Abstract
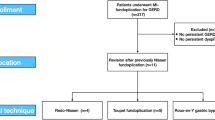
Background: The role of surgery is debated for children with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), particularly when they show atypical symptoms. This study was designed to evaluate the safety and outcome of laparoscopic Nissen-Rossetti fundoplication performed in a selected population of children with gastroesophageal reflux and atypical supraesophageal symtpoms. Methods: This prospective study included 595 patients younger than 14 years with GERD who reported recurrent respiratory symptoms and had no benefit from standard medical treatment. Surgery was performed for 48 patients with anatomic anomalies, life-threatening events, or respiratory complications after ineffective medical treatment. The subjective and objective outcomes were evaluated. Results: No major intraoperative complications were experienced, and there was no recurrence of gastroesophageal reflux during a postoperative follow-up period of 12 months. The parents’ final subjective evaluation of the outcomes 12 months after surgery was positive in 44 cases and negative in 4 cases. Conclusions: Children with difficult-to-treat chronic respiratory symptoms must be evaluated for GERD, even if the need for surgery is low (8%), because complete eradication of reflux is mandatory. Radical treatment of GERD allows the pulmonologist to perform correct respiratory treatment and to prevent the development chronic and life-threatening complications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
GO Andze ML Brandt D St Vil AL Bensoussan H Blanchard (1991) ArticleTitleDiagnosis and treatment of gastroesophageal reflux in 500 children with respiratory symptoms: the value of pH-monitoring. J Pediatr Surg 26 295–300 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By6B3s3gslc%3D Occurrence Handle2030475
A Arana B Bagucka B Hauser B Hegar D Urbain L Kaufman Y Vandenplas (2001) ArticleTitlepH monitoring in the distal and proximal esophagus in symptomatic infants. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 32 259–264 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00005176-200103000-00005 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXjvVagur4%3D Occurrence Handle11345172
B Bagucka H Badriul K Vandemaele E Troch Y Vandenplas (2000) ArticleTitleNormal ranges of continuous pH monitoring in the proximal esophagus. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 31 244–247 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3Mris1Sjtw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10997366
RB Colletti DL Christie SR Orenstein (1995) ArticleTitleIndications for pediatric esophageal pH monitoring. Statement of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition (NASPGN). J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 21 253–262 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymC3Mnis1Q%3D Occurrence Handle8523208
D Collier (1997) ArticleTitleDetection of aspiration: scintigraphic techniques. Am J Med 24 135s–137s Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0002-9343(97)00339-2
J DeCaestecker (1997) ArticleTitleMedical therapy from supraesophageal complications of gastroesophageal reflux. Am J Med 103 138s–143s Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0002-9343(97)00340-9 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c%2FotlWjsQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9422640
TR DeMeester L Bonavina C Lascone (1990) ArticleTitleChronic respiratory symptoms and occult gastroesophageal reflux: a prospective study and results of surgical therapy. Ann Surg 211 337–345 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BC2sbivFY%3D Occurrence Handle2310240
I Eizaguirre JA Tovar (1992) ArticleTitlePredicting preoperatively the outcome of respiratory symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux. J Pediatr Surg 27 848–851 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2A2cbhvV0%3D Occurrence Handle1640331
SK Field GAJ Gelfand SD McFadden (1999) ArticleTitleThe effects of antireflux surgery on asthmatics with gastroesophageal reflux. Chest 116 766–774 Occurrence Handle10.1378/chest.116.3.766 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1MvitVSgtg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10492285
SK Field LR Sutherland (1998) ArticleTitleDoes medical antireflux therapy improve asthma in asthmatics with gastroesophageal reflux? A critical review of the literature. Chest 114 275–283 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXltVSnsrc%3D Occurrence Handle9674479
EW Fonkalsrud ME Ament (1996) ArticleTitleGastroesophageal reflux in children. Curr Probl Surg . 1–68
P Gorrotxategui Y Eizaguirre A Saenz de Ugarte (1995) ArticleTitleCharacteristics of continuous esophageal pH metering in infants with gastroesophageal reflux and apparent life-threatening events. Eur J Pediatr Surg 5 136–138 Occurrence Handle7547796
LM Halpern SG Jolley WP Tunell (1991) ArticleTitleThe mean duration of gastroesophageal reflux during sleep as an indicator of respiratory symptoms from gastroesophageal reflux in children. J Pediatr Surg 26 686–690 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2D2crisVE%3D Occurrence Handle1941458
SG Jolley (1995) ArticleTitleGastroesophageal reflux disease as a cause for emesis in infants. Semin Pediatr Surg 4 176–189 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymD38jgvFc%3D Occurrence Handle7582888
SG Jolley CT Halpern CE Sterling BH Feldman (1990) ArticleTitleThe relationship of respiratory complications from gastroesophageal reflux to prematurity in infants. J Pediatr Surg 25 755–757 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BA3sbjt1Q%3D Occurrence Handle2380892
