Abstract
Background
Minimal access approaches to inguinal hernia repair have added to the ongoing debate over the “best groin hernia repair.” The present prospective randomized controlled trial was done to compare the totally extraperitoneal (TEP) and transabdominal preperitoneal (TAPP) techniques of laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair.
Methods
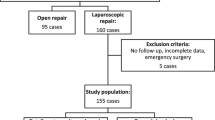
The present prospective randomized study was conducted between May 2007 and March, 2009 and included 100 patients suffering from uncomplicated primary groin hernia. Patients were randomized into group I (TEP) and group II (TAPP). Intraoperative variables and postoperative pain scores were recorded in a prestructured form.
Results
One hundred patients were included in the study (TEP, 53; TAPP, 47). Both groups were comparable in terms of demographic profile and hernia characteristics. The average operative time was higher in the TAPP group (p = 0.209). The pain scores at 1 h and 24 h after surgery and at 3-month follow-up were significantly higher in the TAPP group (p < 0.05). The average follow-up was 30.5 months. In the TEP group, 37.8% of patients had seroma compared to 18.3% in the TAPP group (p = 0.021). However, there was a higher incidence of scrotal edema in the TAPP group (16 vs. 9, p = 0.009). The wound infection rates were equal (2% vs. 3%). There has been no recurrence in either group during the follow-up period of 44 months. Overall, the patients were more satisfied with TEP rather than TAPP (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
In the present study, TEP had a significant advantage over TAPP for significantly reduced postoperative pain up to 3 months, which resulted in a better patient satisfaction score. The other intraoperative complications, postoperative complications, and cost were similar in both groups. In terms of results, both repair techniques seemed equally effective, but TEP had an edge over TAPP.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassini E (1887) Nuovo metodo sulla cura radicale dell’ernia inguinale. Arch Soc Ital Chir 4:380
[No authors listed] (1999) Laparoscopic versus open repair of groin hernia: a randomized comparison. The MRC Laparoscopic Groin Hernia Trial Group. Lancet 354:185–190
Neumayer L, Giobbie-Hurder A, Jonasson O (2004) Open mesh versus laparoscopic mesh repair of inguinal hernia. N Engl J Med 350:1819–1827
National Institute for Clinical Excellence (2001) Guidance on the use of laparoscopic surgery for inguinal hernia, technological appraisal guidance No. 18. NICE, London
Arregui ME, Davis CJ, Yucel O, Nagan RF (1992) Laparoscopic mesh repair of inguinal hernia using a preperitoneal approach: a preliminary report. Surg Laparosc Endosc 2:53–58
McKernan JB, Laws HL (1993) Laparoscopic repair of inguinal hernias using a totally extraperitoneal prosthetic approach. Surg Endosc 7:26–28
Camps J, Nguyen N, Annabali R, Fitzgibbons RJ Jr (1995) Laparoscopic inguinal herniorrhaphy: transabdominal techniques. Int Surg 80:18–25
Corbitt JD (1993) Transabdominal preperitoneal herniorrhaphy. Surg Laparosc Endosc 3:328–332
Misra MC, Bansal VK, Kumar S, Prashant B, Bhattacharjee HK (2008) Total extra-peritoneal repair of groin hernia: prospective evaluation at a tertiary care center. Hernia 12:65–71
Wake BL, McCormack K, Fraser C, Vale L, Perez J, Grant AM (2005) Transabdominal pre-peritoneal (TAPP) versus totally extraperitoneal (TEP). Cochrane Database Syst Rev (1):CD004703
Lichtenstein IL, Shulman AG, Amid PK, Montllor MM (1989) The tension-free hernioplasty. Am J Surg 157:188–193
Ferzli G, Masaad A, Albert P, Worth MH (1993) Endoscpoic extraperitoneal herniorrhaphy versus conventional hernia repair: a comparative study. Curr Surg 50:291–294
Khoury N (1995) A comparative study of laparoscopic extraperitoneal and transabdominal preperitoneal herniorrhaphy. J Laparoendosc Surg 56:349–355
Felix EL, Harbertson N, Vartanian S (1999) Laparoscopic hernioplasty: significant complications. Surg Endosc 13:328–331
Bringman S, Blomqvist P (2005) Intestinal obstruction after inguinal and femoral hernia repair: a study of 33, 275 operations during 1992–2000 in Sweden. Hernia 9:178–183
