Abstract
Feeding difficulties and dysphagia are common in cerebral palsy (CP) and can lead to deficiencies of development and aspiration pneumonia; a leading cause of death in CP. Motor learning interventions have shown positive results in other clinical areas and may be beneficial for this population. This systematic review appraises research that addresses the question: are motor learning-based interventions more effective than compensatory strategies alone in treating dysphagia in infants with, or at risk of, CP?. Systematic searches were conducted in nine electronic databases. All levels of evidence, with at least one infant between 37 weeks post-menstrual age and 12 months corrected age who were at risk of, or diagnosed with CP, implemented interventions which aimed to improve oropharyngeal function for feeding, and aligned with at least two motor learning principles, were included. Studies were appraised by two independent reviewers using the Cho & Bero Instrument and GRADE. One historical case–control study and four case series met inclusion criteria. All involved a combination of motor learning interventions and compensatory strategies, which do not traditionally align with motor learning principles. All studies reported improvements in oral feeding outcomes, however, only three reported statistical analysis. The best available evidence collectively demonstrated a very weak positive effect for motor learning-based interventions for feeding difficulties in infants with, or at risk of, CP.


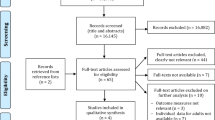
From Moher et al. [41]
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosenbaum P, Paneth N, Leviton A, Goldstein M, Bax M, Damiano D, Dan B, Jacobsson B. A report: the definition and classification of cerebral palsy April 2006. Dev Med Child Neurol Suppl. 2007;109:8–14.
Oskoui M, Coutinho F, Dykeman J, Jette N, Pringsheim T. An update on the prevalence of cerebral palsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2013;55:509–19.
McIntyre S, Morgan C, Walker K, Novak I. Cerebral palsy–don’t delay. Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2011;17:114–29.
Benfer KA, Weir KA, Bell KL, Ware RS, Davies PS, Boyd RN. Oropharyngeal dysphagia and gross motor skills in children with cerebral palsy. Pediatrics. 2013;131:e1553–62.
Calis EA, Veugelers R, Sheppard JJ, Tibboel D, Evenhuis HM, Penning C. Dysphagia in children with severe generalized cerebral palsy and intellectual disability. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2008;50:625–30.
Sullivan PB, Lambert B, Rose M, Ford-Adams M, Johnson A, Griffiths P. Prevalence and severity of feeding and nutritional problems in children with neurological impairment: Oxford Feeding Study. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2000;42:674–80.
Erkin G, Culha C, Ozel S, Kirbiyik EG. Feeding and gastrointestinal problems in children with cerebral palsy. Int J Rehabil Res. 2010;33:218–24.
Reid SM, Carlin JB, Reddihough DS. Survival of individuals with cerebral palsy born in Victoria, Australia, between 1970 and 2004. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2012;54:353–60.
Strauss D, Cable W, Shavelle R. Causes of excess mortality in cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1999;41:580–5.
Reilly S, Skuse D, Poblete X. Prevalence of feeding problems and oral motor dysfunction in children with cerebral palsy: a community survey. J Pediatr. 1996;129:877–82.
Novak I. Evidence-based diagnosis, health care, and rehabilitation for children with cerebral palsy. J Child Neurol. 2014;29:1141–56.
Arvedson J, Clark H, Lazarus C, Schooling T, Frymark T. Evidence-based systematic review: effects of oral motor interventions on feeding and swallowing in preterm infants. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2010;19:321–40.
Greene Z, O’Donnell CP, Walshe M. Oral stimulation for promoting oral feeding in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD009720.
Boiron M, Da Nobrega L, Roux S, Henrot A, Saliba E. Effects of oral stimulation and oral support on non-nutritive sucking and feeding performance in preterm infants. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2007;49:439–44.
Fucile S, Gisel EG, McFarland DH, Lau C. Oral and non-oral sensorimotor interventions enhance oral feeding performance in preterm infants. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2011;53:829–35.
Gillman A, Winkler R, Taylor NF. Implementing the free water protocol does not result in aspiration pneumonia in carefully selected patients with dysphagia: a systematic review. Dysphagia. 2017;32:345–61.
Logemann JA. Approaches to management of disordered swallowing. Baillieres Clin Gastroenterol. 1991;5:269–80.
