Abstract
Background
Measurements of optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD) with noninvasive ocular ultrasonography have been shown to be accurate in determining increased intracranial pressure. Obesity is associated with chronic increases in intraabdominal pressure that could consequently result in intracranial hypertension. By utilizing ONSD ultrasonographic measurements, we compare the difference that may exist between obese and non-obese patients.
Study Design
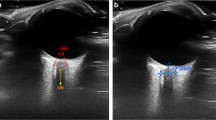
We prospectively collected data from patients who underwent laparoscopic procedures in the supine position between July 2013 and March 2014. Ophthalmic pathology was not present in any patient. Ultrasonographic measurement of the ONSD was obtained sagittally with a 12-MHz transducer 3 mm from its origin. The measurements were taken at 0, 15, and 30 min, and at the end of surgery.
Results
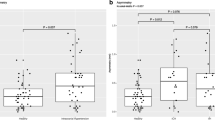
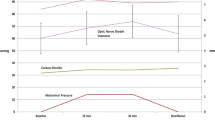
There were 62 subjects, 28 females (45.2 %) and 34 males (54.8 %), with a mean age of 44.22 ± 10.44 years (range 23–66). Forty-eight percent of patients were non-obese, and 52 % of patients were obese. The mean body mass index was 30.70 ± 7.61 kg/m2 (range 20.0–59.5). The mean ONSD of non-obese and obese patients was 4.7 and 5.5 mm at baseline (p = 0.01), 5.4 and 6.2 mm at 15 min (p = 0.01), 5.8 and 6.6 mm at 30 min (p = 0.01), and 5.1 and 5.7 mm after deflation of pneumoperitoneum (p = 0.03), respectively.
Conclusions
Utilizing a noninvasive method to measure the ONSD, a chronic increase in intracranial pressure in obese patients was demonstrated. The increase in the ONSD during laparoscopic procedures reflects a temporary increase in the intracranial pressure from baseline.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haslam DW, James WP (2005) Obesity. Lancet 366(9492):1197–1209
Wakerley B, Tan M, Ting E (2014) Idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Cephalalgia. 2014 May 20. [Epub ahead of print]
Willenberg T, Clemens R, Haegeli LM, Amann-Vesti B, Baumgartner I, Husmann M (2011) The influence of abdominal pressure on lower extremity venous pressure and hemodynamics: a human in vivo model simulating the effect of abdominal obesity. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 41(6):849–855
Varela JE, Hinojosa M, Nguyen N (2009) Correlations between intra-abdominal pressure and obesity-related co-morbidities. Surg Obes Relat Dis 5(5):524–528
Sugerman HJ (2001) Effects of increased intra-abdominal pressure in severe obesity. Surg Clin North Am 81(5):1063–1075
Rosenthal RJ, Friedman RL, Kahn AM, Martz J, Thiagarajah S, Cohen D, Shi Q, Nussbaum M (1998) Reasons for intracranial hypertension and hemodynamic instability during acute elevations of intra-abdominal pressure: observations in a large animal model. J Gastrointest Surg 2(5):415–425
Rosin D, Brasesco O, Varela J, Saber AA, You S, Rosenthal RJ, Cohn SM (2002) Low-pressure laparoscopy may ameliorate intracranial hypertension and renal hypoperfusion. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 12(1):15–19
Kimberly HH, Shah S, Marill K (2008) Correlation of optic nerve sheath diameter with direct measurement of intracranial pressure. Acad Emerg Med 15:201–204
Geeraerts T, Merceron S, Benhamou D, Vigué B, Duranteau J (2008) Non-invasive assessment of intracranial pressure using ocular sonography in neurocritical care patients. Intensive Care Med 34:2062–2067
Moretti R, Pizzi B, Cassini F, Vivaldi N (2009) Reliability of optic nerve ultrasound for the evaluation of patients with spontaneous intracranial hemorrhage. Neurocrit Care 11:406–410
Rajajee V, Vanaman M, Fletcher JJ, Jacobs TL (2011) Optic nerve ultrasound for the detection of raised intracranial pressure. Neurocrit Care 15(3):506–515
