Abstract
Background
To date, therapeutic guidelines and pattern of reflux for patients with no-dysplasia (ND) or low-grade dysplasia (LGD) Barrett’s esophagus (BE) remain unclear. We aimed to analyze pattern of reflux and regression of ND- or LGD-BE after medical and surgical treatment.
Methods
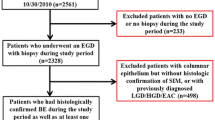
We studied a cohort of ND- and LGD-BE patients who underwent laparoscopic total fundoplication and a cohort of ND- and LGD-BE patients managed medically. Patients were matched for age, sex, and disease duration. After 1 year of follow-up at least, all patients underwent upper endoscopy with esophageal biopsies to evaluate any histological changes, as well as manometry and impedance-pH-metry to re-assess reflux patterns.
Results
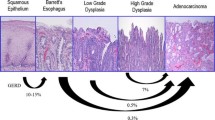
Thirty-seven patients (20 LGD, 17 ND) undergoing laparoscopic fundoplication were enrolled and compared with 25 patients (13 LGD, 12 ND) managed with proton pump inhibitors (PPI). Laparoscopic fundoplication resulted in a better control of both acidic and weakly acidic reflux (P < 0.001) and was associated with a higher probability of reversion for LGD (P < 0.01). Esophageal motility did not differ between surgically and medically treated patients.
Conclusions
In patients with ND- or LGD-BE, laparoscopic fundoplication seems to warrant a better control of all kinds of refluxate and it is associated with a higher likelihood of reversion of both LGD- and ND-BE, compared with PPI therapy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Falk JW (2002) Barrett’s esophagus. Gastroenterology 122:1569–1591
Cameron AJ, Ott BJ, Payne WS (1985) The incidence of adenocarcinoma in columnar-lined (Barrett’s) esophagus. N Engl J Med 313:857–859
Fitzgerald RC, Saeed IT, Khoo D, Farthing MJ, Burnham WR (2001) Rigorous surveillance protocol increases detection of curable cancers associated with Barrett’s esophagus. Dig Dis Sci 46:1892–1898
Wani S, Falk G, Hall M, Gaddam S, Wang A, Gupta N, Singh M, Singh V, Chuang KY, Boolchand V, Gavini H, Kuczynski J, Sud P, Reddymasu S, Bansal A, Rastogi A, Mathur SC, Young P, Cash B, Lieberman DA, Sampliner RE, Sharma P (2011) Patients with nondysplastic Barrett’s esophagus have low risks for developing dysplasia or esophageal adenocarcinoma. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 9:220–227; quiz e26
Spechler SJ (2002) Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapy. Med Clin North Am 86:1423–1445
Eloubeidi MA, Desmond R, Arguedas MR, Reed CE, Wilcox CM (2002) Prognostic factors for the survival of patients with esophageal carcinoma in the US: the importance of tumor length and lymph node status. Cancer 95:1434–1443
Richter JE (2003) What is the long-term significance of low-grade dysplasia? In: Giuli R (ed) Barrett’s esophagus, vol 1. John Libbey Eurotext, Paris, p 306
Spechler SJ, Sharma P, Souza RF, Inadomi JM, Shaheen NJ (2011) American Gastroenterological Association technical review on the management of Barrett’s esophagus. Gastroenterology 140:e18–e52
Winters C Jr, Spurling TJ, Chobanian SJ, Curtis DJ, Esposito RL, Hacker JF 3rd, Johnson DA, Cruess DF, Cotelingam JD, Gurney MS (1987) Barrett’s esophagus: a prevalent, occult complication of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology 92:118–124
Csendes A, Smok G, Burdiles P, Korn O, Gradiz M, Rojas J, Recio M (2003) Prevalence of intestinal metaplasia according to the length of the specialized columnar epithelium lining the distal esophagus in patients with gastroesophageal reflux. Dis Esophagus 16:24–28
Huo X, Zhang HY, Zhang XI, Lynch JP, Strauch ED, Wang JY, Melton SD, Genta RM, Wang DH, Spechler SJ, Souza RF (2010) Acid and bile salt induced CDX2 expression differs in squamous cells from patients with and without Barrett’s esophagus. Gastroenterology 139(194–203):e1
