Abstract
Background and aims
Endoscopic augmentation of the esophagogastric junction (EGJ) with polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) has been reported in an experimental short-term study. We assessed whether endoscopic augmentation of the EGJ with PMMA is durable, safe, and efficacious after 6 months in mini-pigs.
Methods
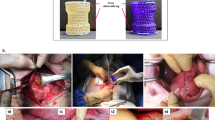
Ten mini-pigs were studied under anesthesia. After a pilot study in two animals, eight mini-pigs underwent lower esophageal sphincter (LES) manometry and gastrostomy with measurement of gastric yield volume (GYV) and gastric yield pressure (GYP). Endoscopic implantation of PMMA was performed aiming for the submucosa of the EGJ. Six months later, LES manometry and GYV and GYP measurements were repeated and animals were sacrificed, followed by microscopic analyses of the EGJ.
Results
Out of 32 implants (four per animal), 29 (91%) were identified as submucosal nodules postmortem. PMMA deposits were found at microscopic analysis in all animals and located as follows [mean (range)]: submucosa 61.5% (37.5–91%), muscularis propria 21.5% (0–58%), mucosa 11% (0–25%), and subserosa 6% (0–17%). Neither esophageal perforation nor death was observed. A significant increase in GYV (1,404 versus 905 ml; p = 0.02) and a borderline increase in GYP (8.1 versus 6.5 mmHg; p = 0.057) were detected 6 months later.
Conclusions
Endoscopic augmentation of the esophagogastric junction with PMMA was durable and had no complications after 6 months. However, the occurrence of implants in the subserosa requires technical refinement before use in clinical trials.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PMMA:
-
Polymethylmethacrylate
- EGJ:
-
Esophagogastric junction
- GERD:
-
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- LES:
-
Lower esophageal sphincter
- GYV:
-
Gastric yield volume
- GYP:
-
Gastric yield pressure
References
Dent J, El-Serag HB, Wallander MA, Johansson S (2005) Epidemiology of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review. Gut 54(5):710–717
Liker H, Hungin P, Wiklund I (2005) Managing gastroesophageal reflux disease in primary care: the patient perspective. J Am Board Fam Pract 18(5):393–400
Mokrowiecka A, Jurek K, Pinkowski D, Malecka-Panas E (2006) The comparison of Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQL) in patients with GERD, peptic ulcer disease and ulcerative colitis. Adv Med Sci 51:142–147
Shaheen NJ, Hansen RA, Morgan DR, Gangarosa LM, Ringel Y, Thiny MT, Russo MW, Sandler RS (2006) The burden of gastrointestinal and liver diseases, 2006. Am J Gastroenterol 101:2128–2138
Dominitz JA, Dire CA, Billingsley KG, Todd-Stenberg JA (2006) Complications and antireflux medication use after antireflux surgery. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 4(3):299–305
Falk GW, Fennerty MB, Rothstein RI (2006) AGA Institute technical review on the use of endoscopic therapy for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology 131(4):1315–1336
Harewood GC, Gostout CJ (2003) Cost analysis of endoscopic antireflux procedures: endoluminal plication vs radiofrequency coagulation vs. treatment with a proton pump inhibitor. Gastrointest Endosc 58(4):493–499
Deviere J, Costamagna G, Neuhaus H, Voderholzer W, Louis H, Tringali A, Marchese M, Fiedler T, rb-Esfahani P, Schumacher B (2005) Nonresorbable copolymer implantation for gastroesophageal reflux disease: a randomized sham-controlled multicenter trial. Gastroenterology 128(3):532–540
Fockens P, Bruno MJ, Gabbrielli A, Odegaard S, Hatlebakk J, Allescher HD, Rosch T, Rhodes M, Bastid C, Rey J, Boyer J, Muehldorffer S, van den HU, Costamagna G (2004) Endoscopic augmentation of the lower esophageal sphincter for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease: multicenter study of the Gatekeeper Reflux Repair System. Endoscopy 36(8):682–689
Hogan WJ (2006) Clinical trials evaluating endoscopic GERD treatments: is it time for a moratorium on the clinical use of these procedures? Am J Gastroenterol 101(3):437–439
Shaheen NJ (2005) Raising the bar in studies of endoscopic anti-reflux procedures. Gastroenterology 128(3):779–782
Noh KW, Loeb DS, Stockland A, Achem SR (2005) Pneumomediastinum following Enteryx injection for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol 100(3):723–726
Tintillier M, Chaput A, Kirch L, Martinet JP, Pochet JM, Cuvelier C (2004) Esophageal abscess complicating endoscopic treatment of refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease by Enteryx injection: a first case report. Am J Gastroenterol 99(9):1856–1858
