Abstract
Objective
Middle pancreatectomy (MP) is safe and feasible in patients with benign or low-grade malignant tumors located at the neck or proximal body of the pancreas. As a tissue-sparing operation, MP can preserve normal pancreatic function and reduce the risk of postoperative endocrine and exocrine insufficiency. However, the morbidity, especially the postoperative pancreatic fistula (POPF) rate, remains high. A robot-assisted surgical system may provide patients with less trauma; however, there are few reports on robot-assisted middle pancreatectomy (RMP). We describe the experience of RMP at our center to illustrate the learning curve (LC).
Methods
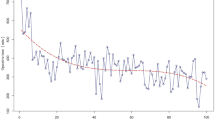
From August 2010 to July 2017, 100 patients underwent RMP in the Pancreatic Disease Center of Shanghai Ruijin Hospital affiliated to Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine. Patient characteristics, operative outcomes, and oncological outcomes were collected and analyzed. The CUSUM curve was analyzed according to operative time and estimated blood loss (EBL) and was used to describe the LC and identify the flexion points.
Results
Among the 100 patients who underwent RMP in our hospital, the mean age was 47.5 ± 14.2 years, and 69 patients were female. From the CUSUM curve, we found two flexion points: cases 12 and 44. After 44 cases, the rate of improvement was much faster. We separated the patients into two groups based on the LC (cases 1–44 and cases 45–100). There were significant improvements in operative time (173.1 ± 44.7 min vs. 137.3 ± 30.1 min, p < 0.001) and EBL (103.4 ± 90.0 ml vs. 69.3 ± 53.9 ml, p = 0.021). The overall POPF rate was 32% (32/100), while the incidence rate of biochemical leakage was 14% (14/100). However, there was no significant difference in the risk of POPF or other complications between the two groups. The postoperative length of stay (LOS) was also not different. The 90-day mortality rate was 1%. From our long-term follow-up, pancreatic function was preserved in most patients, with only three cases of endocrine insufficiency and two cases of exocrine insufficiency.
Conclusion
RMP was helpful and a good choice for the selected patients. PF was the main complication and has not been improved until now. There were two flexion points in the LC at cases 12 and 44. More cases are needed to gain more experience. A larger sample size and prospective studies are needed to verify the advantage of RMP.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fitzgerald TL, Hickner ZJ, Schmitz M, Kort EJ (2008) Changing incidence of pancreatic neoplasms: a 16-year review of statewide tumor registry. Pancreas 37(2):134–138
Gaujoux S, Brennan MF, Gonen M, D’Angelica MI, DeMatteo R, Fong Y, Schattner M, DiMaio C, Janakos M, Jarnagin WR, Allen PJ (2011) Cystic lesions of the pancreas: changes in the presentation and management of 1,424 patients at a single institution over a 15-year time period. J Am Coll Surg 212(4):590–600 discussion 600-3
Giulianotti PC, Sbrana F, Bianco FM, Addeo P, Caravaglios G (2010) Robot-assisted laparoscopic middle pancreatectomy. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 20(2):135–139
Xiao W, Zhu J, Peng L, Hong L, Sun G, Li Y (2018) The role of central pancreatectomy in pancreatic surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. HPB (Oxford) 20(10):896–904
Crippa S, Bassi C, Warshaw AL, Falconi M, Partelli S, Thayer SP, Pederzoli P, Fernandez-del Castillo C (2007) Middle pancreatectomy: indications, short- and long-term operative outcomes. Ann Surg 246(1):69–76
Goudard Y, Gaujoux S, Dokmak S, Cros J, Couvelard A, Palazzo M, Ronot M, Vullierme MP, Ruszniewski P, Belghiti J, Sauvanet A (2014) Reappraisal of central pancreatectomy a 12-year single-center experience. JAMA Surg 149(4):356–363
Paiella S, De Pastena M, Faustini F, Landoni L, Pollini T, Bonamini D, Giuliani T, Bassi C, Esposito A, Tuveri M, Salvia R (2018) Central pancreatectomy for benign or low-grade malignant pancreatic lesions - A single-center retrospective analysis of 116 cases. Eur J Surg Oncol 45(5):788–792
Pulvirenti A, Ramera M, Bassi C (2017) Modifications in the International Study Group for Pancreatic Surgery (ISGPS) definition of postoperative pancreatic fistula. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol 2:107