Souza RF, Krishnan K, Spechler SJ (2008) Acid, bile, and CDX: the ABCs of making Barrett’s metaplasia. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 295:G211–G218
Triadafilopoulos G (2001) Acid and bile reflux in Barrett’s esophagus: a tale of two evils. Gastroenterology 121:1502–1506
Hong J, Behar J, Wands J, Resnick M, Wang LJ, DeLellis RA, Lambeth D, Souza RF, Spechler SJ, Cao W (2010) Role of a novel bile acid receptor TGR5 in the development of oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Gut 59:170–180
Dvorak K, Payne CM, Chavarria M, Ramsey L, Dvorakova B, Bernstein H, Holubec H, Sampliner RE, Guy N, Condon A, Bernstein C, Green SB, Prasad A, Garewal HS (2007) Bile acids in combination with low pH induce oxidative stress and oxidative DNA damage: relevance to the pathogenesis of Barrett’s oesophagus. Gut 56:763–771
Savarino E, Zentilin P, Frazzoni M, Cuoco DL, Pohl D, Dulbecco P, Marabotto E, Sammito G, Gemignani L, Tutuian R, Savarino V (2010) Characteristics of gastro-esophageal reflux episodes in Barrett’s esophagus, erosive esophagitis and healthy volunteers. Neurogastroenterol Motil 22:1061-e280
Krishnan K, Pandolfino JE, Kahrilas PJ, Keefer L, Boris L, Komanduri S (2012) Increased risk for persistent intestinal metaplasia in patients with Barrett’s esophagus and uncontrolled reflux exposure before radiofrequency ablation. Gastroenterology 143:576–581
Lundell LR, Dent J, Bennett JR, Blum AL, Armstrong D, Galmiche JP, Johnson F, Hongo M, Richter JE, Spechler SJ, Tytgat GN, Wallin L (1999) Endoscopic assessment of esophagitis: clinical and functional correlates and further validation of the Los Angeles classification. Gut 45:172–180
Wang KK, Samplimer RE (2008) Updated guidelines 2008 for the diagnosis, surveillance and therapy of Barrett’s esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol 103:788–797
Riddell RH, Goldman H, Ransohoff DF, Appelman HD, Fenoglio CM, Haggitt RC, Ahren C, Correa P, Hamilton SR, Morson BC (1983) Dysplasia in inflammatory bowel disease: standardized classification with provisional clinical application. Hum Pathol 14:931–938
Roman S, Lin Z, Kwiatek MA, Pandolfino JE, Kahrilas PJ (2011) Weak peristalsis in esophageal pressure topography: classification and association with dysphagia. Am J Gastr 106:349–356
Tutuian R, Vela MF, Shay SS, Castell DO (2003) Multichannel intraluminal impedance in esophageal function testing and gastroesophageal reflux monitoring. J Clin Gastroenterol 37:206–215
Sifrim D, Castell D, Dent J, Kahrilas PJ (2004) Gastro-esophageal reflux monitoring: review and consensus report on detection and definitions of acid, non-acid, and gas reflux. Gut 53:1024–1031
Del Genio G, Rossetti G, Brusciano L, Limongelli P, Pizza F, Tolone S, Fei L, Maffettone V, Napolitano V, del Genio A (2007) Laparoscopic Nissen-Rossetti fundoplication with routine use of intraoperative endoscopy and manometry: technical aspects of a standardized technique. World J Surg 31:1099–1106
Amato G, Limongelli P, Pascariello A, Rossetti G, Del Genio G, Del Genio A, Iovino P (2008) Association between persistent symptoms and long-term quality of life after laparoscopic total fundoplication. Am J Surg 196:582–586
Rugge M, Correa P, Dixon MF, Hattori T, Leandro G, Lewin K, Riddell RH, Sipponen P, Watanabe H (2000) Gastric dysplasia: the Padova International classification. Am J Surg Path 24:167–176
Cooper BT, Neumann CS, Cox MA, Iqbal TH (1998) Continuous treatment with omeprazole 20 mg daily for up to 6 years in Barrett’s oesophagus. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 12:893–897
Sharma P, Morales TG, Bhattacharyya A, Garewal HS, Sampliner RE (1998) Squamous islands in Barrett’s esophagus: what lies underneath? Am J Gastroenterol 93:332–335
Spechler SJ, Sharma P, Traxler B, Levine D, Falk GW (2006) Gastric and esophageal pH in patients with Barrett’s esophagus treated with three esomeprazole dosages: a randomized, double-blind, crossover trial. Am J Gastroenterol 101:1964–1971