Hair A, Duffy K, McLean J, Taylor S, Smith H, Walker A (2000) Groin hernia repair in Scotland. Br J Surg 87:1722–1726
Cohen RV (1998) Laparoscopic extraperitoneal repair of inguinal hernias. Surg Laparosc Endosc 8:14–16
Felix EL, Michas CA, Gonzalez MH Jr (1995) Laparoscopic hernioplasty: TAPP vs TEP. Surg Endosc 9:984–989
Van Hee R, Goverde P, Hendrickx L, Van der Schelling G, Totte E (1998) Laparoscopic transperitoneal versus extraperitoneal inguinal hernia repair: a prospective clinical trial. Acta Chir Belg 98:132–135
Baca I, Schultz C, Gotzen V, Jazek G (2000) Laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair. A review of 2500 cases. In: Lomanto D, Kum CK, So JBY, Goh PMY (eds) Proceedings of the 7th world congress of endoscopic surgery, Singapore, June 1–4, 2000. Monduzzi editore, Bologna, Italy, pp 425–430
Tamme C, Scheidbach H, Hampe C, Schneider C, Kockerling F (2003) Totally extraperitoneal endsocopic inguinal hernia repair (TEP). Surg Endosc 17:190–195
Leibl BJ, Schmedt CG, Ulrich M, Kraft K, Bittner R (2000) Laparoscopic hernia therapy (TAPP) as a teaching operation. Chirurg 71:939–942
Dalessandri KM, Bhoyrul S, Mulvihill SJ (2001) Laparoscopic hernia repair and bladder injury. JSLS 5:175–177
Moreno-Egea A, Aguayo JL, Canteras M (2000) Intraoperative and postoperative complications of totally extraperitoneal laparoscopic inguinal hernioplasty. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 10:30–33
Misra MC, Kumar S, Bansal VK (2008) Total extraperitoneal (TEP) mesh repair of inguinal hernia in the developing world: comparison of low-cost indigenous balloon dissection versus direct telescopic dissection: a prospective randomized controlled study. Surg Endosc 22:1947–1958
Lau H, Lee F (2003) Seroma following endoscopic extraperitoneal inguinal hernioplasty. Surg Endosc 17:1773–1777
Lepere M, Benchetrit S, Debaert M, Detruit B, Dufilho A, Gaujoux D (2000) A multicentric comparison of transabdominal versus totally extraperitoneal laparoscopic hernia repair using PARIETEX meshes. JSLS 4:147–153
Lau H, Patil NG, Yuen WK, Lee F (2003) Prevalence and severity of chronic groin pain after endoscopic totally extraperitoneal inguinal hernioplasty. Surg Endosc 17:1620–1623
Poobalan A, Bruce T, King PM, Chambers WA, Krukowski ZH, Smith WCS (2001) Chronic pain and quality of life following open inguinal hernia repair. Br J Surg 88:1122–1126
Page B, Paterson C, Young D (2002) Pain from primary inguinal hernia and the effect of repair on pain. Br J Surg 89:1315–1318
Bringman S, Ek A, Haglind E, Heikkinen T, Kald A, Kylberg F, Ramel S, Wallon C (2001) Is a dissection balloon beneficial in totally extraperitoneal endoscopic hernioplasty (TEP)? A randomized prospective multicenter study. Surg Endosc 15:266–270
Knook MT, Weidema WF, Stassen LP (1999) Endoscopic total extraperitoneal repair of bilateral inguinal hernias. Br J Surg 86:1312–1316
Wellwood J, Sculpher MJ, Stoker D, Nicholls GJ (1998) Randomised controlled trial of laparoscopic versus open mesh repair of inguinal hernia: outcome and cost. BMJ 12:317–331
Fitzgibbons RJ Jr, Puri V (2006) Laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair. Am Surg 72:197–206
Weiser HF, Klinge B (2000) Endoscopic hernia repair - experiences and characteristic features. Viszeralchirurgie 35:316–320
Lehr SC, Schuricht AL (2001) A minimally invasive approach for treating postoperative seromas after incisional hernia repair. JSLS 5:267–271
Srivastava A, Srinivas G, Misra MC, Pandav CS, Seenu V, Goyal A (2001) Cost effectiveness analysis of laparoscopic versus minilaparotomy cholecystectomy for gallstone disease. Int J Technol Assess Health Care 17:497–502
Disclosure
Dr. Asuri Krishna, Dr. M. C. Misra, Dr. Virinder Kumar Bansal, Dr. Subodh Kumar, Dr. S. Rajeshwari, and Dr. Anjolie Chabra have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishna, A., Misra, M.C., Bansal, V.K. et al. Laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair: transabdominal preperitoneal (TAPP) versus totally extraperitoneal (TEP) approach: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Surg Endosc 26, 639–649 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-011-1931-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-011-1931-7