Abstract
Background
This study aimed to evaluate the authors’ initial experience with antegrade stenting. It focused on the success rate, time required for stent insertion, possible complications, and relative solutions in the first 44 procedures.
Methods
Between March 2005 and April 2008, 44 patients (21 women and 23 men) with a mean age of 33 years (range, 17–59 years) underwent transperitoneal laparoscopic Anderson–Hynes pyeloplasty in the authors’ department. Antegrade stenting was attempted for all the patients. The time required for stent insertion was recorded as the time from cannula insertion to the correct positioning of the stent in the pelvis. A 4.8-Fr, 26-cm stent was the stent of choice for the first four cases. Then the 6-Fr, 26-cm stent was adopted for all the remaining patients except for one, for whom a 6-Fr, 28-cm stent was adopted.
Results
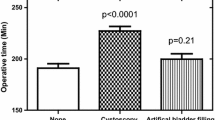
The mean operative time was 197 min (median, 180 min; range, 150–390 min). No conversions to open surgery were required. The stent was positioned correctly in the bladder at the end of the antegrade procedure in 97.7% of the patients without the need for a postoperative X-ray in 95% of the cases. The mean time required for antegrade insertion of the stent was 7 min 30 s (median, 6 min 13 s; range, 3 min 40 s to 22 min 30 s). In the final 12 procedures, the time for stent insertion was constantly reduced to a mean of 4 min 10 s (median, 4 min; range, 3 min 40 s to 7 min). Neither intraoperative nor postoperative complications related to antegrade stent positioning were observed.
Conclusion
Our data confirm the antegrade procedure to be an easy-to-learn, safe, and reliable stenting technique, with an overall mean time of 7 min 30 s required for insertion, and with a mean time of 4 min 10 s required for insertion in the final 12 procedures. It obviates the problem of having the stent in the renal pelvis during dissection and suturing and of repositioning the patient onto the flank for the laparoscopic procedure.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Notley RG, Beaugie JM (1973) The long-term follow-up of Anderson–Hynes pyeloplasty for hydronephrosis. Br J Urol 45:464–467
Lowe FC, Marshall FF (1984) Ureteropelvic junction obstruction in adults. Urology 23:331–335
Davenport K, Minervini A, Timoney AG, Keeley FX Jr (2005) Our experience with retroperitoneal and transperitoneal laparoscopic pyeloplasty for pelvi-ureteric junction obstruction. Eur Urol 48:973–977
Schuessler WW, Grune MT, Tecuanhuey LV, Preminger GM (1993) Laparoscopic dismembered pyeloplasty. J Urol 150:1795–1799
Calvert RC, Morsy MM, Zelhof B, Rhodes M, Burgess NA (2008) Comparison of laparoscopic and open pyeloplasty in 100 patients with pelvi-ureteric junction obstruction. Surg Endosc 22:411–414. doi:10.1007/s00464-007-9436-0
Bauer JJ, Bishoff JT, Moore RG, Chen RN, Iverson AJ, Kavoussi LR (1999) Laparoscopic versus open pyeloplasty: assessment of objective and subjective outcome. J Urol 162:692–695
Klingler HC, Remzi M, Janetschek G, Kratzik C, Marberger MJ (2003) Comparison of open versus laparoscopic pyeloplasty techniques in treatment of uretero-pelvic junction obstruction. Eur Urol 44:340–345
Turk IA, Davis JW, Winkelmann B, Deger S, Richter F, Fabrizio MD, Schönberger B, Jordan GH, Loening SA (2002) Laparoscopic dismembered pyeloplasty: the method of choice in the presence of an enlarged renal pelvis and crossing vessels. Eur Urol 42:268–275
Jarrett TW, Chan DY, Charambura TC, Fugita O, Kavoussi LR (2002) Laparoscopic pyeloplasty: the first 100 cases. J Urol 167:1253–1256
El-Shazly MA, Moon DA, Eden CG (2007) Laparoscopic pyeloplasty: status and review of literature. J Endourol 21:673–678
Arumainayagam N, Minervini A, Davenport K, Kumar V, Masieri L, Serni S, Carini M, Timoney AG, Keeley FX Jr (2008) Antegrade versus retrograde stenting in laparoscopic pyeloplasty. J Endourol 22:671–674
Rodrigues H, Rodrigues P, Ruela M, Bernabé A, Buogo G (2002) Dismembered laparoscopic pyeloplasty with antegrade placement or ureteral stent: simplification of the technique. Int Braz J Urol 28:439–445
Chandrasekharam VVSS (2005) Is retrograde stenting more reliable than antegrade stenting for pyeloplasty in infants and children? Urology 66:1301–1304
Mandhani A, Goel S, Bhandari M (2004) Is antegrade stenting superior to retrograde stenting in laparoscopic pyeloplasty? J Urol 171:1440–1442
Nouira Y, Horchani A (2004) How to insert a double J stent in laparoscopic retroperitoneal dismembered pyeloplasty: a new technique. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 14:306–308
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minervini, A., Siena, G., Masieri, L. et al. Antegrade stenting in laparoscopic pyeloplasty: feasibility of the technique and time required for stent insertion. Surg Endosc 23, 1831–1834 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-008-0272-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-008-0272-7