Abstract
Introduction
Plasma vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels are elevated for 2–4 weeks after minimally invasive colorectal resection (MICR). VEGF induces wound and tumor angiogenesis by binding to endothelial cell (EC)-bound VEGF-receptor 1 (VEGFR1) and VEGFR2. Soluble receptors (sVEGFR1, sVEGFR2) sequester VEGF in the blood and decrease VEGF’s proangiogenic effect. The importance of the MICR-related VEGF changes depends on the effect of surgical procedures on sVEGFR1 and sVEGFR2; this study assessed levels of these proteins after MICR for benign indications.
Methods
Blood samples were taken (n = 39) preoperatively (preop) and on postoperative days (POD) 1 and 3; in most cases a fourth sample was drawn between POD 7 and 30. sVEGFR1 and sVEGFR2 levels were measured via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), which detects free and VEGF bound soluble receptor. Late samples were bundled into POD 7–13 and POD 14–30 time points. Results are reported as mean and standard deviation. The data was assessed with paired-samples t-test.
Results
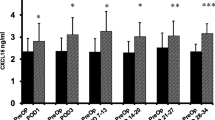
Preop, mean plasma sVEGFR2 level (9,203.7 ± 1,934.3 pg/ml) was significantly higher than the sVEGFR1 value (132.5 ± 126.2 pg/ml). sVEGFR2 levels were significantly lower on POD 1 (6,957.8 ± 1,947.7 pg/ml,) and POD 3 (7,085.6 ± 2,000.2 pg/ml), whereas sVEGFR1 levels were significantly higher on POD 1 (220.0 ± 132.8 pg/ml) and POD 3 (182.7 ± 102.1 pg/ml) versus preop results. No differences were found on POD 7–13 or 14–30.
Conclusions
sVEGFR2 values decreased and sVEGFR1 levels increased early after MICR; due to its much higher baseline, the sVEGFR2 changes dominate. The net result is less VEGF bound to soluble receptor and more free plasma VEGF.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belizon A, Balik E, Feingold DL, Bessler M, Arnell TD, Forde KA, Horst PK, Jain S, Cekic V, Kirman I, Whelan RL (2006) Major abdominal surgery increases plasma levels of vascular endothelial growth factor: open more so than minimally invasive methods. Ann Surg 244(5):792–798
Belizon A, Balik E, Horst P, Feingold D, Arnell T, Azarani T, Cekic V, Skitt R, Kumara S, Whelan RL (2008) Persistent elevation of plasma vascular endothelial growth factor levels during the first month after minimally invasive colorectal resection. Surg Endosc 22(2):287–297
Hicklin DJ, Ellis LM (2005) Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol 23(5):1011–1027
Ferrara N, Davis-Smyth T (1997) The biology of vascular endothelial growth factor [Review]. Endocr Rev 18:4–25
Hanahan D, Folkman J (1996) Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis [Review]. Cell 86:353–364
Jelkmann W (2001) Pitfalls in the measurement of circulating vascular endothelial growth factor. Clin Chem 47(4):617–623
Neufeld G, Cohen T, Gengrinovitch S, Poltorak Z (1999) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptors [Review]. FASEB J 13:9–22
Grad S, Ertel W, Keel M, Infanger M, Vonderschmitt DJ, Maly FE (1998) Strongly enhanced serum levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) after polytrauma and burn. Clin Chem Lab Med 36(6):379–383
Bottomley MJ, Webb NJ, Watson CJ, Holt L, Bukhari M, Denton J, Freemont AJ, Brenchley PE (2000) Placenta growth factor (PlGF) induces vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) secretion from mononuclear cells and is co-expressed with VEGF in synovial fluid. Clin Exp Immunol 119(1):182–188
Seko Y, Imai Y, Suzuki S, Kamijukkoku S, Hayasaki K, Sakomura Y, Tobe K, Kadowaki T, Maekawa H, Takahashi N, Yazaki Y (1997) Serum levels of vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with acute myocardial infarction undergoing reperfusion therapy. Clin Sci (Lond) 92(5):453–454
Shoab SS, Scurr JH, Coleridge-Smith PD (1998) Increased plasma vascular endothelial growth factor among patients with chronic venous disease. J Vasc Surg 28(3):535–540
Solovey A, Gui L, Ramakrishnan S, Steinberg MH, Hebbel RP (1999) Sickle cell anemia as a possible state of enhanced anti-apoptotic tone: survival effect of vascular endothelial growth factor on circulating and unanchored endothelial cells. Blood 93(11):3824–3830
Terai M, Yasukawa K, Narumoto S, Tateno S, Oana S, Kohno Y (1999) Vascular endothelial growth factor in acute Kawasaki disease. Am J Cardiol 83(3):337–339
Rak J, Mitsuhashi Y, Sheehan C, Tamir A, Viloria-Petit A, Filmus J, Mansour SJ, Ahn NG, Kerbel RS (2000) Oncogenes and tumor angiogenesis: differential modes of vascular endothelial growth factor up-regulation in ras-transformed epithelial cells and fibroblasts. Cancer Res 60:490–498
