Abstract
Introduction
Incarceration and obstruction of an intrathoracic stomach are potentially devastating complications of paraesophageal hernias (PEH). Gastric decompression and resuscitation are important elements of preoperative management of acutely presenting PEH. The optimal time for surgical repair after decompression is unknown. We hypothesized that in obstructed PEH, early surgery may improve outcomes.
Methods
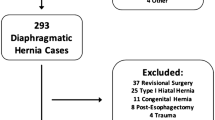
From the 2005–2010 National Surgical Quality Improvement Project database, we selected PEH repairs with a diagnosis of obstruction. Patients were divided by time to surgery: ≤1 day of admission (early) or >1 day (interval). Outcomes were mortality and morbidity. Multivariable regression controlled for age and cardiopulmonary comorbidities.
Results
Of 224 patients, 149 (67 %) were early and 75 (33 %) were interval, with mean 3.6 days. Repairs were 89 % transabdominal, 9 % included fundoplication, and 18 % gastrostomy. Early and interval groups experienced similar morbidity 23 versus 31 % (p = 0.2) and mortality 5.4 versus 4 % (p = 0.7). Pulmonary, wound, or VTE complications were equivalent. Sepsis was less (2.7 vs. 13 %, p = 0.002) and length of stay was shorter (5 vs. 11 days, p < 0.001) for early vs. interval patients. On adjusted analysis, the early group had an 80 % reduction in sepsis (95 % confidence interval (CI), 0.05–0.6, p = 0.005). Odds of overall or other morbidity or mortality were statistically similar between groups.
Conclusions
Patients who required emergency surgery for PEH have disease complicated by strangulation, perforation, bleeding, or sepsis. Emergency surgery for PEH repair is inherently high-risk and preoperative resuscitation and decompression is critical. In our analysis, patients with an obstructed PEH had less postoperative sepsis and fewer days in the hospital if surgery was performed within the first hospital day. However, there was no difference in mortality between early and delayed treatment. Deferring surgery for resuscitation permits optimization, but prolonged delay may worsen patient outcomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Larusson HJ, Zingg U, Hahnloser D, Delport K, Seifert B, Oertli D (2009) Predictive factors for morbidity and mortality in patients undergoing laparoscopic paraesophageal hernia repair: age, ASA score and operation type influence morbidity. World J Surg 33(5):980–985
Skinner DB, Belsey RH (1967) Surgical management of esophageal reflux and hiatus hernia. Long-term results with 1,030 patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 53(1):33–54
Sihvo EI, Salo JA, Räsänen JV, Rantanen TK (2009) Fatal complications of adult paraesophageal hernia: a population-based study. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 137(2):419–424
Velanovich V, Karmy-Jones R (2001) Surgical management of paraesophageal hernias: outcome and quality of life analysis. Dig Surg 18(6):432–437
Schauer PR, Ikramuddin S, McLaughlin RH, Graham TO, Slivka A, Lee KK, Schraut WH, Luketich JD (1998) Comparison of laparoscopic versus open repair of paraesophageal hernia. Am J Surg 176(6):659–665
Gangopadhyay N, Perrone JM, Soper NJ, Matthews BD, Eagon JC, Klingensmith ME, Frisella MM, Brunt LM (2006) Outcomes of laparoscopic paraesophageal hernia repair in elderly and high-risk patients. Surgery 140(4):491–498
Stylopoulos N, Gazelle GS, Rattner DW (2002) Paraesophageal hernias: operation or observation? Ann Surg 236(4):492–500
Poulose BK, Gosen C, Marks JM, Khaitan L, Rosen MJ, Onders RP, Trunzo JA, Ponsky JL (2008) Inpatient mortality analysis of paraesophageal hernia repair in octogenarians. J Gastrointest Surg 12(11):1888–1892
Polomsky M, Hu R, Sepesi B, O’Connor M, Qui X, Raymond DP, Litle VR, Jones CE, Watson TJ, Peters JH (2010) A population-based analysis of emergent versus elective hospital admissions for an intrathoracic stomach. Surg Endosc 24(6):1250–1255
Mehta S, Boddy A, Rhodes M (2006) Review of outcome after laparoscopic paraesophageal hiatal hernia repair. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 16(5):301–306
Senagore AJ, Stulberg JJ, Byrnes J, Delaney CP (2009) A national comparison of laparoscopic versus open colectomy using the National Surgical Quality Improvement Project data. Dis Colon Rectum 52(2):183–186
Steele SR, Brown TA, Rush RM, Martin MJ (2008) Laparoscopic vs open colectomy for colon cancer: results from a large nationwide population-based analysis. J Gastrointest Surg 12(3):583–591
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Amy Roth.
Disclosures
Drs. Bhayani, Kurian, Sharata, Reavis, Dunst, and Swanstrom have no conflict of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhayani, N.H., Kurian, A.A., Sharata, A.M. et al. Wait only to resuscitate: early surgery for acutely presenting paraesophageal hernias yields better outcomes. Surg Endosc 27, 267–271 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-012-2436-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-012-2436-8