Abstract
Background and aims
The emerging endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection (ESTD) is becoming an alternative method for superficial esophageal neoplastic lesions. This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness and feasibility of ESTD for superficial esophageal neoplastic lesions.
Methods
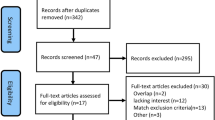
A comprehensive literature review was conducted to search relevant studies through PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science before 1 December 2018. Studies relating to ESTD for superficial esophageal neoplastic lesions were included. Rates of effectiveness (en bloc resection rate, R0 resection rate, and curative resection rate), rates of feasibility (muscular damage rate, perforation rate, postprocedural bleeding rate, and emphysema rate), and rates of follow-up (recurrence rate and stricture rate) were pooled and analyzed. Forest plots were constructed based on the random-effects model. Sensitivity analyses were also performed if significant heterogeneity existed.
Results
Six studies including 414 patients and 436 superficial esophageal neoplastic lesions that underwent ESTD were available for analysis. The pooled estimates of en bloc resection rate, R0 resection rate, and curative resection rate were 98% (95% CI 95.8–99.0%), 87.0% (95% CI 78.2–92.5%), and 87.6% (95% CI 67.4–96.0%), respectively. The pooled outcomes of muscular damage rate, perforation rate, postprocedural bleeding rate and emphysema rate were 19.1% (95% CI 9.8–33.8%), 2.2% (95% CI 1.1–4.1%), 1.6% (95% CI 0.7–3.5%), and 12.2% (95% CI 4.3–29.9%), respectively. Finally, the pooled results of recurrence and stricture were 4.7% (0.9–20.5%) and 20.9% (11.3–35.2%), respectively.
Conclusions
ESTD appears to be an effective and feasible approach for treating superficial esophageal neoplastic lesions. However, future research is needed for new and comprehensive methods to decrease the stricture rate after ESTD.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Inoue H, Minami H, Kaga M, Sato Y, Kudo SE (2010) Endoscopic mucosal resection and endoscopic submucosal dissection for esophageal dysplasia and carcinoma. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 20(25–34):v–vi
Zhai YQ, Li HK, Linghu EQ (2016) Endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection for large superficial esophageal squamous cell neoplasms. World J Gastroenterol 22:435–445
Linghu E, Feng X, Wang X, Meng J, Du H, Wang H (2013) Endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection for large esophageal neoplastic lesions. Endoscopy 45:60–62
Arantes V, Albuquerque W, Freitas Dias CA, Demas Alvares Cabral MM, Yamamoto H (2013) Standardized endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection for management of early esophageal tumors (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 78:946–952
Pioche M, Mais L, Guillaud O, Hervieu V, Saurin JC, Ponchon T, Lepilliez V (2013) Endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection for large esophageal neoplastic lesions. Endoscopy 45:1032–1034
Stang A (2010) Critical evaluation of the Newcastle–Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol 25:603–605
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ (Clin Res Ed) 327:557–560
Zhang W, Zhai Y, Chai N, Linghu E, Li H, Feng X (2018) Single- and double-tunnel endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection for large superficial esophageal squamous cell neoplasms. Endoscopy 50:505–510
Yang JL, Gan T, Zhu LL, Wang YP, Yang L, Wu JC (2017) Endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection: a feasible solution for large superficial rectal neoplastic lesions. Dis Colon Rectum 60:866–871
Zhang X, Shi D, Yu Z, Li R, Chen W, Bai F, Wu X, Cheng C, Shi R, Liu P (2018) A multicenter retrospective study of endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection for large lesser gastric curvature superficial neoplasms. Surg Endosc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-018-6471-y
Gan T, Yang JL, Zhu LL, Wang YP, Yang L, Wu JC (2016) Endoscopic submucosal multi-tunnel dissection for circumferential superficial esophageal neoplastic lesions (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc 84:143–146
Ye LP, Zheng HH, Mao XL, Zhang Y, Zhou XB, Zhu LH (2016) Complete circular endoscopic resection using submucosal tunnel technique combined with esophageal stent placement for circumferential superficial esophageal lesions. Surg Endosc 30:1078–1085
Huang R, Cai H, Zhao X, Lu X, Liu M, Lv W, Liu Z, Wu K, Han Y (2017) Efficacy and safety of endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection for superficial esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a propensity score matching analysis. Gastrointest Endosc 86:831–838
Wang J, Zhu XN, Zhu LL, Chen W, Ma YH, Gan T, Yang JL (2018) Efficacy and safety of endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection for superficial esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and precancerous lesions. World J Gastroenterol 24:2878–2885
Zhang W, Zhai Y, Chai N, Linghu E, Lu Z, Li H, Feng X (2018) Endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection and endoscopic submucosal dissection for large superficial esophageal squamous cell neoplasm: efficacy and safety study to guide future practice. Surg Endosc 32:2814–2821
Wang AY (2013) Endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection: the space between. Gastrointest Endosc 78:953–955
Ma MX, Bourke MJ (2018) Endoscopic submucosal dissection in the West: current status and future directions. Dig Endosc Off J Jpn Gastroenterol Endosc Soc 30:310–320
Acknowledgements
Special thanks to Dr. Bin Ma for his selfless teaching and help for Dr. Peiwen Li to conduct this study.
Funding
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (Grant No. 2015020561), The Fund for Scientific Research of The First Hospital of China Medical University (Grant No. fsfh1514), and Wu Jieping Medical Foundation Grant No. 320.6750.18293).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Dr. Peiwen Li, Dr. Bin Ma, Dr. Shulei Gong, Dr. Xinyu Zhang, and Dr. Wenya Li have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Ma, B., Gong, S. et al. Endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection for superficial esophageal neoplastic lesions: a meta-analysis. Surg Endosc 34, 1214–1223 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-019-06875-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-019-06875-y