Gosa M, Schooling T, Coleman J. Thickened liquids as a treatment for children with dysphagia and associated adverse effects. Infant, Child, Adolesc Nutr. 2011;3:344–50.
Robbins J, Butler SG, Daniels SK, Gross RD, Langmore S, Lazarus CL, Martin-Harris B, McCabe D, Mussan N, Rosenbek JC. Swallowing and dysphagia rehabilitation: translating principles of neural plasticity into clinically oriented evidence. J Speech Lang Hearing Res. 2008;51:S276–300.
Sheppard JJ. Using motor learning approaches for treating swallowing and feeding disorders: a review. Lang Speech Hearing Services in Schools. 2008;39:227–36.
Kleim JA, Jones TA. Principles of experience-dependent neural plasticity: implications for rehabilitation after brain damage. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2008;51:S225–39.
Morgan C, Novak I, Dale RC, Badawi N. Optimising motor learning in infants at high risk of cerebral palsy: a pilot study. BMC Pediatr. 2015;15:30.
Hoare B, Imms C, Carey L, Wasiak J. Constraint-induced movement therapy in the treatment of the upper limb in children with hemiplegic cerebral palsy: a Cochrane systematic review. Clin Rehabil. 2007;21:675–85.
Murray E, McCabe P, Ballard KJ. A comparison of two treatments for childhood apraxia of speech: methods and treatment protocol for a parallel group randomised control trial. Bmc Pediatr. 2012;12:112.
Geeganage C, Beavan J, Ellender S, Bath PM. Interventions for dysphagia and nutritional support in acute and subacute stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD000323.
Archambault M, Millen K, Gisel EG. Effect of bite size on eating development in normal children 6 months to 2 years of age. Phys Occup Ther Pediatr. 1991;10:29–47.
Chorna OD, Slaughter JC, Wang L, Stark AR, Maitre NL. A pacifier-activated music player with mother’s voice improves oral feeding in preterm infants. Pediatrics. 2014;133:462–8.
Morgan AT, Dodrill P, Ward EC. Interventions for oropharyngeal dysphagia in children with neurological impairment. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.
Higgins JP, Green S: Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions: John Wiley & Sons, 2011.
McIntyre S, Taitz D, Keogh J, Goldsmith S, Badawi N, Blair E. A systematic review of risk factors for cerebral palsy in children born at term in developed countries. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2013;55:499–508.
Cho MK, Bero LA. Instruments for assessing the quality of drug studies published in the medical literature. JAMA. 1994;272:101–4.
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Kunz R, Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P, Schunemann HJ, Group GW. GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ. 2008;336:924–6.
Jadcherla SR, Peng J, Moore R, Saavedra J, Shepherd E, Fernandez S, Erdman SH, DiLorenzo C. Impact of personalized feeding program in 100 NICU infants: pathophysiology-based approach for better outcomes. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2012;54:62–70.
Jadcherla SR, Stoner E, Gupta A, Bates DG, Fernandez S, Di Lorenzo C, Linscheid T. Evaluation and management of neonatal dysphagia: impact of pharyngoesophageal motility studies and multidisciplinary feeding strategy. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2009;48:186–92.
Rendon-Macias ME, Cruz-Perez LA, Mosco-Peralta MR, Saraiba-Russell MM, Levi-Tajfeld S, Morales-Lopez MG. Assessment of sensorial oral stimulation in infants with suck feeding disabilities. Indian J Pediatr. 1999;66:319–29.
Rice KL. Neuromuscular electrical stimulation in the early intervention population: a series of five case studies. Internet Journal of Allied Health Sciences and Practice. 2012;10:9.
Senez C, Guys JM, Mancini J, Paz Paredes A, Lena G, Choux M. Weaning children from tube to oral feeding. Childs Nerv Syst. 1996;12:590–4.
Hoffmann TC, Glasziou PP, Boutron I, Milne R, Perera R, Moher D, Altman DG, Barbour V, Macdonald H, Johnston M, Lamb SE, Dixon-Woods M, McCulloch P, Wyatt JC, Chan AW, Michie S: Better reporting of interventions: template for intervention description and replication (TIDieR) checklist and guide. Bmj-Brit Med J 348, 2014.
