Abstract
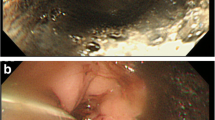
Esophago-gastric necrosis is a surgical emergency associated with high morbidity and mortality. We report a laparoscopic transhiatal esophago-gastrectomy performed on a 43-year-old male, presenting two hours after hydrochloric acid ingestion. A gastroscopy showed several oral mucosal ulcers, a significant edema of the pharynx and larynx, a necrosis of the middle and lower esophagus and of the gastric fundus and antrum. A conservative strategy with intensive care observation was initially followed. After a change of clinical signs, chest-abdominal computed tomography was realized and a pneumoperitoneum with free fluid in the left subphrenic space and bilateral pleural effusions was in evidence. A laparoscopic exploration was proposed to the patient, and confirmed the presence of free peritoneal fluid and necrosis with perforation of the upper part of the stomach. A laparoscopic total gastrectomy with subtotal esophagectomy was performed; the procedure finished with an esophagostomy on the left side of the neck and a laparoscopic feeding jejunostomy (video). Total operative time was 235 minutes. After six months a digestive reconstruction with esophagocoloplasty by laparotomy and cervicotomy was easily realized thanks to the advantages (few adhesions, bloodless, and simple colic mobilization) of the previous minimally invasive surgery.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mamede RC, de Mello Filho FV (2001) Ingestion of caustic substances and its complications. Sao Paulo Med J 119:10–15
Arevalo-Silva C, Eliashar R, Wohlgelernter J, Elidan J, Gross M (2006) Ingestion of caustic substances: a 15 years experience. Laryngoscope 116:1422–1426
Ertekin C, Alimoglu O, Akyildiz H, Guloglu R, Taviloglu K (2004) The results of caustic ingestions. Hepatogastroenterology 51:1397–1400
Baskin D, Urganci N, Abbasoglu L, Alkim C, Yalcin M, Karadag C, Sever N (2004) A standardized protocol for the acute management of corrosive ingestion in children. Pediatr Surg Int 20:824–828
Havanond C (2003) Clinical features of corrosive ingestion. J Med Assoc Thai 86:918–924
Poley JW, Steyerberg EW, Kuipers EJ, Dees J, Hartmans R, Tilanus HW, Siersema PD (2004) Ingestion of acid and alkaline agents: outcome and prognostic value of early upper endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 60: 372–377
Sarfati E, Gossot D, Assens P, Celerier M (1987) Management of caustic ingestion in adults. Br J Surg 74:146–148
Schaffer SB, Hebert AF (2000) Caustic ingestion. J La State Med Soc 152:590–596
Zargar SA, Kochhar R, Nagi B, Mehta S, Mehta SK (1992) Ingestion of strong corrosive alkalis: spectrum of injury to upper gastrointestinal tract and natural history. Am J Gastroenterol 87:337–341
Zargar SA, Kochhar R, Nagi B, Mehta S, Mehta SK (1989) Ingestion of corrosive acids. Spectrum of injury to upper gastrointestinal tract and natural history. Gastroenterology 97:702–707
Deneuville M, Andreassian B, Charbonnier JY, Assens P, Dubost CL, Celerier M (1984) Complications tracheo-bronchiques graves des ingestions de caustiques chez l’adulte. J Chir 121:1–6
Gupta NM, Gupta R (2004) Transhiatal esophageal resection for corrosive injury. Ann Surg 239:359–363
De Wilde RL (1991) Goodbye to late bowel obstruction after appendectomy. Lancet 338:1012
Lundor P, Thorburn J, Hahlin M, Kallfelt B, Lindblom B (1991) Laparoscopic surgery in ectopic pregnancy. A randomized trial versus laparotomy. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 70:343–348
Ribet M, Chambon JP, Pruvot FR (1990) Oesophagectomy for severe corrosive injuries: is it always legitimate? Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 4: 347–350
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper received an award as one of the six best original contributions to the EAES video session at the 14th International EAES Congress in Berlin (Germany), 13–16 September 2006.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dapri, G., Himpens, J., Mouchart, A. et al. Laparoscopic transhiatal esophago-gastrectomy after corrosive injury. Surg Endosc 21, 2322–2325 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-007-9559-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-007-9559-3