Abstract
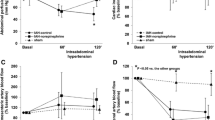
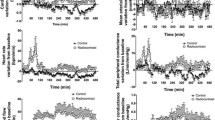
Background: The aim of the study was to investigate the effect of the angiotensin II receptor antagonist losartan on renal hemodynamics and diuresis in pigs with increased intraabdominal pressure (IAP). Methods: The IAP was maintained at 30 mmHg for 3 h by intraperitoneal instillation of Ringer’s solution. Ten animals were treated with losartan; another 10 animals served as controls. Renal blood flow, hormones in renal vein blood, and diuresis were measured. Results: In control animals, the renal vascular resistance increased renal blood flow remained constant, the blood concentration of aldosterone increased and the diuresis decreased during increased IAP. Losartan prevented the increase in vascular resistance and improved renal blood flow under increased IAP. It also prevented the rise in aldosterone concentration and increased the urine output to baseline level. Conclusion: Our results suggest that the renal vasoconstriction associated with increased IAP is due to increased production of angiotensin II. The oliguria associated with increased IAP is probably due, at least partly, to increased reabsorbtion of sodium and water in the renal tubuli caused by increased tissue concentration of aldosterone.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
J Bendahan CJ Coetzee C Papagianopoulos R Muller (1995) ArticleTitleAbdominal compartment syndrome. J Trauma 38 152–153 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqB28vjvVM%3D Occurrence Handle7745647
GL Bloomfield CR Blocher IF Fakhry DA Sica HJ Sugerman (1997) ArticleTitleElevated intra-abdominal pressure increases plasma renin activity and aldosterone levels. J Trauma 42 997–1005 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXkslCntLY%3D Occurrence Handle9210531
CB Caldwell JJ Ricotta (1987) ArticleTitleChanges in visceral blood flow with elevated intraabdominal pressure. J Surg Res 43 14–20
CB Caldwell JJ Ricotta (1986) ArticleTitleEvaluation of intra-abdominal pressure and renal hemodynamics. Curr Surg 43 495–498 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiiC3cvjs1Y%3D Occurrence Handle3802901
DJ Cullen JP Coyle R Teplick MC Long (1989) ArticleTitleCardiovascular, pulmonary, and renal effects of massively increased intra-abdominal pressure in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med 17 118–121 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiaC38%2FhsVM%3D Occurrence Handle2914444
JM Doty BH Saggi CR Blocher I Fakhry T Gehr D Sica HJ Sugerman (2000) ArticleTitleEffects of increased renal parenchymal pressure on renal function. J Trauma 48 874–877 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c3otFSgtA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10823530
JM Doty BH Saggi HJ Sugerman CR Blocher R Pin I Fakhry T Gehr DA Sica (1999) ArticleTitleEffect of increased renal venous pressure on renal function. J Trauma 47 1000–1003 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c%2FnsVagtA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10608524
FC Fan GB Schuessler RYZ Chen S Chien (1979) ArticleTitleDetermination of blood flow and shunting of 9- and 15-µm spheres in regional beds. Am J Physiol 237 H25–H33 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CSaB38bjtlM%3D Occurrence Handle464066
FF Gudmundsson H Gislason A Dicko A Horn A Viste K Grong K Svanes (2001) ArticleTitleEffects of prolonged intraabdominal pressue on gastrointestinal blood flow in pigs. Surg Endosc 15 854–860 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MrksFSiuw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11443466
FF Gudmundsson HG Gislason OL Myking A Viste K Grong K Svanes (2001) ArticleTitleHormonal changes related to decreased renal blood flow and low urine output under prolonged increased intra-abdominal pressure in pigs. Eur J Surg 168 178–186 Occurrence Handle10.1080/110241502320127801
ME Gunning JR Ingelfinger AJ King BM Brenner (1995) Vasoactive peptides and the kidney. BM Brenner FC Rector (Eds) The kidney WB Saunders Philadelphia 242–244
PK Harman IL Kron HD McLachlan AE Freedlender SP Nolan (1982) ArticleTitleElevated intra-abdominal pressure and renal function. Ann Surg 196 594–597 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiyD387ksV0%3D Occurrence Handle7125746
MA Heymann BD Payne JI Hoffman AM Rudolph (1977) ArticleTitleBlood flow measurements with radionuclide-labeled particles. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 20 55–79 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2sXkvFyht74%3D Occurrence Handle877305
SM Lankford D Plummer P Hellyer DD Christ SA Bai (1997) ArticleTitlePharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic relations of losartan and EXP3174 in a porcine animal model. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 30 583–590 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00005344-199711000-00008 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c%2FkslagsQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9388040
DA Maddox BM Brenner (1995) Glomerular ultrafiltration. BM Brenner FC Rector (Eds) The kidney WB Saunders Philadelphia 296–300
R Mo OL Myking P Lund-Johansen P Omvik (1994) ArticleTitleThe Bergen blood pressure study: inappropriately low levels of circulating atrial natriuretic peptide in offspring of hyper-tensive families. Blood Pressure 3 223–230 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXmt1OktLc%3D Occurrence Handle7661920
WO Richards W Scovill B Shin W Reed (1983) ArticleTitleAcute renal failure associated with increased intra-abdominal pressure. Ann Surg 197 183–187 Occurrence Handle6600601
BH Saggi HJ Sugerman RR Ivatury GL Bloomfield (1998) ArticleTitleAbdominal compartment syndrome. J Trauma 45 597–609 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1cvit1Wkug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9751558
M Schein DH Wittman CC Aprahamian RE Condon (1995) ArticleTitleThe abdominal compartment syndrome: the physiological and clinical consequences of elevated intra-abdominal pressure. J Am Coll Surg 180 745–753 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqB1M7lsFU%3D Occurrence Handle7773495
JH Smith RC Merrell TA Raffin (1985) ArticleTitleReversal of postoperative anuria by decompressive celiotomy. Arch Intern Med 145 553–554 Occurrence Handle10.1001/archinte.145.3.553 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiqC2cfis1w%3D Occurrence Handle3156569
BJ Winer (1971) Statistical principles in experimental design., 2nd ed. McGraw-Hill New York 529–532
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gudmundsson, F., Viste, A., Myking, O. et al. Role of angiotensin II under prolonged increased intraabdominal pressure (IAP) in pigs . Surg Endosc 17, 1092–1097 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-002-9123-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-002-9123-0