Abstract
Background
Atrial fibrillation is the most common form of serious arrhythmia in humans. The therapeutic options offered are medical, surgical, and interventional. The surgical approach is justified in cases of atrial fibrillation already subjected to cardiac surgery for an associated organic heart disease such as a valvular or ischemic disease. A minimally invasive surgical approach is needed to extend the possibility of surgical treatment to patients with lone atrial fibrillation and those who cannot be treated by interventional procedures. This study aimed to use sheep as an experimental model in developing a minimally invasive surgical procedure for chronic atrial fibrillation therapy in humans.
Methods
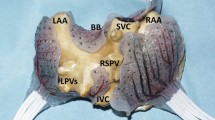
The investigation was conducted with 20 animals using a video-assisted thoracoscopic approach, in which a flexible microwave energy ablating probe was positioned on the epicardial surface encircling the pulmonary veins.
Results
In 10 of the 20 animals, it was possible to encircle the pulmonary veins using the thoracoscopic approach in less than 3 h without major complications.
Conclusion
The epicardial ablation procedure using the thoracoscopic approach is feasible, safe, and reproducible.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zipes DP (1997) Atrial fibrillation: from cell to bedside. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 8: 927–938
Levy S, Breithardt G, Campbell RWF, Camm AJ, Daubert JC, Allessie M, Aliot E, Capucci A, Cosio F, Crijns H, Jordaens L, Hauer RNW, Lombardi F, Luderliz B on behalf of the Working Group on Arrhythmias of the European Society of Cardiology (1998) Atrial fibrillation: current knowledge and recommendations for management. Eur Heart J 19: 1294–1320
Kannel WB, Wolf PA, Benjamin EJ, Levy D (1998) Prevalence, incidence, prognosis, and predisposing conditions for atrial fibrillation: population-based estimates. Am J Cardiol 82: 2N–9N
Fuster V, Rydén LE, Gibbons RJ, Antman EM, Klein WW (2001) ACC/AHA/ESC guidelines for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: executive summary. J Am Coll Cardiol 38: 1–35
Cox JL, Schuessler RB, D’Agostino HJ, Stone CM, Chang BC, Cain ME, Corr PB, Boineau JP (1991) The surgical treatment of atrial fibrillation: III. Development of a definitive surgical procedure. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 101: 569–583
Cox JL (1991) The surgical treatment of atrial fibrillation. IV. Surgical technique. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 101: 584–592
Cox JL, Boineau JP, Schuessler RB, Jaquiss RDB, Lappas DG (1995) Modification of the maze procedure for atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation. I. Rationale and surgical results. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 110: 473–484
Cox JL, Jaquiss RDB, Schuessler RB, Boineau JP (1995) Modification of the maze procedure for atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation. II. Surgical technique of the maze III procedure. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 110: 485–495
Cox JL, Ad N, Palazzo T, Fitzpatrick S, Suyderhoud JP, De Grood KW, Pirovic EA, Lou HC, Duvall WZ, Kim YD (2000) Current status of the maze procedure for the treatment of atrial fibrillation. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 12: 15–19
Raanani E, Albage A, David TE, Yau TM, Armstrong S (2001) The efficacy of the Cox/maze procedure combined with mitral valve surgery: a matched control study. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 19: 438–442
Manasse E, Colombo P, Roncalli M, Gallotti R (2000) Myocardial acute and chronic histological modifications induced by cryoablation. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 17: 339–340
Gaita F, Gallotti R, Calò L, Manasse E, Riccardi R, Garberoglio L, Nicolini F, Scaglione M, Di Donna P, Capone D, Franciosi G (2000) Limited posterior left atrial cryoablation in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation undergoing valvular heart surgery. J Am Coll Cardiol 36: 159–166
Williams MR, Stewart JR, Bolling SF, Freeman S, Anderson JT, Argenziano M, Smith CR, Oz MC (2001) Surgical treatment of atrial fibrillation using radiofrequency energy. Ann Thorac Surg 71: 1939–1944
