Abstract
Background
Increased intra-abdominal pressure (IAP) (pneumoperitoneum) during laparoscopic surgery may result in adverse effects on kidney function. The mechanisms underlying this phenomenon have not been fully determined.
Objective
The present study was designed to: (1) investigate the effects of incremental increases in IAP on renal function in normal rats and (2) evaluate whether the nitric oxide (NO) system is involved in renal dysfunction characterizing pneumoperitoneum.
Methods
Male rats were organized into two groups. The first group was subjected to IAP of 0 (baseline), 7 or 14 mmHg, over 1 h for each pressure, followed by a deflation period of 60 min (recovery). Two additional groups were pretreated with: (1) non-depressor dose of nitroglycerine (NTG) and (2) nitro-L-arginine-methylester (L-NAME), an NO synthase inhibitor, before applying 14 mmHg for 1 h. Urine flow rate (V), Na+ excretion (UNaV), glomerular filtration rate (GFR), renal plasma flow (RPF), and blood pressure were determined throughout the experiments.
Results
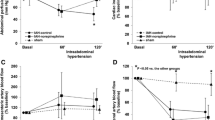
There were no significant changes in V, UNaV, GFR, and RPF during 7 mmHg insufflation. However, significant reductions in these parameters were observed during 14 mmHg: V from 8.49 ± 0.92 to 6.12 ± 0.54 μl/min, UNaV from 1.29 ± 0.28 to 0.39 ± 0.09 μEq/min, and FENa from 0.37 ± 0.11 to 0.27 ± 0.04%. These alterations in excretory functions were associated with a considerable decline in GFR from 1.85 ± 0.09 to 0.88 ± 0.09 ml/min, p < 0.05, (−46.3 ± 5.2% from baseline) and RPF from 8.66 ± 0.62 to 4.33 ± 0.49 ml/min, p < 0.05, (−51.93 ± 5.24% from baseline), without a significant change in mean arterial blood pressure (MAP). When the animals were pretreated with NTG, the adverse effects of pneumoperitoneum on V, UNaV, GFR, and RPF were substantially improved, suggesting that NO system plays a beneficial counter-regulatory role during laparoscopy. In line with this notion, pretreatment with L-NAME remarkably aggravated pneumoperitoneum-induced renal hypoperfusion and dysfunction.
Conclusion
Decreased renal perfusion and function are induced by IAP pressure of 14 mmHg. These adverse effects are probably related to interference with the NO system, and could be partially ameliorated by pretreatment with NTG.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abassi ZA, Brodsky S, Karram T, Dobkin I, Winaver J, Hoffman A (2001) Temporal changes in natriuretic and antinatriuretic systems after closure of a large arteriovenous fistula. Cardiovasc Res 3:567–576
Abassi ZA, Gurbanov K, Mulroney SE, Potlog C, Opgenorth TJ, Hoffman A, Haramati A, Winaver J (1997) Impaired nitric oxide-mediated renal vasodilation in rats with experimental heart failure: role of angiotensin II. Circulation 10:3655–3664
Bachmann S, Mundel P (1994) Nitric oxide in the kidney: synthesis, localization and function. Am J Kidney Dis 24:112–129
Bolte SL, Chin LT, Moon TD, D’Alessandro AM, Nakada SY, Becker YT, Hedican SP (2006) Maintaining urine production and early allograft function during laparoscopic donor nephrectomy. Urology 68(4):747–750
Borba MR, Lopes RI, Carmona M, Neto BM, Nahas SC, Pereira PR (2005) Effects of enalaprilat on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and on renal function during CO2 pneumoperitoneum. J Endourol 8:1026–1031
Brodsky S, Gurbanov K, Abassi Z, Hoffman A, Ruffolo RR Jr, Feuerstein GZ, Winaver J (1998) Effects of eprosartan on renal function and cardiac hypertrophy in rats with experimental heart failure. Hypertension 32:746–752