Arvedson J, Clark H, Lazarus C, Schooling T, Frymark T. The effects of oral-motor exercises on swallowing in children: an evidence-based systematic review. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2010;52:1000–13.
Snider L, Majnemer A, Darsaklis V. Feeding interventions for children with cerebral palsy: a review of the evidence. Phys Occup Ther Pediatr. 2011;31:58–77.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ (CR)-print. 2009;338(7716):332.
Acknowledgements
This systematic review was supported by Neurodisability Assist Trust, Cerebral Palsy Alliance and The Children’s Hospital at Westmead.
Funding
This systematic review and its dissemination was financially supported by Neurodisability Assist Trust, and in-kind by Cerebral Palsy Alliance and The Children’s Hospital at Westmead.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have stated that they had no interests to disclose which might be perceived as posing a conflict or bias. The authors are employed by Cerebral Palsy Alliance, Liverpool Hospital or The Children’s Hospital at Westmead, who provide services to children at risk of or diagnosed with cerebral palsy.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendix 1
The following electronic databases were searched:
Medline: 1946 – present
Cochrane Library:
Cinahl: from 1982 – present
EMBASE: from 1974 – present
Wiley Interscience
Web of Science
SpeechBITE
Google Scholar
The following keyword search strategy was used in all Medline, Cochrane Library, Cinahl, EMBASE, Wiley Interscience and Web of Science to find relevant studies from the listed electronic databases:
(cerebral pals* or neuromuscula* or neurolog* or neurophysi* or brain injur* or brain damage* or Encephalopath* or HIE or Periventricular leukomalacia or PVL or at risk or high risk or sick or ill or NICU or PICU or intensive care or disab* or handicap*) AND (neonat* or infant* or (baby not boomer) or babies or preemie* or premie* or newborn* or preterm* or pre term*) AND (chew* or masticat* or swallow* or deglut* or dysphagia* or (feed* NOT feedback) or suck*) AND (difficult* or disorder* or deficit* or impair*) OR (((aspirat* or penetrat*) not meconium) AND (chest or pulmonary or respirat* or airway* or pneumonia)) OR (silent aspiration) or ((oral motor) or (oro motor) or (oral muscula*) or (oro muscula*) or oromotor or oromuscula*) AND (NMES or neuromuscular electrical stimulation or oral appliance or sensorimotor or myofunctional or therap* or treat* or outcome* or effect* or interven* or exercis* or practi* or management or managing or rehab* or maneuvre* or alter* or modif* or compensat* or precaution* or train* or prevent* or minimis* or minimiz* or stimulat* or strengthen* or program* or behavio*r* or ((non-nutritive or nonnutritive or nutritive) and suck*) or pacifier* or nipple* or teat* or physio* or physical therap* or (speech and (patholog* or language patholog* or therap* or language patholog* “and language patholog*” or “and language therap*”)) or occupational therap*) NOT (allerg* or cleft* or adolescen* or ankyloglossia or (tongue tie*) or frenul*)
The following included databases have medical subject heading (MeSH) available and the following MeSH search strategies were conducted.
Medline: Dates From 1946–Present
-
1. Musculoskeletal diseases/or cerebral palsy/or exp brain injuries/or exp encephalitis/or hydrocephalus/or exp hypoxia, brain/or leukoencephalopathies/or exp movement disorders/or neuromuscular diseases/
-
3. Cerebral palsy.mp. or exp Cerebral Palsy/
-
19. Bottle feeding/or parenteral nutrition/
-
20. exp Breast Feeding/or exp Feeding Behavior/or exp Bottle Feeding/or exp “Feeding and Eating Disorders of Childhood”/or exp “Feeding and Eating Disorders”/or exp Feeding Methods/
-
21. Motor disorders/or exp neurocognitive disorders/or neurodevelopmental disorders/
-
23. swallow.mp. or exp Deglutition/or exp Swallows/or exp Deglutition Disorders/
-
24. Sucking Behavior/
-
25. exp breast feeding/or exp eating/or exp drinking/or exp mastication/or nutritional status/
-
26. exp Child Development/
-
27. exp mouth/or exp lip/
-
28. exp Pacifiers/
-
30. infant.mp. or Infant Equipment/or exp Infant Behavior/or exp Infant Food/or exp Infant/or exp Infant Nutritional Physiological Phenomena/or exp Infant, Newborn/or exp Infant, Newborn, Diseases/or exp Infant Care/or exp Infant, Postmature/or exp Infant Formula/or exp Infant Nutrition Disorders/or Infant Welfare/
-
32. exp Infant, Newborn, Diseases/or baby.mp. or exp Infant, Premature, Diseases/
-
38. exp “Early Intervention (Education)”/or exp Early Medical Intervention/
-
39. exp Exercise/or exp Exercise Therapy/or exp Exercise Movement Techniques/
-
40. exp Neuronal Plasticity/
-
41. Disease management/
-
42. exp Rehabilitation, Vocational/or exp Neurological Rehabilitation/or exp Rehabilitation/or exp Mouth Rehabilitation/
-
43. exp Behavior Therapy/
-
48. exp Pathology, Oral/
-
49. exp Tongue Diseases/or exp Tongue/
-
56. *Deglutition Disorders/or *Deglutition/or deglutition.mp.
