Abstract
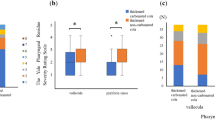
The ability of sour and sweet–sour mixtures to improve swallowing in 11 nursing home residents with neurogenic oropharyngeal dysphagia was investigated using fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing. Citric acid (2.7%) significantly reduced aspiration and penetration compared with water. Teaspoon delivery of liquids significantly reduced aspiration and penetration compared with natural cup drinking. Subjects tended to appropriately self-regulate the cup volume they consumed after the first trial. A significant increase in spontaneous dry swallows was observed after both taste stimuli. The mechanisms for improved swallowing due to citric acid are not understood but may be due to increased gustatory and trigeminal stimulation of acid to the brainstem in neurologically impaired subjects.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
P Linden A Siebens (1983) ArticleTitleDysphagia: predicting laryngeal penetration. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 64 281–284 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiyB3s%2FhslY%3D Occurrence Handle6860100
ML Huckabee CA Pelletier (1999) Management of Adult Neurogenic Dysphagia. Singular Publishing Group San Diego, CA
HM Finestone NC Foley MG Woodbury L Greene–Finestone (2001) ArticleTitleQuantifying fluid intake in dysphagic stroke patients: a preliminary comparison of oral and nonoral strategies. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 82 1744–1746 Occurrence Handle10.1053/apmr.2001.27379 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD38%2Flslansw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11733894
JA Logemann BR Pauloski L Colangelo C Lazarus M Fujiu PJ Kahrilas (1995) ArticleTitleEffects of a sour bolus on oropharyngeal swallowing measures in patients with neurogenic dysphagia. J Speech Hear Res 38 556–563 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqH3cvps10%3D Occurrence Handle7674647
LM Bartoshuk (1975) ArticleTitleTaste mixtures: Is mixture suppression related to compression? Physiol Behav 14 643–649 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CSqC2sjhvFw%3D Occurrence Handle1135328
HT Lawless (1986) ArticleTitleSensory interactions in mixtures. J Sens Stud 1 259–274
DW Curtis DA Stevens HT Lawless (1984) ArticleTitlePerceived intensity of the taste of sugar mixtures and acid mixtures. Chem Senses 9 107–120 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2cXltVyis7o%3D
HT Lawless (1977) ArticleTitleThe pleasantness of mixtures in taste and olfaction. Sens Processes 1 227–237 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CSiB3snhtVw%3D Occurrence Handle887952
Pelletier CA, Lawless HT, Horne J: Sweet-sour mixture suppression in older and young adults. Food Quality and Preference.
JHA Kroeze LM Bartoshuk (1985) ArticleTitleBitterness suppression as revealed by split-tongue taste stimulation in humans. Physiol Behav 35 779–783 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BimD1MvnsFI%3D Occurrence Handle4080842
HT Lawless (1979) ArticleTitleEvidence for neural inhibition in bittersweet taste mixtures. J Comp Physiol Psychol 93 538–547 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:Bi%2BD3cjgs1w%3D Occurrence Handle479396
JC Rosenbek J Robbins EB Roecker JL Coyle JL Wood (1996) ArticleTitleA penetration–aspiration scale. Dysphagia 11 93–98 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymA3sbgt1U%3D Occurrence Handle8721066
GA Pfaff (2000) Evaluation of the sourness of a ReaLemonTM/barium sulfate solution. Cornell University Ithaca, NY
RL McBride RL Johnson (1987) ArticleTitlePerception of sugar–acid mixtures in lemon juice drink. Food Sci Technol 22 399–408 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2sXmtFGgu7g%3D
H Diamont BSL Oakley R Zotterman (1965) ArticleTitleA comparison of neural and psychophysical responses to taste stimuli in man. Acta Physiol Scand 64 67–74 Occurrence Handle14348506
J Murray (1999) Manual of Dysphagia Assessment in Adults. Singular Publishing Group, Inc. San Diego, CA
JB Palmer NJ Rudin G Lara AW Crompton (1992) ArticleTitleCoordination of mastication and swallowing. Dysphagia 7 187–200 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyD2cfhvFw%3D Occurrence Handle1308667
A Miller D Bieger JL Conklin (1997) Functional controls of deglutition. AL Perlman K Schulze-Delrieu (Eds) Deglutition and its Disorders. San Diego, CA Singular Publishing Group 43–97
T Shinghai K Shimada (1976) ArticleTitleReflex swallowing elicited by water and chemical substances applied in the oral cavity, pharynx, and larynx of the rabbit. Jpn J Physiol 26 455–469 Occurrence Handle1011388
DV Smith MB Vogt (1997) The neural code and integrative processes of taste. GK Beauchamp LM Bartoshuk (Eds) Tasting and Smelling. Academic Press San Diego, CA 25–76