Katzka DA, Castell DO (1994) Successful elimination of reflux symptoms does not insure adequate control of acid reflux in patients with Barrett’s esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol 89:989–991
Stein HJ, Barlow AP, DeMeester TR, Hinder RA (1992) Complications of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Role of the lower esophageal sphincter, esophageal acid and acid/alkaline exposure, and duodenogastric reflux. Ann Surg 216:35–43
Csendes A, Burdiles P, Braghetto I, Smok G, Castro C, Korn O, Henríquez A (2002) Dysplasia and adenocarcinoma after classic antireflux surgery in patients with Barrett’s esophagus: the need for long-term subjective and objective follow-up. Ann Surg 235:178–185
Del Genio G, Tolone S, del Genio F, Rossetti G, Brusciano L, Pizza F, Fei L, del Genio A (2008) Total fundoplication controls acid and non acid reflux: evaluation by pre- and postoperative 24-hour pH-multichannel intraluminal impedance. Surg Endosc 22:2518–2523
Mainie I, Tutuian R, Agrawal A, Adams D, Castell DO (2006) Combined multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH monitoring to select patients with persistent gastro-oesophageal reflux for laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Br J Surg 93:1483–1487
del Genio G, Tolone S, del Genio F, D’Alessandro A, Brusciano L, Aggarwal R, Conzo G, Orditura M, Docimo L, Del Genio A (2012) Impact of total fundoplication on esophageal transit: analysis by combined multichannel intraluminal impedance and manometry. J Clin Gastroenterol 46:e1–e5
Oelschager BK, Barreca M, Chang L, Oleynikov D, Pellegrini CA (2003) Clinical and pathologic response of Barrett’s esophagus after antireflux surgery. Ann Surg 238:458–466
Gurski RR, Peters JH, Hagen JA, DeMeester SR, Bremner CG, Chandrasoma PT, DeMeester TR (2003) Barrett’s esophagus can and does regress after antireflux surgery: a study of prevalence and predictive factors. J Am Coll Surg 196:706–713
Zaninotto G, Cassaro M, Pennelli G, Battaglia G, Farinati F, Ceolin M, Costantini M, Ruol A, Guirroli E, Rizzetto C, Portale G, Ancona E, Rugge M (2005) Barrett’s epithelium after antireflux surgery. J Gastrointest Surg 9:1253–1261
Csendes A, Braghetto I, Burdiles P, Smok G, Henríquez A, Burgos AM (2009) Late results of the surgical treatment of 125 patients with short-segment Barrett Esophagus. Arch Surg 144:921–927
Sharma P, Falk GW, Weston AP, Reker D, Johnston M, Sampliner RE (2002) Natural history of low-grade dysplasia: an infrequent finding which usually regresses. Preliminary results from the Barrett’s esophagus study. Gastroenterology 122:A20
Parrilla P, Martinez de Haro LF, Ortiz A, Munitiz V, Molina J, Bermejo J, Canteras M (2003) Long-term results of a randomized prospective study comparing medical and surgical treatment of Barrett’s esophagus. Ann Surg 237:291–298
Conio M, Blanchi S, Lapertosa G, Ferraris R, Sablich R, Marchi S, D’Onofrio V, Lacchin T, Iaquinto G, Missale G, Ravelli P, Cestari R, Benedetti G, Macrì G, Fiocca R, Munizzi F, Filiberti R (2003) Long-term endoscopic surveillance of patients with Barrett’s esophagus: incidence of dysplasia and adenocarcinoma. A prospective study. Am J Gastroenterol 98:1931–1939
Disclosures
Salvatore Tolone, Paolo Limongelli, Marco Romano, Alessandro Federico, Giovanni Docimo, Roberto Ruggiero, Luigi Brusciano, Gianmattia Del Genio, and Ludovico Docimo have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Tolone and Limongelli shared co-first authorship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tolone, S., Limongelli, P., Romano, M. et al. The patterns of reflux can affect regression of non-dysplastic and low-grade dysplastic Barrett’s esophagus after medical and surgical treatment: a prospective case–control study. Surg Endosc 29, 648–657 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3713-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3713-5