Rak J, Yu JL, Kerbel RS, Coomber BL (2002) What do oncogenic mutations have to do with angiogenesis/vascular dependence of tumors. Cancer Res 62:1931–1934
Brown LF, Yeo KT, Berse B, Yeo TK, Senger DR, Dvorak HF, van de Water L (1992) Expression of vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) by epidermal keratinocytes during wound healing. J Exp Med 176(5):1375–1379
Detmar M, Yeo KT, Nagy JA, Van de Water L, Brown LF, Berse B, Elicker BM, Ledbetter S, Dvorak HF (1995) Keratinocyte-derived vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) is a potent mitogen for dermal microvascular endothelial cells. J Invest Dermatol 105(1):44–50
Karayiannakis AJ, Zbar A, Polychronidis A, Simopoulos C (2003) Serum and drainage fluid vascular endothelial growth factor levels in early surgical wounds. Eur Surg Res 35(6):492–496
Hormbrey E, Han C, Roberts A et al (2003) The relationship of human wound vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) after breast cancer surgery to circulating VEGF and angiogenesis. Clin Cancer Res 9(12):4332–4339
Yamaguchi T, Bando H, Mori T, Takahashi K, Matsumoto H, Yasutome M, Weich H, Toi M (2007) Overexpression of soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 in colorectal cancer: association with progression and prognosis. Cancer Sci 98(3):405–410
Matsumoto T, Claesson-Welsh L (2001) VEGF receptor signal transduction. Sci STKE 112:RE21
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J (2003) The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med 9:669–676
Toi M, Bando H, Ogawa T, Muta M, Hornig C, Weich HA (2002) Significance of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)/soluble VEGF receptor-1 relationship in breast cancer. Int J Cancer 98(1):14–18
Yamaguchi T, Bando H, Mori T, Takahashi K, Matsumoto H, Yasutome M, Weich H, Toi M (2007) Overexpression of soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 in colorectal cancer: Association with progression and prognosis. Cancer Sci 98(3):405–410
Hu Q, Dey AL, Yang Y, Shen Y, Jilani IB, Estey EH, Kantarjian HM, Giles FJ, Albitar M (2004) Soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1, and not receptor 2, is an independent prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes. Cancer 100(9):1884–1891
Gill M, Dias S, Hattori K, Rivera ML, Hicklin D, Witte L, Girardi L, Yurt R, Himel H, Rafii S (2001) Vascular trauma induces rapid but transient mobilization of VEGFR2(+)AC133(+) endothelial precursor cells. Circ Res 88(2):167–174
Shantha Kumara HMC, Hoffman A, Kim IY, Feingold D, Dujovny N, Kallady M, Luchtefeld M, Whelan RL (2008) Colorectal resection, both open and laparoscopic-assisted, in patients with benign indications is associated with proangiogenic changes in plasma angiopoietin 1 and 2 levels. Surg Endosc [Epup ahead of print]. doi:10.1007/s00464-008-0132-5
Choi SH, Park EY, Jung HL, Shim JW, Kim DS, Park MS, Shim JY (2006) Serum vascular endothelial growth factor in pediatric patients with community-acquired pneumonia and pleural effusion. J Korean Med Sci 21(4):608–613
Lange M, Hamahata A, Enkhbaatar P, Esechie A, Connelly R, Nakano Y, Jonkam C, Cox RA, Traber LD, Herndon DN, Traber DL (2008) Assessment of vascular permeability in an ovine model of acute lung injury and pneumonia-induced Pseudomonas aeruginosa sepsis. Crit Care Med 36(4):1284–1289
Maitre B, Boussat S, Jean D, Gouge M, Brochard L, Housset B, Adnot S, Delclaux C (2001) Vascular endothelial growth factor synthesis in the acute phase of experimental and clinical lung injury. Eur Respir J 18(1):100–106
Shapiro NI, Yano K, Okada H, Fischer C, Howell M, Spokes KC, Ngo L, Angus DC, Aird WC (2008) A prospective, observational study of soluble FLT-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor in sepsis. Shock 29(4):452–457
Tsokos M, Pufe T, Paulsen F, Anders S, Mentlein R (2003) Pulmonary expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in sepsis. Arch Pathol Lab Med 127(3):331–335
Shantha Kumara HMC, Kirman I, Feingold D, Cekic V, Nasar A, Arnell T, Balik E, Hoffman A, Baxter R, Conte S, Whelan RL (2008) Perioperative GMCSF limits the pro-angiogenic plasma protein changes associated with colorectal cancer resection. Eur J Surg Oncol [Epup ahead of print]. doi:10.1016/j.ejso.2008.07.012
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shantha Kumara, H.M.C., Cabot, J.C., Hoffman, A. et al. Minimally invasive colon resection is associated with a transient increase in plasma sVEGFR1 levels and a decrease in sVEGFR2 levels during the early postoperative period. Surg Endosc 23, 694–699 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-008-0323-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-008-0323-0