factors.
Results
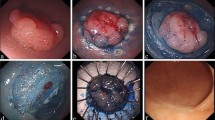
A total of 254 LCPs with HGD were resected in 229 patients. Mean polyp size was 29.2 mm. There were 138 lesions resected in piecemeal fashion and 116 en-bloc. After a median follow-up of 28.7 months for the entire cohort, local recurrence with malignancy was diagnosed in six cases. Median time to malignancy diagnosis was 28.5 months. All malignant cases occurred after piecemeal resection and none after en-bloc resection (HR 11.4; 95% CI 0.48–273).
Conclusion
Malignancy after endoscopic resection of LCPs with HGD is uncommon and may be associated with piecemeal resection. When possible, en-bloc resection should be the goal for the management of LCPs.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ESD:
-
Endoscopic submucosal dissection
- HGD:
-
High-grade dysplasia
- LCP:
-
Large colon polyp
- LGD:
-
Low-grade dysplasia
- P-EMR:
-
Piecemeal endoscopic mucosal resection
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2019) Cancer statistics, 2019. CA: Cancer J Clin 69(1):7–34
Heitman SJ, Ronksley PE, Hilsden RJ et al (2009) Prevalence of adenomas and colorectal cancer in average risk individuals: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 7(12):1272–1278
Ahlawat SK, Gupta N, Benjamin SB et al (2011) Large colorectal polyps: endoscopic management and rate of malignancy: does size matter? J Clin Gastroenterol 45(4):347–354
Church JM (2003) Experience in the endoscopic management of large colonic polyps. ANZ J Surg 73(12):988–995
Binmoeller KF, Bohnacker S, Seifert H et al (1996) Endoscopic snare excision of “giant” colorectal polyps. Gastrointest Endosc 43(3):183–188
Waye JD (2005) Advanced polypectomy. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 15(4):733–756
Kaltenbach T, Soetikno R (2013) Endoscopic resection of large colon polyps. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 23(1):137–152
Hurlstone DP, Sanders DS, Cross SS et al (2004) Colonoscopic resection of lateral spreading tumours: a prospective analysis of endoscopic mucosal resection. Gut 53(9):1334–1339
Swan MP, Bourke MJ, Alexander S et al (2009) Large refractory colonic polyps: is it time to change our practice? A prospective study of the clinical and economic impact of a tertiary referral colonic mucosal resection and polypectomy service (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc 70(6):1128–1136
Moss A, Williams SJ, Hourigan LF et al (2015) Long-term adenoma recurrence following wide-field endoscopic mucosal resection (WF-EMR) for advanced colonic mucosal neoplasia is infrequent: results and risk factors in 1000 cases from the Australian Colonic EMR (ACE) study. Gut 64(1):57–65
Belderbos TDG, Leenders M, Moons LMG et al (2014) Local recurrence after endoscopic mucosal resection of nonpedunculated colorectal lesions: systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy 46(5):388–402
Knabe M, Pohl J, Gerges C et al (2014) Standardized long-term follow-up after endoscopic resection of large, nonpedunculated colorectal lesions: a prospective two-center study. Am J Gastroenterol 109(2):183–189
Oka S, Tanaka S, Saito Y et al (2015) Local recurrence after endoscopic resection for large colorectal neoplasia: a multicenter prospective study in Japan. Am J Gastroenterol 110(5):697–707
Saito Y, Fukuzawa M, Matsuda T et al (2010) Clinical outcome of endoscopic submucosal dissection versus endoscopic mucosal resection of large colorectal tumors as determined by curative resection. Surg Endosc 24(2):343–352
Tajika M, Niwa Y, Bhatia V et al (2011) Comparison of endoscopic submucosal dissection and endoscopic mucosal resection for large colorectal tumors. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 23(11):1042–1049
Lee EJ, Lee JB, Lee SH et al (2012) Endoscopic treatment of large colorectal tumors: comparison of endoscopic mucosal resection, endoscopic mucosal resection-precutting, and endoscopic submucosal dissection. Surg Endosc 26(8):2220–2230
Makazu M, Sakamoto T, So E et al (2015) Relationship between indeterminate or positive lateral margin and local recurrence after endoscopic resection of colorectal polyps. Endosc Int Open 3(3):E252–E257
Kobayashi N, Saito Y, Uraoka T et al (2009) Treatment strategy for laterally spreading tumors in japan: before and after the introduction of endoscopic submucosal dissection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 24(8):1387–1392
Tanaka S, Kashida H, Saito Y et al (2015) JGES guidelines for colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection/endoscopic mucosal resection. Dig Endosc 27(4):417–434
Seo GJ, Sohn DK, Han KS et al (2010) Recurrence after endoscopic piecemeal mucosal resection for large sessile colorectal polyps. World J Gastroenterol 16(22):2806–2811
Saito Y, Yamada M, So E et al (2014) Colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection: technical advantages compared to endoscopic mucosal resection and minimally invasive surgery. Dig Endosc 26(Suppl1):52–61
Bartel MJ, Brahmbhatt BS, Wallace MB (2016) Management of colorectal T1 carcinoma treated by endoscopic resection from the western perspective. Dig Endosc 28(3):330–341
Friedel D, Stavropoulos SN (2018) Introduction of endoscopic submucosal dissection in the west. World J Gastroint Endosc 10(10):225–238
Arezzo A, Passera R, Marchese N et al (2016) Systematic review and meta-analysis of endoscopic submucosal dissection vs endoscopic mucosal resection for colorectal lesions. United Eur Gastroenterol J 4(1):18–29
Bourke M (2009) Current status of colonic endoscopic mucosal resection in the west and the interface with endoscopic submucosal dissection. Dig Endosc 21(Suppl1):S22–27