Wong RF, Davis TV, Peterson KA (2005) Complications involving the mediastinum after injection of Enteryx for GERD. Gastrointest Endosc 61(6):753–756
Mason RJ, Hughes M, Lehman GA, Chiao G, Deviere J, Silverman DE, Demeester TR, Peters JH (2002) Endoscopic augmentation of the cardia with a biocompatible injectable polymer (Enteryx) in a porcine model. Surg Endosc 16(3):386–391
Gabbrielli A, Cipolloni L, Pandolfi M, Emerenziani S, Cicala M, Costamagna G (2004) GatekeeperTM reflux repair system: results of two years follow-up. Gastrointest Endosc 59:AB244
Lemperle G, Romano JJ, Busso M (2003) Soft tissue augmentation with artecoll: 10-year history, indications, techniques, and complications. Dermatol Surg 29(6):573–587
Lemperle G, Morhenn V, Charrier U (2003) Human histology and persistence of various injectable filler substances for soft tissue augmentation. Aesthetic Plast Surg 27(5):354–366
Feretis C, Benakis P, Dimopoulos C, Dailianas A, Filalithis P, Stamou KM, Manouras A, Apostolidis N (2001) Endoscopic implantation of Plexiglas (PMMA) microspheres for the treatment of GERD. Gastrointest Endosc 53(4):423–426
Freitag CP, Kruel CR, Duarte ME, Sanches PR, Thome PR, Fornari F, Driemeier D, Teixeira F, Mollerke RO, Callegari-Jacques SM, Barros SG (2008) Endoscopic implantation of polymethylmethacrylate augments the gastroesophageal antireflux barrier: a short-term study in a porcine model. Surg Endosc. doi:10.1007/s00464-008-0145-0
Martinez-Serna T, Davis RE, Mason R, Perdikis G, Filipi CJ, Lehman G, Nigro J, Watson P (2000) Endoscopic valvuloplasty for GERD. Gastrointest Endosc 52(5):663–670
Utley DS, Kim M, Vierra MA, Triadafilopoulos G (2000) Augmentation of lower esophageal sphincter pressure and gastric yield pressure after radiofrequency energy delivery to the gastroesophageal junction: a porcine model. Gastrointest Endosc 52(1):81–86
Duarte ME, Freitag CPF, Kruel CRP, Sanches PRS, Thomé PRO, Konlós F, Callegari-Jacques SM, Fornari F, Barros SGS (2007) Validation of a swine model for gastroesophageal reflux: reproducibility of gastric yield volume (GYV) and gastric yield pressure (GYP). Gastrointest Endosc 65:AB137
Ryou M, Thompson CC (2008) Endoscopic therapy for GERD: does it have a future? Curr Gastroenterol Rep 10(3):215–221
Schwartz MP, Smout AJ (2007) Review article: the endoscopic treatment of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 26(Suppl 2):1–6
Lemperle G, Ott H, Charrier U, Hecker J, Lemperle M (1991) PMMA microspheres for intradermal implantation: Part I. Animal research. Ann Plast Surg 26(1):57–63
Peters JH, Silverman DE, Stein A (2003) Lower esophageal sphincter injection of a biocompatible polymer: accuracy of implantation assessed by esophagectomy. Surg Endosc 17(4):547–550
Morhenn VB, Lemperle G, Gallo RL (2002) Phagocytosis of different particulate dermal filler substances by human macrophages and skin cells. Dermatol Surg 28(6):484–490
Lemperle G, Morhenn VB, Pestonjamasp V, Gallo RL (2004) Migration studies and histology of injectable microspheres of different sizes in mice. Plast Reconstr Surg 113(5):1380–1390
Donahue PE, Carvalho PJ, Davis PE, Shen YJ, Miidla I, Bombeck CT, Nyhus LM (1990) Endoscopic sclerosis of the gastric cardia for prevention of experimental gastroesophageal reflux. Gastrointest Endosc 36(3):253–256
Cicala M, Gabbrielli A, Emerenziani S, Guarino MP, Ribolsi M, Caviglia R, Costamagna G (2005) Effect of endoscopic augmentation of the lower oesophageal sphincter (Gatekeeper reflux repair system) on intraoesophageal dynamic characteristics of acid reflux. Gut 54(2):183–186
Kahrilas PJ, Lee TJ (2005) Gatekeeper reflux repair system; a mechanistic hypothesis. Gut 54(2):179–180
Acknowledgements
Study supported by CAPES (Ministry of Education and Culture), CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico—Ministry of Science and Technology), and FIPE (Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre), Brazil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fornari, F., Freitag, C.P.F., Duarte, M.E.S. et al. Endoscopic augmentation of the esophagogastric junction with polymethylmethacrylate: durability, safety, and efficacy after 6 months in mini-pigs. Surg Endosc 23, 2430–2437 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-009-0376-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-009-0376-8