Chang DT, Kirsch AJ, Sawczuk IS (1994) Oliguria during laparoscopic surgery. J Endourol 8:349–352
Chiu AW, Azadzoi KM, Hatzichristou DG, Siroky MB, Krane RJ, Babayan RK (1994) Effects of intra-abdominal pressure on renal tissue perfusion during laparoscopy. J Endourol 8:99–103
Chiu AW, Chang LS, Birkett DH, Babayan RK (1996) A porcine model for renal hemodynamic study during laparoscopy. J Surg Res 60:61–68
Cisek LJ, Gobet RM, Peters CA (1998) Pneumoperitoneum produces reversible renal dysfunction in animals with normal and chronically reduced renal function. J Endourol 2:95–100
Demyttenaere SV, Feldman LS, Bergman S, Gholoum S, Moriello C, Unikowsky B, Fraser S, Carli F, Fried GM (2006) Does aggressive hydration reverse the effects of pneumoperitoneum on renal perfusion? Surg Endosc 2:274–280
Demyttenaere S, Feldman LS, Fried GM (2007) Effect of pneumoperitoneum on renal perfusion and function: a systematic review. Surg Endosc 21:152–160
Dunn MD, McDougall EM (2000) Renal physiology. Laparoscopic considerations. Urol Clin North Am 4:609–614
Dzau VJ (1987) Renal and circulatory mechanisms in congestive heart failure. Kidney Int 31:1402–1415
Gudmundsson FF, Viste A, Myking OL, Bostad L, Grong K, Svanes K (2003) Role of angiotensin II under prolonged increased intraabdominal pressure (IAP) in pigs. Surg Endosc 17:1092–1097
Hamilton BD, Chow GK, Inman SR, Stowe NT, Winfield HN (1998) Increased intra-abdominal pressure during pneumoperitoneum stimulates endothelin release in a canine model. J Endourol 12:193–197
Harman PK, Kron IL, McLachlan HD, Freedlender AE, Nolan SP (1982) Elevated intra-abdominal pressure and renal function. Ann Surg 196:594–597
Hashikura Y, Kawasaki S, Munakata Y, Hashimoto S, Hayashi K, Makuuchi M (1994) Effects of peritoneal insufflation on hepatic and renal blood flow. Surg Endosc 7:759–761
Hazebroek EJ, de Bruin RW, Bouvy ND, Marquet RL, Bonthuis F, Bajema IM, Hayes DP, Ijzermans JN, Bonjer HJ (2003) Long-term impact of pneumoperitoneum used for laparoscopic donor nephrectomy on renal function and histomorphology in donor and recipient rats. Ann Surg 237:351–357
Ho HS, Saunders CJ, Gunther RA, Wolfe BM (1995) Effector of hemodynamics during laparoscopy: CO2 absorption or intra-abdominal pressure? J Surg Res 59:497–503
Imig JD, Roman RJ (1992) Nitric oxide modulates vascular tone in preglomerular arterioles. Hypertension 19:770–774
Joris JL, Chiche JD, Canivet JL, Jacquet NJ, Legros JJ, Lamy ML (1998) Hemodynamic changes induced by laparoscopy and their endocrine correlates: effects of clonidine. J Am Coll Cardiol 32:1389–1396
Junghans T, Bohm B, Grundel K, Schwenk W, Muller JM (1997) Does pneumoperitoneum with different gases, body positions, and intraperitoneal pressures influence renal and hepatic blood flow? Surgery 121:206–211
Kirsch AJ, Hensle TW, Chang DT, Kayton ML, Olsson CA, Sawczuk IS (1994) Renal effects of CO2 insufflation: oliguria and acute renal dysfunction in a rat pneumoperitoneum model. Urology 43:453–459
Koivusalo AM, Kellokumpu I, Scheinin M, Tikkanen I, Halme L, Lindgren L (1996) Randomized comparison of the neuroendocrine response to laparoscopic cholecystectomy using either conventional or abdominal wall lift techniques [see comments]. Br J Surg 83:1532–1536
Kone BC (2004) Nitric oxide synthesis in the kidney: isoforms, biosynthesis, and functions in health. Semin Nephrol. 4:299–315