Williams MR, Knaut M, Bérubé D, Oz MC (2002) Application of microwave energy in cardiac tissue ablation: from in vitro analyses to clinical use. Ann Thorac Surg 74: 1500–1505
Benussi S, Pappone C, Nascimbene S, Oreto G, Caldarola A, Stefano PL, Casati V, Alfieri O (2000) A simple way to treat atrial fibrillation during mitral valve surgery: the epicardial radiofrequency approach. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 17: 524–529
Melo J, Adragao P, Neves J, Ferreira M, Timoteo A, Santiago T, Ribeiras R, Canada M (2000) Endocardial and epicardial radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of atrial fibrillation with a new intraoperative device. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 18: 182–186
Mazzitelli D, Park CH, Park KY, Benetti FJ, Lange R (2002) Epicardial ablation of atrial fibrillation on the beating heart without cardiopulmonary bypass. Ann Thorac Surg 73: 320–321
Manasse E, Ghiselli S, Barbone A, Citterio E, Ornaghi D, Gallotti R (2002, January 25) A new surgical technique for chronic atrial fibrillation. Abstract No. 66. Cardiothoracic Techniques and Technologies VIII, Miami
Chen SA, Tai CT, Tsai CF, Hsieh MH, Ding YA, Chang MS (2000) Radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation initiated by pulmonary vein ectopic beats. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 11: 218–227
Haissaguerre M, Jais P, Shah DC, Garrigue S, Takahashi A, Lavergne T, Hocini M, Peng JT, Rodaut R, Clementy J (2000) Electrophysiological end point for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation initiated from multiple pulmonary venous foci. Circulation 101: 1409–1417
Sohn RH, Schiller NB (2000) Left upper pulmonary vein stenosis 2 months after radiofrequency catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. Circulation 101: e154–e155
Mangrum JM, Mounsey JP, Kok LC, DiMarco JP, Haines DE (2002) Intracardiac echocardiography-guided, anatomically based radiofrequency ablation of focal atrial fibrillation originating from pulmonary veins. J Am Coll Cardiol 39: 1964–1972
Ng FS, Camm AJ (2002) Catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Clin Cardiol 25: 384–394
Hindricks G, Kottkamp H (2002) Potential benefits, risks, and complications of catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: more questions than answers. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 13: 768–769
Chen SA (2002) Catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: fact and controversy. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 13: 1074–1075
Gaita F, Riccardi R, Gallotti R (2002) Surgical approaches to atrial fibrillation. Cardiac Electrophysiol Rev 6: 401–405
Viola N, Williams MR, Oz MC, Ad N (2002) The technology in use for the surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 14: 198–205
Manasse E, Colombo PG, Barbone A, Braidotti P, Bulfamante G, Roncalli M, Gallotti R (2003, April) Clinical histopathology and ultrastructural analysis of myocardium following microwave energy ablation. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 23: 573–577
Saltman AE, Rosenthal LS, Francalancia NA, Lahey SJ (2003) A completely endoscopic approach to microwave ablation for atrial fibrillation. Heart Surg Forum 6: E38–E41
Bolotin G, Kypson AP, Nifong LW, Chitwood WR Jr (2004) Robotically assisted left atrial fibrillation ablation and mitral valve repair through a right mini-thoracotomy. Ann Thorac Surg 78: e63–e64
Bisleri G, Manzato A, Argenziano M, Vigilance DW, Muneretto C (2005) Thoracoscopic epicardial pulmonary vein ablation for lone paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Europace 7: 145–148
Wolf RK, Schneeberger EW, Osterday R, Miller D, Merril W, Flege JB Jr, Gillinov AM (2005) Video-assisted bilateral pulmonary vein isolation and left atrial appendage exclusion for atrial fibrillation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 130: 797–802
Gillinov AM, Wolf RK (2005) Surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 48: 169–177
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Addis, A., Vanosi, G., Manasse, E. et al. An experimental sheep model used to develop an ablation procedure for chronic atrial fibrillation. Surg Endosc 21, 1626–1630 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-007-9213-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-007-9213-0