Abstract
Background
The goal of this study was to evaluate high-field open magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for intraoperative real-time imaging during hand-assisted laparoscopic liver resection. MR guidance has several advantages compared to ultrasound and may represent a future technique for abdominal surgery. Various MRI-safe and -compatible instruments were developed, tested, and applied to realize minimally invasive liver surgery under MR guidance. As proof of the concept, liver resection was performed in a porcine model.
Methods
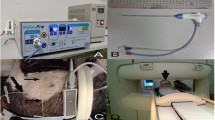
All procedures were conducted in a 1.0-T open MRI unit. Imaging quality and surgical results were documented during three cadaveric and two live animal procedures. A nonferromagnetic hand port was used for manual access and the liver tissue was dissected using a Nd:YAG laser.
Results
The intervention time ranged from 126 to 145 min, with a dissection time from 11 to 15 min. Both live animals survived the intervention with a blood loss of 250 and 170 ml and a specimen weight of 138 and 177 g. A dynamic T2W fast spin-echo sequence allowed real-time imaging (1.5 s/image) with good delineation of major and small hepatic vessels. The newly developed MR-compatible instruments and camera system caused only minor interferences and artifacts of the MR image.
Conclusion
MR-guided liver resection is feasible and provides additional image information to the surgeon. We conclude that MR-guided laparoscopic liver resection improves the anatomical orientation and may increase the safety of future minimally invasive liver surgery.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Santambrogio R, Opocher E, Ceretti AP, Barabino M, Costa M, Leone S, Montorsi M (2007) Impact of intraoperative ultrasonography in laparoscopic liver surgery. Surg Endosc 21(2):181–188
Bao P, Warmath J, Galloway R Jr, Herline A (2005) Ultrasound-to-computer-tomography registration for image-guided laparoscopic liver surgery. Surg Endosc 19(3):424–429
Beller S, Hunerbein M, Eulenstein S, Lange T, Schlag PM (2007) Feasibility of navigated resection of liver tumors using multiplanar visualization of intraoperative 3-dimensional ultrasound data. Ann Surg 246(2):288–294
Cash DM, Miga MI, Glasgow SC, Dawant BM, Clements LW, Cao Z, Galloway RL, Chapman WC (2007) Concepts and preliminary data toward the realization of image-guided liver surgery. J Gastrointest Surg 11(7):844–859
Beller S, Hunerbein M, Lange T, Eulenstein S, Gebauer B, Schlag PM (2007) Image-guided surgery of liver metastases by three-dimensional ultrasound-based optoelectronic navigation. Br J Surg 94(7):866–875
Hall WA, Truwit CL (2008) Intraoperative MR-guided neurosurgery. J Magn Reson Imaging 27(2):368–375
Clasen S, Pereira PL (2008) Magnetic resonance guidance for radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors. J Magn Reson Imaging 27(2):421–433
Mahnken AH, Buecker A, Spuentrup E, Krombach GA, Henzler D, Gunther RW, Tacke J (2004) MR-guided radiofrequency ablation of hepatic malignancies at 1.5 T: initial results. J Magn Reson Imaging 19(3):342–348
Gould SW, Gedroyc W, Darzi A (1999) Laparoscopic surgery in a 0 5-t interventional magnetic resonance unit. Surg Endosc 13(6):604–610
Chopra SS, Rump J, Schmidt SC, Streitparth F, Seebauer C, Schumacher G, Van der Voort I, Teichgraber U (2009) Imaging sequences for intraoperative MR-guided laparoscopic liver resection in 1.0-T high field open MRI. Eur Radiol 19(9):2191–2196
Chopra SS, Wiltberger G, Teichgraeber U, Papanikolaou I, Schwabe M, Schmidt S, Fikatas P, Streitparth F, Philipp C, Wichlas F, Seebauer C, Schumacher G (2009) Evaluation of laparoscopic liver resection with two different Nd:YAG lasers for future use in a high-field open MRI. Photomed Laser Surg 27(2):281–286
Boll DT, Lewin JS, Duerk JL, Aschoff AJ, Merkle EM (2004) Comparison of MR imaging sequences for liver and head and neck interventions: is there a single optimal sequence for all purposes? Acad Radiol 11(5):506–515
Jersenius U, Fors D, Rubertsson S, Arvidsson D (2007) Laparoscopic parenchymal division of the liver in a porcine model: comparison of the efficacy and safety of three different techniques. Surg Endosc 21(2):315–320
Rau HG, Schardey HM, Buttler E, Reuter C, Cohnert TU, Schildberg FW (1995) A comparison of different techniques for liver resection: blunt dissection, ultrasonic aspirator and jet-cutter. Eur J Surg Oncol 21(2):183–187
Joffe SN, Brackett KA, Sankar MY, Daikuzono N (1986) Resection of the liver with the Nd:YAG laser. Surg Gynecol Obstet 163(5):437–442
Vogl TJ, Straub R, Zangos S, Mack MG, Eichler K (2004) MR-guided laser-induced thermotherapy (LITT) of liver tumours: experimental and clinical data. Int J Hyperth 20(7):713–724
Vogl TJ, Eichler K, Zangos S, Mack MG (2005) Interstitial laser therapy of liver tumors. Med Laser Appl 20(2):115–118
Kariniemi J, Sequeiros RB, Ojala R, Tervonen O (2006) Feasibility of MR imaging-guided percutaneous drainage of pancreatic fluid collections. J Vasc Interv Radiol 17(8):1321–1326
Feng L, Dumoulin CL, Dashnaw S, Darrow RD, Delapaz RL, Bishop PL, Pile-Spellman J (2005) Feasibility of stent placement in carotid arteries with real-time MR imaging guidance in pigs. Radiology 234(2):558–562
Acknowledgments
The project was funded by the TSB Technologiestiftung Berlin–Zukunftsfonds Berlin, Germany, and the European Union–European Fund for regional development, Berlin, Germany. Official project partners were Philips Medical Systems, Hamburg, Germany (open MR, MR monitors); WOM, World of Medicine AG, Berlin, Germany (camera prototype, ORCAP documentation system); MGB, Berlin, Germany (laparoscope prototype); Somatex, Teltow, Germany (MR-compatible needle).
Disclosures
Authors S. S. Chopra, S. C. Schmidt, R. Eisele, U. Teichgräber, I. Van der Voort, C. Seebauer, F. Streitparth, and G. Schumacher have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chopra, S.S., Schmidt, S.C., Eisele, R. et al. Initial results of MR-guided liver resection in a high-field open MRI. Surg Endosc 24, 2506–2512 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-010-0994-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-010-0994-1