Guillemin P, Bessot M (1957) Chronic calcifying pancreatitis in renal tuberculosis: pancreatojejunostomy using an original technic. Mem Acad Chir (Paris) 83(27–28):869–871
Lee KE, Koo do H, Kim SJ, Lee J, Park KS, Oh SK, Youn YK (2010) Outcomes of 109 patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma who underwent robotic total thyroidectomy with central node dissection via the bilateral axillo-breast approach. Surgery 148(6):1207–1213
Wexner SD, Bergamaschi R, Lacy A, Udo J, Brolmann H, Kennedy RH, John H (2009) The current status of robotic pelvic surgery: results of a multinational interdisciplinary consensus conference. Surg Endosc 23(2):438–443
Memon S, Heriot AG, Murphy DG, Bressel M, Lynch AC (2012) Robotic versus laparoscopic proctectomy for rectal cancer: a meta-analysis. Ann Surg Oncol 19(7):2095–2101
Anderson B, Karmali S (2014) Laparoscopic resection of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: dream or reality? World J Gastroenterol 20(39):14255–14262
Chen S, Zhan Q, Jin JB, Wu ZC, Shi Y, Cheng DF, Chen H, Deng XX, Shen BY, Peng CH, Li HW (2017) Robot-assisted laparoscopic versus open middle pancreatectomy: short-term results of a randomized controlled trial. Surg Endosc 31(2):962–971
Napoli N, Kauffmann EF, Palmeri M, Miccoli M, Costa F, Vistoli F, Amorese G, Boggi U (2016) The learning curve in robotic pancreaticoduodenectomy. Dig Surg 33(4):299–307
Zhang T, Zhao ZM, Gao YX, Lau WY, Liu R (2018) The learning curve for a surgeon in robot-assisted laparoscopic pancreaticoduodenectomy: a retrospective study in a high-volume pancreatic center. Surg Endosc 33(9):2927–2933
Liu R, Zhao GD, Tang WB, Zhang KD, Zhao ZM, Gao YX, Hu MG, Li CG, Tan XL, Zhang X (2018) A single-team experience with robotic pancreatic surgery in 1010 cases. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 38(2):130–134
Iacono C, Verlato G, Ruzzenente A, Campagnaro T, Bacchelli C, Valdegamberi A, Bortolasi L, Guglielmi A (2013) Systematic review of central pancreatectomy and meta-analysis of central versus distal pancreatectomy. Br J Surg 100(7):873–885
Que W, Fang H, Yan B, Li J, Guo W, Zhai W, Zhang S (2015) Pancreaticogastrostomy versus pancreaticojejunostomy after pancreaticoduodenectomy: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Surg 209(6):1074–1082
Cheng Y, Briarava M, Lai M, Wang X, Tu B, Cheng N, Gong J, Yuan Y, Pilati P, Mocellin S (2017) Pancreaticojejunostomy versus pancreaticogastrostomy reconstruction for the prevention of postoperative pancreatic fistula following pancreaticoduodenectomy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 9:CD012257
Topal B, Fieuws S, Aerts R, Weerts J, Feryn T, Roeyen G, Bertrand C, Hubert C, Janssens M, Closset J, Belgian Section of H, and Pancreatic S (2013) Pancreaticojejunostomy versus pancreaticogastrostomy reconstruction after pancreaticoduodenectomy for pancreatic or periampullary tumours: a multicentre randomised trial. Lancet Oncol 14(7):655–662
Tittelbach-Helmrich D, Keck T, Wellner UF (2017) [Pancreaticogastrostomy: when and how?]. Chirurg 88(1):11–17
Guerrini GP, Soliani P, D’Amico G, Di Benedetto F, Negri M, Piccoli M, Ruffo G, Orti-Rodriguez RJ, Pissanou T, Fusai G (2016) Pancreaticojejunostomy versus pancreaticogastrostomy after pancreaticoduodenectomy: an up-to-date meta-analysis. J Invest Surg 29(3):175–184
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all of the participating patients and their families, as well as the investigators, research nurses, study coordinators, and operation staff. Yusheng Shi, Yang Ma and Yue Wang contributed equally to this work, and all should be considered first authors. Xiaxing Deng, Baiyong Shen and Cheng-hong Peng also contributed equally, and they should be considered co-corresponding authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Yusheng Shi, Yang Ma, Yue Wang, Jian Wang, Zhen Huo, Jiabin Jin, Yuanchi Weng, Shulin Zhao, Xiaxing Deng, Baiyong Shen and Chenghong Peng have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Y., Wang, Y., Wang, J. et al. Learning curve of robot-assisted middle pancreatectomy (RMP): experience of the first 100 cases from a high-volume pancreatic center in China. Surg Endosc 34, 3513–3520 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-019-07133-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-019-07133-x