Abstract
Background
Endoscopic stapler diverticulotomy (ESD) has become an accepted primary treatment for Zenker’s diverticulum (ZD). Recurrence of symptoms after surgical treatment of ZD is not uncommon, and traditionally patients with recurrent symptomatic ZD were referred to revision surgery by the transcervical Zenker’s diverticulectomy approach. Our objective was to evaluate the technical feasibility, safety and effectiveness of revision endoscopic stapler diverticulotomy (RESD) for recurrent ZD.
Methods
A case series with chart review study conducted in a tertiary referral center. The records of all patients who underwent ESD at our institute between 2002 and 2013 were retrieved and those who underwent RESD were identified and screened for primary surgical history, symptoms of recurrent ZD, time to recurrence, intraoperative and postoperative RESD course, complications and symptom resolution. The surgical history and outcome results of RESD and primary ESD (PESD) patients were compared.
Results
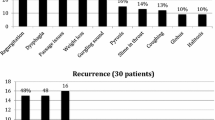
Eighty-nine ESDs were performed. Twenty were RESDs for recurrent ZD, and 69 were PESDs. Nine RESDs were performed for recurrent ZD after transcervical Zenker’s diverticulectomy, 10 RESDs for recurrent ZD after ESD, and one initial surgical approach was unknown. The mean time from first operation for ZD to RESD was 4.7 years. The average RESD surgery time and hospital stay were 21.4 min and 2.8 days, respectively. Endoscopic stapling of the ZD was feasible in 19 of 20 RESDs. Relief of symptoms without recurrence was achieved after 18 RESDs. Four RESD patients experienced minor postoperative complications. There were no significant differences in operative time, technical feasibility, hospital stay and complication rate between the RESD and PESD groups (P > .05).
Conclusion
RESD for ZD is technically feasible, safe and effective. The results are comparable to those of PESD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ryland A (1921) Some contemporary notes of a case of pharyngeal pouch—first reported 1764. Epidiascopic demonstration. Proc R Soc Med 14(Laryngol Sect):47–48
Ferguson B (1991) Evolution of therapy for pharyngoesophageal (Zenker’s) diverticulum. Ann Thorac Surg 51:848–852
Mosher HP (1917) Webs and pouches of the esophagus: their diagnosis and treatment. Surg Gynecol Obstet 25:175–187
Collard JM, Otte JB, Kestens PJ (1993) Endoscopic stapling technique of esophagodiverticulostomy for Zenker’s diverticulum. Ann Thorac Surg 56:573–576
Scher RL, Richtsmeier WJ (1998) Long-term experience with endoscopic staple-assisted esophagodiverticulostomy for Zenker’s diverticulum. Laryngoscope 108:200–205
Omote K, Feussner H, Stein HJ, Ungeheuer A, Siewert JR (1999) Endoscopic stapling diverticulostomy for Zenker’s diverticulum. Surg Endosc 13:535–538
Smith SR, Genden EM, Urken ML (2002) Endoscopic stapling technique for the treatment of Zenker diverticulum vs standard open-neck technique: a direct comparison and charge analysis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 128:141–144
Chang CY, Payyapilli RJ, Scher RL (2003) Endoscopic staple diverticulostomy for Zenker’s diverticulum: review of literature and experience in 159 consecutive cases. Laryngoscope 113:957–965
Cook RD, Huang PC, Richstmeier WJ, Scher RL (2000) Endoscopic staple-assisted esophagodiverticulostomy: an excellent treatment of choice for Zenker’s diverticulum. Laryngoscope 110:2020–2025
Peracchia A, Bonavina L, Narne S, Segalin A, Antoniazzi L, Marotta G (1998) Minimally invasive surgery for Zenker diverticulum: analysis of results in 95 consecutive patients. Arch Surg 133:695–700
Narne S, Narne S, Cutrone C, Bonavina L, Chella B, Peracchia A (1999) Endoscopic diverticulotomy for the treatment of Zenker’s diverticulum: results in 102 patients with staple-assisted endoscopy. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 108:810–815
Adam SI, Paskhover B, Sasaki CT (2013) Revision Zenker diverticulum: laser versus stapler outcomes following initial endoscopic failure. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 122:247–253
Kaoy CB, Commins D, Bates GJ (1998) The role of endoscopic stapling diverticulotomy in recurrent pharyngeal pouch. J Laryngol Otol 112:954–955
Scher R (2003) Endoscopic staple diverticulostomy for recurrent Zenker’s diverticulum. Laryngoscope 113:63–67
Acknowledgments
Esther Eshkol is thanked for editorial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Drs. Yael Oestreicher-Kedem, Oshri Wasserzug, Boaz Sagi, Narin Nard Carmel and Daniel Zikk have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oestreicher-Kedem, Y., Wasserzug, O., Sagi, B. et al. Revision endoscopic stapler Zenker’s diverticulotomy. Surg Endosc 30, 2022–2025 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4435-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4435-z