-
60. exp Disabled Children/
-
62. exp Neuromuscular Diseases/
-
exp Muscular Diseases/
Cochrane Library
-
MeSH descriptor: [Stomatognathic System] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Mastication] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Deglutition] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: B51 explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Movement Disorders] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Pneumonia, Aspiration] this term only
-
MeSH descriptor: [Feeding and Eating Disorders of Childhood] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Feeding Behavior] 2 tree(s) exploded
-
MeSH descriptor: [Bottle Feeding] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Infant Nutritional Physiological Phenomena] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Developmental Disabilities] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Communication Disorders] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Learning Disorders] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Disabled Persons] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Motor Skills Disorders] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Disabled Children] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Sucking Behavior] this term only
-
MeSH descriptor: [Breast Feeding] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Bottle Feeding] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Pacifiers] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Cerebral Palsy] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Cerebral Hemorrhage] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [+ B51] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Hypoxia, Brain] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Fetal Hypoxia] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Hypoxia–Ischemia, Brain] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Anoxia] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Stroke] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Neuromuscular Diseases] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Neurologic Manifestations] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Gait Disorders, Neurologic] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Neuromuscular Manifestations] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Neurological Rehabilitation] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Motor Skills Disorders] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Motor Skills] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Brain Injuries] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Brain Diseases] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Critical Care] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Therapeutics] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Neuronal Plasticity] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Health Occupations] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Infant] explode all trees
-
MeSH descriptor: [Intensive Care, Neonatal] explode all trees
Cinahl: From 1982–Present
-
(MH “Infant + ”) OR (MH “Infant, Very Low Birth Weight”) OR (MH “Infant, Premature”) OR (MH “Infant Behavior”) OR (MH “Infant, High Risk”) OR (MH “Infant Nutritional Physiology + ”) OR (MH “Infant, Small for Gestational Age”) OR (MH “Infant, Large for Gestational Age”) OR (MH “Infant, Drug-Exposed”) OR (MH “Infant Food + ”) OR (MH “Infant Equipment + ”) OR (MH “Infant, Premature, Diseases + ”) OR (MH “Infant, Newborn, Diseases + ”) OR (MH “Infant, Newborn + ”) OR (MH “Infant, Low Birth Weight + ”) OR (MH “Infant Nutrition + ”) OR (MH “Infant Physiology”) OR (MH “Infant Nutrition Disorders”) OR (MH “Infant Feeding + ”) OR (MH “Infant Development Disorders”) OR (MH “Infant Development”) OR (MH “Infant Care + ”) OR (MH “Term Birth”) OR (MH “Neonatology”) OR (MH “Child, Hospitalized”)
-
(MH “Intensive Care, Neonatal + ”) OR (MH “Infant, Newborn, Diseases + ”) OR (MH “Infant Physiology”)
-
(MH “Occupational Therapists”)