Caffery TS, Perret JN, Musso MW, Jones GN (2014) Optic nerve sheath diameter and lumbar puncture opening pressure in nontrauma patients suspected of elevated intracranial pressure. Am J Emerg Med. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2014.09.014
Lambert DM, Marceau S, Forse RA (2005) Intra-abdominal pressure in the morbidly obese. Obes Surg 15(9):1225–1232
Noblett KL, Jensen JK, Ostergard DR (1997) The relationship of body mass index to intra-abdominal pressure as measured by multichannel cystometry. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct 8(6):323–326
Schein M, Wittmann DH, Aprahamian CC, Condon RE (1995) The abdominal compartment syndrome: the physiological and clinical consequences of elevated intra-abdominal pressure. J Am Coll Surg 180:745–753
Cullen DJ, Coyle JP, Teplick R, Long MC (1989) Cardiovascular, pulmonary, and renal effects of massively increased intra-abdominal pressure in critically ill patients. Crit Care 17:118–121
Sugerman HJ, Wolfe LG, Sica DA, Clore JN (2003) Diabetes and hypertension in severe obesity and effects of gastric bypass-induced weight loss. Ann Surg 237:751–756
Sugerman H, Windsor A, Bessos M, Kellum J, Reines H, DeMaria E (1998) Effects of surgically induced weight loss on urinary bladder pressure, sagittal abdominal diameter and obesity co-morbidity. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 22:230–235
Sugerman H, Windsor A, Bessos M, Wolfe L (1997) Intra-abdominal pressure, sagittal abdominal diameter and obesity comorbidity. J Intern Med 241:71–79
Dip F, Nguyen D, Lo Menzo E, Szomstein S, Rosenthal R (2014) Non-invasive intracranial pressure methods during pneumoperitoneum in an animal model. J Am Coll Surg 219(3):S1–S162
Whiteley JR, Taylor J, Henry M, Epperson TI, Hand WR (2014) Detection of elevated intracranial pressure in robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy using ultrasonography of optic nerve sheath diameter. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol 27(2):155–159
Frumin E, Schlang J, Wiechmann W, Hata S, Rosen S, Anderson C, Pare L, Rosen M, Fox JC (2014) Prospective analysis of single operator sonographic optic nerve sheath diameter measurement for diagnosis of elevated intracranial pressure. West J Emerg Med 15(2):217–220
Brainar L, Chen DA, Aziz KM, Hillman TA (2012) Association of benign intracranial hypertension and spontaneous encephalocele with cerebrospinal fluid leak. Otol Neurotol 33(9):1621–1624
Kim MS, Bai SJ, Lee JR, Choi YD, Kim YJ, Choi SH (2014) Increase in intracranial pressure during carbon dioxide pneumoperitoneum with steep trendelenburg positioning proven by ultrasonographic measurement of optic nerve sheath diameter. J Endourol 28(7):801–806
Ballantyne SA, O’Neill G, Hamilton R, Hollman AS (2002) Observer variation in the sonographic measurement of optic nerve sheath diameter in normal adults. Eur J Ultrasound 15:145–149
Bäuerle J, Schuchardt F, Schroeder L, Egger K, Weigel M, Harloff A (2013) Reproducibility and accuracy of optic nerve sheath diameter assessment using ultrasound compared to magnetic resonance imaging. BMC Neurol 1(13):187
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Dr. Rosenthal is a speaker for Ethicon and has educational grants from Ethicon, Covidien, and Karl Storz. Dr. Lo Menzo is a consultant for Baxter Healthcare Corporation. Dr. Szomstein is a consultant for Covidien and Ethicon. Drs. Dip, Nguyen, and Sasson have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose. The authors declare conflicts of interest on Page 9 under Author Disclosures. The authors have no support or funding to report.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dip, F., Nguyen, D., Sasson, M. et al. The relationship between intracranial pressure and obesity: an ultrasonographic evaluation of the optic nerve. Surg Endosc 30, 2321–2325 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4458-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4458-5