SG Jolley JJ Herbst DG Johnson (1981) ArticleTitleEsophageal pH monitoring during sleep identifies children with respiratory symptoms. Gastroenterology 80 1501–1505 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:Bi6C1cbns1Q%3D Occurrence Handle7227775
M Krishnamoorthy A Mintz T Liem H Applebaum (1994) ArticleTitleDiagnosis and treatment of respiratory symptoms of initially unsuspected gastroesophageal reflux in infants. Am Surg 60 783–785 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqD3s%2FmsFQ%3D Occurrence Handle7944042
B LeLuyer O Mouterde P LeRoux JP Chabralle E Mollet CH de Menibus (1986) ArticleTitleReflux gastroesophagien et affections respiratoires aigues et chroniques du nourrison et de I’enfant. Ann Pediatr 33 509–518 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BimB1MvhtVM%3D
G Mattioli G Montobbio A Pini Prato P Repetto C Carlini V Gentilino M Castagnetti S Leggio M Della Rocca Z Kotitsa V Jasonni (2003) ArticleTitleAnesthesiologic aspects of laparoscopic fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux in children with chronic respiratory and gastroenterological symptoms Surg Endosc 17 559–566 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00464-002-9077-2 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3s7nvFGrsA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle12582762
G Mattioli P Repetto C Carlini A Pini Prato C Mazzola S Leggio G Montobbio P Gandullia A Barabino A Cagnazzo O Sacco V Jasonni (2002) ArticleTitleLaparoscopic vs open approach for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux in children. Surg Endosc 16 750–752 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00464-001-9040-7 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD383lvVaisg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11997815
G Mattioli P Repetto S Leggio M Castagnetti V Jasonni (2002) ArticleTitleLaparoscopic Nissen–Rossetti fundoplication in children. Semin Laparosc Surg 9 153–162 Occurrence Handle10.1053/slas.2002.126995 Occurrence Handle12407523
SR Orenstein (1997) ArticleTitleInfantile reflux: different from adult reflux. Am J Med 103 114s–119s Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c%2FotlSqug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9422635
MG Patti M Arcerito A Tamburini U Diener CV Feo B Safadi P Fisichella LW Way (2000) ArticleTitleEffect of laparoscopic fundoplication on gastroesophageal reflux disease–induced respiratory symptoms. J Gastrointest Surg 4 143–149 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1091-255X(00)80050-5 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c7jvFKktQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10675237
A Ponticelli ML Capitanucci BD lacobelli S Nappo (1995) ArticleTitlepHmetric parameters potentially predictive of asthmatic symptomatology: clinical and statistical research. Pediatr Med Chir 17 513–514 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymB2svltVU%3D Occurrence Handle8668585
SS Rothemberg D Bratton G Larsen (1997) ArticleTitleLaparoscopic fundoplication to enhance pulmonary function in children with severe reactive airway disease and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Surg Endosc 11 1088–1090 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004649900536 Occurrence Handle9348380
O Sacco B Fregonese M Silvestri F Sabatini G Mattioli GA Rossi (2000) ArticleTitleBronchoalveolar lavage and esophageal pH monitoring data in children with “difficult-to-treat respiratory symptoms. Pediatr Pulmonol 30 313–319 Occurrence Handle10.1002/1099-0496(200010)30:4<313::AID-PPUL7>3.0.CO;2-H Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M%2FmtFSltw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11015132
V Tolia (2002) ArticleTitleGastroesophageal reflux and supraesophageal complications: really true or ballyhoo? J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 34 278–280 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00005176-200203000-00009 Occurrence Handle11964951
Y Vandenplas (1997) ArticleTitleAsthma and gastroesophageal reflux. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 24 89–99 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00005176-199701000-00019 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiB2cjoslQ%3D Occurrence Handle9093993
R Veyrac P Buries H Collet (1986) ArticleTitleGastroesphageal scintigraphy and pH monitoring in asthmatic adults with gastroesophageal reflux. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 10 400–404 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BimB2srosFM%3D Occurrence Handle3732745
InstitutionalAuthorNameWorking Group of the ESPAN (1992) ArticleTitleA standardized protocol for the methodology of esophageal pH monitoring and interpretation of the data for diagnosis of GE reflux. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 14 467–471 Occurrence Handle1517953
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Anna Capurro for her English language support. They also thank Francesca Roncallo for her help in administrative support and computerized data collection during the study period.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mattioli, G., Sacco, O., Gentilino, V. et al. Outcome of laparoscopic Nissen–Rossetti fundoplication in children with gastroesophageal reflux disease and supraesophageal symptoms . Surg Endosc 18, 463–465 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-003-9108-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-003-9108-7