-
(MH “Physical Therapists”)
-
(MH “Occupational Therapy + ”) OR (MH “Pediatric Occupational Therapy”)
-
(MH “Pediatric Physical Therapy”) OR (MH “Physical Therapy + ”)
-
(MH “Speech Therapy + ”) OR (MH “Speech-Language Pathology”) OR (MH “Speech-Language Pathologists”)
-
(MH “Aspiration Precautions (Iowa NIC)”)
-
(MH “Neuronal Plasticity”)
-
(MH “Pacifiers”) OR (MH “Infant Equipment + ”)
-
(MH “Swallowing Therapy (Iowa NIC)”)
-
(MH “Sensory Motor Integration”)
-
(MH “Electrical Stimulation, Neuromuscular”) OR (MH “Electrical Stimulation, Functional”) OR (MH “Electric Stimulation + ”) OR (MH “Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (Iowa NIC)”) OR (MH “Transcutaneous Electric Nerve Stimulation”) OR (MH “Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation”) OR (MH “Neuromuscular Facilitation”)
-
(MH “Child, Disabled”) OR (MH “Disabled + ”)
-
(MH “Brain Injuries + ”) OR (MH “Head Injuries + ”) OR (MH “Hypoxia–Ischemia, Brain + ”) OR (MH “Hypoxia, Brain + ”)
-
(MH “Diagnosis, Neurologic + ”) OR (MH “Neurology”) OR (MH “Motor Skills Disorders”) OR (MH “Neonatal Assessment + ”) OR (MH “Diagnosis, Brain + ”) OR (MH “Developmental Disabilities”)
-
(MH “Cerebral Palsy”) OR (MH “Hypoxia–Ischemia, Brain, Neonatal”) OR (MH “Hypoxia–Ischemia, Brain + ”) OR (MH “Cerebral Ischemia, Transient”) OR (MH “Hypoxia, Brain + ”) OR (MH “Stroke + ”)
-
(MH “Nonnutritive Sucking (Iowa NIC)”) OR (MH “Latching, Breastfeeding”) or (MH “Sucking Behavior”)
-
(MH “Aspiration”) OR (MH “Risk for Aspiration (NANDA)”) OR (MH “Pneumonia, Aspiration”) OR (MH “Aspiration Risk (Saba CCC)”) OR (MH “Feeding of Disabled”)
-
(MH “Deglutition”) OR (MH “Deglutition Disorders”) OR (MH “Impaired Swallowing (NANDA)”) OR (MH “Swallowing Impairment (Saba CCC)”) OR (MH “Orofacial Myofunctional Disorders”)
-
(MH “Mastication”) OR (MH “Stomatognathic System + ”)
EMBASE: From 1974–Present
exp musculoskeletal diseases/or exp cerebral palsy/or exp brain injury/or exp encephalitis/or exp hydrocephalus/or exp leukoencephalopathies/or exp movement disorders/or exp neuromuscular diseases/or exp hypoxia/or exp brain hypoxia/or exp newborn hypoxia/or exp disabled person/or exp handicapped child/or exp muscle disease/or exp child development/or exp motor dysfunction/or exp developmental disorder/or exp neurologic disease/or exp cerebrovascular accident/or exp brain hemorrhage/or exp brain infarction/or exp intensive care/or exp anoxia/
exp sucking/or exp swallowing/or exp dysphagia/or exp mouth gag/or exp mouth/or exp mastication/or exp aspiration pneumonia/or exp feeding/or exp feeding behavior/or exp feeding difficulty/or exp feeding disorder/or exp sham feeding/or exp eating/or exp food/or exp oropharynx/
exp breast feeding/or exp bottle feeding/or exp pacifier/or exp occupational therapy practice/or exp speech therapy/or exp occupational therapy/or exp therapy/or exp physiotherapy/or exp early childhood intervention/or exp early intervention/or exp dynamic exercise/or exp stretching exercise/or exp muscle exercise/or exp static exercise/or exp exercise/or exp motor performance/or exp task performance/or exp motor activity/or exp motor control/or exp muscle training/or exp rehabilitation/or exp speech rehabilitation/or exp neuromuscular electrical stimulation/or nerve cell plasticity/
exp infant/or exp baby/or exp newborn/or exp term birth/or exp prematurity/or exp low birth weight/or exp gestational age/
SpeechBITE all titles categorized under “paediatric feeding” Speech Pathology Practice Area were screened for inclusion.
Proquest Dissertations and Theses “cerebral palsy” AND dysphagia AND infant
Trove “cerebral palsy” AND dysphagia AND infant
Appendix 2
See (Table 4)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khamis, A., Novak, I., Morgan, C. et al. Motor Learning Feeding Interventions for Infants at Risk of Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic Review. Dysphagia 35, 1–17 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-019-10016-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-019-10016-x