Abstract
Background
The safety and efficacy of endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) is very dependent on an effective injection beneath the submucosal lamina and on a controlled cutting technique. After our study group demonstrated the efficacy of the HydroJet in needleless submucosal injections under various physical conditions to create a submucosal fluid cushion (Selective tissue elevation by pressure = STEP technique), the next step was to develop a new instrument to combine the capabilities of an IT-Knife with a high-pressure water-jet in a single instrument. In this experimental study, we compared this new instrument with a standard ESD technique.
Methods
Twelve gastric ESD were performed in six pigs under endotracheal anesthesia. Square areas measuring 4-cm × 4-cm were marked out on the anterior and posterior wall in the corpus-antrum transition region. The HybridKnife was used as an standard needle knife with insulated tip (i.e., the submucosal injection was performed with an injection needle and only the radiofrequency (RF) part of the HybridKnife was used for cutting (conventional technique)) or the HybridKnife was used in all the individual stages of the ESD, making use of the HybridKnife’s combined functions (HybridKnife technique). The size of the resected specimens, the operating time, the frequency with which instruments were changed, the number of bleeding episodes, and the number of injuries to the gastric wall together with the subjective overall assessment of the intervention by the operating physician were recorded.
Results
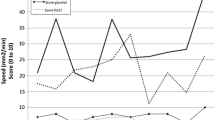
The resected specimens were the same size, with average sizes of 16.96 cm2 and 15.85 cm2 resp (p = 0.8125). Bleeding episodes have been less frequent in the HybridKnife group (2.83 vs. 3.5; p = 0.5625). The standard knife caused more injuries to the lamina muscularis propria (0.17 vs. 1.33; p = 0.0313). The operating times had a tendency to be shorter with the HybridKnife technique (47.18 vs. 58.32 minute; p = 0.0313).
Discussion
The combination of a needle-knife with high-pressure water-jet dissection improved the results of endoscopic submucosal dissection in this experimental setting. Because the frequency of complications is still high, further improvements to the instrument are necessary.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oyama T, Tomori A, Hotta K, Morita S, Kominato K, Tanaka M, Miyata Y (2005) Endoscopic submucosal dissection of early esophageal cancer. Clin Gast Hepat 3:67–70
Kakushima N, Fujishiro M (2008) Endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastrointestinal neoplasms. World J Gastroenterol 14:2962–2967
Yamamoto H, Kawata H, Sunada K, Satch K, Kaneko Y, Ido K, Sugano K (2002) Success rate of curative endoscopic mucosal resection with circumferential mucosa incision assisted by submucosal injection of sodium hyaluronate. Gastrointest Endosc 56:507–512
Yahagi N, Fujishiro M, Kakushima N, Kobayashi K, Hashimoto T, Oka M, Iguchi M, Enomoto S, Ichinose M, Niwa H, Omata M (2004) Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer using the tip of an electrosurgical snare (thin type). Digest Endosc 16:34–38
Conio M, Rajan E, Sorbi D, Norton I, Herman L, Filiberti R, Gostout C (2002) Comparative performance in the porcine esophagus of different solutions used for submucosal injections. Gastrointest Endosc 56:513–516
Feitoza A, Gostout C, Burgart L, Burkert A, Herman L, Rajan E (2003) Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose: a better submucosal fluid cushion for endoscopic mucosal resection. Gastrointest Endosc 57:41–47
Fujisjiro M, Yahagi N, Kashimura K, Mizushima Y, Oka M, Enomoto S, Kakushima N, Kobayashi K, Hashimoto T, Iguchi M, Shimizu Y, Ichinose M, Omata M (2004) Comparison of various submucosal injection solutions for maintaining mucosal elevation during EMR. Endoscopy 36:579–583
Fujisjiro M, Yahagi N, Kashimura K, Mizushima Y, Oka M, Matsuura T, Enomoto S, Kakushima K, Imagawa A, Kobayashi K, Hashimoto T, Iguchi M, Shimizu Y, Ichinose M, Omata M (2004) Different mixtures of sodium hyaluronate and their ability to create SFCs for EMR. Endoscopy 36:584–589
Rajan E, Gostout C, Feitoza A, Leontovich O, Herman L, Burgart L, Chung S, Cotton P, Hawes R, Kalloo A, Kantsevoy S, Pasricha P (2004) Widespread EMR: a new technique for removal of large areas of mucosa. Gastrointest Endosc 60:623–627
Rösch T, Sarbia M, Schumacher B, Deinert E, Frimberger E, Toermer T, Stolte M, Neuhaus M (2004) Attempted endoscopic en bloc resection of mucosal and submucosal tumors using IT-Knives: a pilot series. Endoscopy 36:788–801
Yamamoto H, Sekine Y, Higashizawa T, Kihira K, Kaneko Y, Hosoya Y, Ido K, Saito K, Sugano K (2001) Successful en bloc resection of a large superficial gastric cancer by using sodium hyaluronate and electrocautery incision forceps. Gastrointest Endosc 54:629–632
Farin G (2002) Technology of water-jet dissection. Min Invas Ther Allied Technol 11(5/6):249–256
Schurr MO, Wehrmann M, Kunert W, Melzer A, Lirici MM, Trapp R, Kanehira E, Buess G (1994) Histologic effects of different technologies for dissection in endoscopic surgery: Nd:YAG-laser, high frequency and water-jet. End Surg 2:195–201
Ehrhardt D, Heller T, Nizze H, Benz S, Liebe S, Löhr M (2002) Der Wasserstrahl als Schneidewerkzeug in der gastroenterologischen Endoskopie–eine experimentelle Studie. Endo heute 15:210–213
Kähler G, Sold M, Fischer K, Post S, Enderle M (2007) Selective fluid cushion in the submucosal layer by water jet. Advantage for endoscopic mucosal resection. Eur Surg Res 39:93–97
Sold GM, Grobholz R, Post S, Enderle MD, Kaehler G (2008) Submucosal cushioning with waterjet before endoscopic mucosal resection: which fluids are effective? Surg Endosc 22:443–447
Yamamoto H, Kawata H, Sunada K, Sasaki A, Nakazawa K, Miyata T, Sekine Y, Yano T, Satoh K, Ido K, Sugano K (2003) Successful en bloc resection of large superficial tumors in stomach and colon using sodium hyaluronate and small-caliber-tip transparent hood. Endoscopy 35:690–694
Oka S, Tanaka S, Kaneko I, Mouri R, Hirata M, Kawamura T, Yoshihara M, Chayama K (2006) Advantage of endoscopic submucosal dissection compared with EMR for early gastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc 64:877–883
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lingenfelder, T., Fischer, K., Sold, M.G. et al. Combination of water-jet dissection and needle-knife as a hybrid knife simplifies endoscopic submucosal dissection. Surg Endosc 23, 1531–1535 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-009-0433-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-009-0433-3