Abstract
Introduction
Nissen fundoplication has been performed laparoscopically for over 15 years, being associated with shorter hospital stay and fewer complications than conventional open surgery with good long-term outcomes. Day-case laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication (LNF) is rarely performed in the UK and most series in the literature report length of stay >2 days.
Methods
The objective of this study was to examine the safety and efficacy of day-case LNF. The clinical records of all patients undergoing LNF under the care of three surgeons in a district general hospital (DGH) during a 5-year period (January 2003 to December 2007) were reviewed to examine length of stay, complications, length of procedure, grade of operating surgeon and symptoms on follow-up.
Results
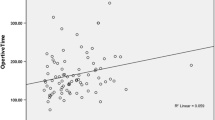
One hundred thirteen day-case LNFs were recorded in this series. Day-case LNF patients had median age of 45 years (range 20–68 years, 65% (64.6%) male) and 98% were American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) grade I or II. Twenty-one cases (19%) were performed by higher surgical trainees. Median operative time was 54 minnutes (range 25–120 min). Only one perioperative complication (port-site bleed) occurred, treated without prolonging length of stay. The proportion of all LNF performed as day cases increased from 8% to 52% during the study period. Median operative time has significantly reduced from the first 20 consecutive LNF cases to the latest 20 cases [65 min (range 40–120 min) versus 48 min (range 25–72 min); p = 0.037]. At follow-up (median 7 weeks, range 2–31 weeks) 82% of patients had improvement in all presenting symptoms. Eight patients had postoperative complications [wound infection (n = 2), persistent regurgitation requiring laparoscopic division of a gastric band adhesion (n = 1), dysphagia (n = 5 with two patients requiring redo partial fundoplication and one patient requiring dilatation) and there were no conversions to open surgery.
Conclusion
Day-case LNF is safe and effective for treating selected patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) in a DGH. The proportion of day-case LNFs is increasing in our unit. Half of the LNFs in a DGH can be done as day cases. Experience is associated with a significant reduction in operative time.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Locke GR, Talley NH, Fett SL, Zinsmeister AR, Melton LJ (1997) Prevalence and clinical spectrum of Gastro-esophagial reflux: a population based study in Olmsted County. Gastroenterology 112(5):1448–56
Nissen VR (1956) Eine einfache Operation zur Beeinflussung der Refluxoesophagitis. Schw Med Wochenschr 86:590–592
Donahue PE, Larson GM, Stewardson RH, Bombeck CT (1977) Floppy Nissen fundoplication. Rev Surg 34:223–224
DeMeester TR, Bonavina L, Albertucci M (1986) Nissen fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease: evaluation of primary repair on 100 consecutive patients. Ann Surg 204:9–20
Dallemange B, Weerts JM, Jehaes C, Markiewicz S, Lombard R (1991) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: preliminary report. Surg Laparosc Endosc 1:138–143
Geagea T (1991) Laparoscopic Nissen’s fundoplication: preliminary report on ten cases. Surg Endosc 5:170–173
Hinder RA, Filipi CJ, Wetscher GJ, Neary P, DeMeester TR, Perkins G (1994) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication is an effective treatment for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Ann Surg 220:472–483
Hinder RA (1994) Laparoscopic surgery: cost credentialing, training, safety and legal issues. Int Surg 79:215–216
Collard JM, DeGheldere CA, DeKock M, Otte JB, Kestens PJ (1994) Laparoscopic antireflux surgery. What is real progress? Ann Sur 220:146–154
Coster DD, Bower WH, Wilson V, Butler DA, Locker SC, Brebrick RT (1995) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication—a curative, safe and cost effective procedure for complicated gastroesophagial reflux disease. Surg Laparosc Endosc 5:111–117
Perdikis G, Hinder RA, Werscher GJ (1996) Nissen fundoplication for gastroesophagial reflux disease: laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication—technique and results. Dis Esophagus 9:272–277
Watson DI, Devitt PG, Jamieson GG (1999) The changing face of treatment for hiatus hernia and gastro-oesophageal reflux. Gut 45:791–792
Bammer T, Hinder RA, Klaus A, Klingler PJ (2001) Five- to Eight- year outcome of first laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. J Gastrointest Surg 5:42–48
Lafullarde T, Watson DI, Jamieson GG, Myers JC, Game PA, Devitt PG (2001) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: five-year results and beyond. Arch Surg 136:180–184
Fenton-Lee DD, Riach E, Cooke TG (1995) Day surgery and gastroenterology. Gut 36:324–326
Milford MA, Pallichta (1997) Ambulators laparoscopic fundoplication. Surg Endosc 11:1150–1152
Mjåland O, Ræder JC, Aaseboe V, Trondsen E, Buanea T (1997) Out patient laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Br J Surg 84:958–961
Ng R, Mullin EJ, Maddern GJ (2005) Systematic review of day-case laparoscopic Nissen fudoplication. ANZ J Surg 75:160–164
Cohn JC, Klingler PJ, Hinder RA (1997) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication as an ambulatory surgery centre procedure. Todays Surg Nurse 19:27–30
Narain PK, Moss JM, DeMaria EJ (2000) Feasibility of 23-hour hospitalization after laparoscopic fundoplication. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 10:5–11
Ray S (2003) Result of 310 consecutive patients undergoing laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication as hospital outpatients or at free-standing surgery centre. Surg Endosc 17:378–380
Finley CR, McKernan JB (2001) Laparoscopic antireflux surgery at an outpatient surgery centre. Surg Endosc 15:823–826
Atwood SEA, Lundell L, Ell C, Galmiche J-P, Hatlebakk J, Fiocca R, Lind T, Eklund S, Junghard O (2008) Standardisation of surgical technique in antireflux surgery: the LOTUS trial experience. World J Surg, (in press)
Bailey ME, Garrett WV, Nisar A, Boyle NH, Slater GH (2003) Day-case laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Br J Surg 90:560–562
Victorzon M, Tolonen P, Vuorialho T (2006) Laparoscopic floppy Nissen fundoplication for gastrooesophageal reflux disease is feasible as a day-case. Scand J Surg 95:162–165
Trondsen E, Mjåland O, Ræder JC, Buanes T (2000) Day-case laparoscopic fundoplication for gastro-oespohageal reflux disease. Br J Surg 87(12):1708–1711
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jensen, C.D., Gilliam, A.D., Horgan, L.F. et al. Day-case laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Surg Endosc 23, 1745–1749 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-008-0178-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-008-0178-4