Lindberg F, Bergqvist D, Bjorck M, Rasmussen I (2003) Renal hemodynamics during carbon dioxide pneumoperitoneum: an experimental study in pigs. Surg Endosc 17:480–484
Lindström P, Wadström J, Ollerstam A, Johnsson C, Persson AE (2003) Effects of increased intra-abdominal pressure and volume expansion on renal function in the rat. Nephrol Dial Transplant 18:2269–2277
London ET, Ho HS, Neuhaus AM, Wolfe BM, Rudich SM, Perez RV (2000) Effect of intravascular volume expansion on renal function during prolonged CO2 pneumoperitoneum. Ann Surg 231:195–201
Mattson DL, Roman RJ, Cowley AW Jr (1992) Role of nitric oxide in renal papillary blood flow and sodium excretion. Hypertension 19:766–769
McDougall EM, Monk TG, Wolf JS Jr, Hicks M, Clayman RV, Gardner S, Humphrey PA, Sharp T, Martin K (1996) The effect of prolonged pneumoperitoneum on renal function in an animal model. J Am Coll Surg 182:317–328
Moncada S, Palmer RM, Higgs EA (1991) Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev 43:109–142
Nguyen NT, Perez RV, Fleming N, Rivers R, Wolfe BM (2002) Effect of prolonged pneumoperitoneum on intraoperative urine output during laparoscopic gastric bypass, J Am Coll Surg 195:476–483
Nishio S, Takeda H, Yokoyama M (1999) Changes in urinary output during laparoscopic adrenalectomy. BJU Int 83:944–947
Nogueira JM, Cangro CB, Fink JC, Schweitzer E, Wiland A, Klassen DK, Gardner J, Flowers J, Jacobs S, Cho E, Philosophe B, Bartlett ST, Weir MR (1999) A comparison of recipient renal outcomes with laparoscopic versus open live donor nephrectomy. Transplantation 67:722–728
Odeberg S, Ljungqvist O, Svenberg T, Sollevi A (1998) Lack of neurohumoral response to pneumoperitoneum for laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Surg Endosc 12:1217–1223
Ratner LE, Hiller J, Sroka M, Weber R, Sikorsky I, Montgomery RA, Kavoussi LR (1997) Laparoscopic live donor nephrectomy removes disincentives to live donation. Transplant Proc 29:3402–3403
Richards WO, Scovill W, Shin B, Reed W (1983) Acute renal failure associated with increased intra-abdominal pressure. Ann Surg 197:183–187
Shuto K, Kitano S, Yoshida T, Bandoh T, Mitarai Y, Kobayashi M (1995) Hemodynamic and arterial blood gas changes during carbon dioxide and helium pneumoperitoneum in pigs. Surg Endosc 11:1173–1178
Smith HW, Finkelstein N, Aliminosa L (1945) The renal clearances of substituted hippuric acid derivatives and other aromatic acids in dogs and men. J Clin Invest 24:388–404
Yilmaz S, Koken T, Tokyol C, Kahraman A, Akbulut G, Serteser M, Polat C, Gokce C, Gokce O (2003) Can preconditioning reduce laparoscopy-induced tissue injury? Surg Endosc 17:819–824
Zacherl J, Thein E, Stangl M, Feussner H, Bock S, Mittlbock M, Erhardt W, Siewert JR (2003) The influence of periarterial papaverine application on intraoperative renal function and blood flow during laparoscopic donor nephrectomy in a pig model. Surg Endosc 17:1231–1236
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Mrs. Hoda Awad, and Aviva Kaballa for their expert technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Bishara Bishara and Tony Karram contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bishara, B., Karram, T., Khatib, S. et al. Impact of pneumoperitoneum on renal perfusion and excretory function: beneficial effects of nitroglycerine. Surg Endosc 23, 568–576 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-008-9881-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-008-9881-4