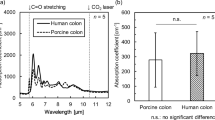
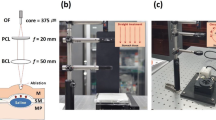
Abstract
Background
Recently, endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) has been performed to treat early gastric cancer. The en bloc resection rate of ESD has been reported to be higher than that of conventional endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR), and ESD can resect larger lesions than EMR. However, ESD displays a higher complication rate than conventional EMR. Therefore, the development of devices that would increase the safety of ESD is desired. Lasers have been extensively studied as a possible alternative to electrosurgical tools. However, laser by itself easily resulted in perforation upon irradiation of the gastrointestinal tract. We hypothesized that performing ESD using a CO2 laser with a submucosal laser absorber could be a safe and simple treatment for early gastric cancer. To provide proof of concept regarding the feasibility of ESD using a CO2 laser with submucosally injected laser absorber solution, an experimental study in ex vivo and in vivo porcine models was performed.
Methods
Five endoscopic experimental procedures using a carbon dioxide (CO2) laser were performed in a resected porcine stomach. In addition, three endoscopic experimental procedures using a CO2 laser were performed in living pigs.
Results
In the ex vivo study, en bloc resections were all achieved without perforation and muscular damage. In addition, histological evaluations could be performed in all of the resected specimens. In the in vivo study, en bloc resections were achieved without perforation and muscular damage, and uncontrollable hemorrhage did not occur during the procedures.
Conclusions
Endoscopic submucosal dissection using a CO2 laser with a submucosal laser absorber is a feasible and safe method for the treatment of early gastric cancer.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Soetikno R, Gotoda T, Nakanishi Y, Soehendra N (2003) Endoscopic mucosal resection. Gastrointest Endosc 57:567
Korenaga D, Haraguchi M, Tsujitani S, Okamura T, Tamada R, Sugimachi K (1986) Clinicopathological features of mucosal carcinoma of the stomach with lymph node metastasis in eleven patients. Br J Surg 73:431–433
Tanabe S, Koizumi W, Mitomi H, Nakai H, Murakami S, Nagaba S, Kida M, Oida M, Saigenji K (2002) Clinical outcome of endoscopic aspiration mucosectomy for early stage gastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc 56:708–713
Ono H, Kondo H, Gotoda T, Shirao K, Yamaguchi H, Saito D, Hosokawa K, Shimoda T, Yoshida S (2001) Endoscopic mucosal resection for treatment of early gastric cancer. Gut 48:225
Ohkuwa M, Hosokawa K, Boku N, Ohtu A, Tajiri H, Yoshida S (2001) New endoscopic treatment for intramucosal gastric tumors using an insulated-tip diathermic knife. Endoscopy 33:221–226
Fujishiro M (2006) Endoscopic submucosal dissection for stomach neoplasms. World J Gastroenterol 12:5108
Hirao M, Masuda K, Asanuma T, Naka H, Noda K, Matsuura K, Yamaguchi O, Ueda N (1988) Endoscopic resection of early gastric cancer and other tumors with local injection of hypertonic saline-epinephrine. Gastrointest Endosc 34:264–269
Toyonaga T, Nishino E, Hirooka T, Dozaiku T, Sugiyama T, Iwata Y, Ono W, Ueda C, Tomita M (2005) Use of short needle knife for esophageal endoscopic submucosal dissection. Dig Endosc 17:246–252
Oyama T, Kikuchi Y (2002) Aggressive endoscopic mucosal resection in the upper GI tract-hook knife EMR method. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 11:291–296
Strauss R, Fallon S (2004) Lasers in contemporary oral and maxillofacial surgery. Dent Clin N Am 48:861
Patel C (1964) Selective excitation through vibrational energy transfer and optical maser action in N2–CO2. Phys Rev Lett 13:617–619
Strong M, Jako G (1972) Laser surgery in the larynx. Early clinical experience with continuous CO2 laser. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 81:791
Anderson R, Parrish J (1983) Selective photothermolysis: precise microsurgery by selective absorption of pulsed radiation. Science 220:524
Brugmans M, Kemper J, Gijsbers G, van der Meulen F, van Gemert M (1991) Temperature response of biological materials to pulsed non-ablative CO2 laser irradiation. Lasers Surg Med 11:587–594
Burke L, Rovin R, Cerullo L, Brown J (1985) Thermal effects of the Nd:YAG and carbon dioxide lasers on the central nervous system. Lasers Surg Med 5:67–71
Kotlow LA (2004) Lasers in pediatric dentistry. Dent Clin N Am 48:889–922
LeCarpentier G, Motamedi M, McMath L, Rastegar S, Welch A (1993) Continuous wave laser ablation of tissue: analysis of thermal and mechanical events. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 40:188–200
Shi Y, Wang Y, Abe Y, Matsuura Y, Miyagi M, Sato S, Taniwaki M, Uyama H (1998) Cyclic olefin polymer-coated silver hollow glass waveguides for the infrared. Appl Opt 37:7758–7762
Anandasabapathy S, Maru D, Klumpp S, Uthamanthil R, Borne A, Bhutani M (2009) Novel endoscopic application of a new flexible-fiber CO2 laser for esophageal mucosal ablation in a porcine model. Endoscopy 41:138–142
Hayashi T, Arai T, Tajiri H, Niwa H (1997) Enhanced diode laser ablation using submucosal injection of indocyanine green solution: part II; irradiation to resected porcine gastric wall and canine gastric walls under laparotomy. Gastroenterol Endosc 39:1753–1765
Kawaguchi A, Nagao S, Takebayashi K, Higashiyama M, Komoto S, Hokari R, Miura S (2008) Long-term outcome of endoscopic semiconductive diode laser irradiation therapy with injection of indocyanine green for early gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 23:1193–1199
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Satoshi Watanabe and Keiichiro Yamada, Division of Sustainable Energy and Environmental Engineering, Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University for their important contributions to the experiments. This work was supported, in part, by grants for the Global COE Program “Global Center of Excellence for Education and Research on Signal Transduction Medicine in the Coming Generation” from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan and grants from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan, the Foundation of Advancement of International Science, and the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan.
Disclosures
Drs. Daisuke Obata, Yoshinori Morita, Rinna Kawaguchi, Katsunori Ishii, Hisanao Hazama, Kunio Awazu, Hiromu Kutsumi, and Takeshi Azuma have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Obata, D., Morita, Y., Kawaguchi, R. et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection using a carbon dioxide laser with submucosally injected laser absorber solution (porcine model). Surg Endosc 27, 4241–4249 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-3029-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-3029-x