Bond JH (2000) Polyp guideline: diagnosis, treatment, and surveillance for patients with colorectal polyps. Practice Parameters Committee of The American College of Gastroenterology. Am J Gastroenterol 95(11):3053–3063
Moss A, Bourke MJ, Williams SJ et al (2011) Endoscopic mucosal resection outcomes and prediction of submucosal cancer from advanced colonic mucosal neoplasia. Gastroenterology 140(7):1909–1918
Puli SR, Kakugawa Y, Gotoda T et al (2009) Meta-analysis and systematic review of colorectal endoscopic mucosal resection. World J Gastroenterol 15(34):4273–4277
Ikematsu H, Yoda Y, Matsuda T et al (2013) Long-term outcomes after resection for submucosal invasive colorectal cancers. Gastroenterology 144(3):551–559
Pohl H, Srivastava A, Bensen SP et al (2013) Incomplete polyp resection during colonoscopy-results of the Complete Adenoma Resection (CARE)Study. Gastroenterology 144(1):74–80.e1
Saito Y, Bhatt A, Matsuda T (2017) Colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection and its journey to the west. Gastrointest Endosc 86(1):90–92
Kim HG, Thosani N, Banerjee S et al (2015) Effect of prior biopsy sampling, tattoo placement, and snare sampling on endoscopic resection of large nonpedunculated colorectal lesions. Gastrointest Endosc 81(1):204–213
Kim HG, Thosani N, Banerjee S et al (2014) Underwater endoscopic mucosal resection for recurrences after previous piecemeal resection of colorectal polyps (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 80(6):1094–1102
Nakajima T, Saito Y, Tanaka S et al (2013) Current status of endoscopic resection strategy for large, early colorectal neoplasia in Japan. Surg Endosc 27(9):3262–3270
Fuccio L, Hassan C, Ponchon T et al (2017) Clinical outcomes after endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal neoplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc 86(1):74–86.e17
Saito Y, Uraoka T, Yamaguchi Y et al (2010) A prospective, multicenter study of 1111 colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissections (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 72(6):1217–1225
Kobayashi N, Yoshitake N, Hirahara Y et al (2012) Matched case-control study comparing endoscopic submucosal dissection and endoscopic mucosal resection for colorectal tumors. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 27(4):728–733
Facciorusso A, Di Maso M, Serviddio G et al (2016) Factors associated with recurrence of advanced colorectal adenoma after endoscopic resection. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 14(8):1148–1154.e4
Lieberman DA, Rex DK, Winawer SJ, Giardiello FM, Johnson DA, Levin TR (2012) Guidelines for colonoscopy surveillance after screening and polypectomy: a consensus update by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology 143(3):844–857
Lakoff J, Paszat LF, Saskin R, Rabeneck L (2008) Risk of developing proximal versus distal colorectal cancer after a negative colonoscopy: a population-based study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 6(10):1117–1121
Baxter NN, Goldwasser MA, Paszat LF et al (2009) Association of colonoscopy and death from colorectal cancer. Ann Intern Med 150(1):1–8
Brenner H, Chang-Claude J, Seiler CM et al (2011) Protection from colorectal cancer after colonoscopy: a population-based, case-control study. Ann Intern Med 154(1):22–30
Yood MU, Oliveria S, Boyer JG et al (2003) Colon polyp recurrence in a managed care population. Arch Intern Med 163(4):422–426
Cottet V, Jooste V, Fournel I et al (2012) Long-term risk of colorectal cancer after adenoma removal: a population-based cohort study. Gut 61(8):1180–1186
Brueckl WM, Fritsche B, Seifert B et al (2006) Non-compliance in surveillance for patients with previous resection of large (≥ 1cm) colorectal adenomas. World J Gastroenterol 12(45):7313–7318
Lund J, Scholefield J, Grainge M et al (2001) Risks, costs, and compliance limit colorectal adenoma surveillance: lessons from a randomised trial. Gut 49(1):91–96
Yoda Y, Ikematsu H, Matsuda T et al (2013) A Large-scale multicenter study of long-term outcomes after endoscopic resection for submucosal invasive colorectal cancer. Endoscopy 45(9):718–724
Kishino T, Matsuda T, Sakamoto T et al (2010) Recurrent advanced colonic cancer occurring 11 years after initial endoscopic piecemeal resection: a case report. BMC Gastroenterol 10:87
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NM, AA, MS, MA, JV, DP, MK, CPD, EG, JC, YS, CAB, AB: Role in manuscript preparation: concept and design; acquisition of data; analysis and/or interpretation of data; drafting of the manuscript and critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. RL: Role in manuscript preparation: statistical analysis and critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Dr. Gorgun is a consultant for Lumendi. Neither are related to the content of this submission. Dr. Bhatt is a consultant for Medtronic and Lumendi. Neither are related to the content of this submission. Neal Mehta, Ashraf Abushahin, Meena Sadaps, Mohammad Alomari, John Vargo, Deepa Patil, Rocio Lopez, Matthew Kalady, Conor P. Delaney, Emre Gorgun, James Church, Yutaka Saito, Carol A. Burke have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehta, N., Abushahin, A., Sadaps, M. et al. Recurrence with malignancy after endoscopic resection of large colon polyps with high-grade dysplasia: incidence and risk factors. Surg Endosc 35, 2500–2508 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-020-07660-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-020-07660-y