A Jean (2001) ArticleTitleBrain stem control of swallowing: neuronal network and cellular mechanisms. Physiol Rev 81 929–969 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M7oslGgtg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11274347
AJ Miller (1999) The neuroscientific principles of swallowing and dysphagia. Singular Publishing Group San Diego, CA
AT Storey (1968) ArticleTitleA functional analysis of sensory units innervating epiglottis and larynx. Exp Neurol 20 366–383 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CCeB1cngtV0%3D Occurrence Handle5656850
AT Storey P Johnson (1975) ArticleTitleLaryngeal water receptors initiating apnea in the lamb. Exp Neurol 47 42–55 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CSqC3s7itVE%3D Occurrence Handle1123009
J Prescott S Allen L Stephens (1993) ArticleTitleInteractions between oral chemical irritation, taste and temperature. Chem Senses 18 389–404 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXmt1aktrY%3D
Y Kajii T Shingai J Kitagawa Y Takahashi Y Taguchi T Noda Y Yamada (2002) ArticleTitleSour taste stimulation facilitates reflex swallowing from the pharynx and larynx in the rat. Physiol Behav 77 321–325 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xotl2ltrc%3D Occurrence Handle12419408
J O’Doherty ET Rolls S Francis R Bowtell F McGlone (2001) ArticleTitleRepresentation of pleasant and aversive taste in the human brain. J Neurophysiol 85 1315–1321 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M3hsFOgsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11248000
Z Bujas D Ajdukovic S Szabo D Mayer M Vodanovic (1995) ArticleTitleCentral processes in gustatory adaptation. Physiol Behav 57 875–880 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXltVahurs%3D Occurrence Handle7610138
HT Lawless (1982) ArticleTitleParadoxical adaptation to taste mixtures. Physiol Behav 25 149–152 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0031-9384(82)90379-1
HT Lawless (1982) ArticleTitleAdapting efficiency of salt–sucrose mixtures. Percept Psychophys 32 419–422 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiyC2czhvVA%3D Occurrence Handle7162942
SE Langmore (2001) Endoscopic Evaluation and Treatment of Swallowing Disorders. Thieme New York
B McCutcheon AM Tennissen (1989) ArticleTitleAcid and NaCl self-adaptation with microdrop stimulation of fungiform papillae. Physiol Behav 46 613–618 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BD1MbmsVY%3D Occurrence Handle2602485
Y Zotterman (1967) ArticleTitleThe neural mechanism of taste. Sensory Mechanisms: Progress in Brain Research 139–154
O’Mahony M: Taste: media and method. Dissertation, Bristol University, 1971
HH Chauncey RP Feller IL Shannon (1963) ArticleTitleEffect of acid solutions on human gustatory chemoreceptors as determined by parotid gland secretion rate. Proc Soc Exp Bio Med 112 917–923 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF3sXksFOns7g%3D
CV Hughes B Baum PC Fox Y Marmary CK Yeh BC Sonies (1987) ArticleTitleOral–pharyngeal dysphagia: a common sequela of salivary gland dysfunction. Dysphagia 1 173–177
TO Närhi JH Meurman A Ainamo JM Nevalainen KG Schmidt–Kaunisaho P Siukosaari (1992) ArticleTitleAssociation between salivary flow rate and the use of systemic medication among 76-, 81-, and 86-year-old inhabitants in Helsinki, Finland. J Dent Res 71 1875–1880 Occurrence Handle1452886
S Hamlet J Choi M Zormeier F Shamsa R Stachler J Muz L Jones (1996) ArticleTitleNormal adult swallowing of liquid and viscous material: scintigraphic data on bolus transit and oropharyngeal residues. Dysphagia 11 41–47 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymC2cfhvV0%3D Occurrence Handle8556878
Steele CM, Van Lieshout PHHM: Estimates of normal sip-size revisited. Tenth Annual Dysphagia Research Society Meeting, Albuquerque, NM, 2001
L Adnerhill O Ekberg ME Groher (1989) ArticleTitleDetermining normal bolus size for thin liquids. Dysphagia 4 1–3 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BA383otVE%3D Occurrence Handle2640173
SE Langmore K Schatz N Olson (1991) ArticleTitleEndoscopic and videofluoroscopic evaluations of swallowing and aspiration. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 100 678–681 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By6A3snlvFY%3D Occurrence Handle1872520
SB Leder CT Sasaki MI Burrell (1998) ArticleTitleFiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of dysphagia to identify silent aspiration. Dysphagia 13 19–21 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c%2FlsVWltA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9391224
C Wu T Hsiao J Chen Y Chang S Lee (1997) ArticleTitleEvaluation of swallowing safety with fiberoptic endoscope: Comparison with videofluoroscopic technique. Laryngoscope 107 396–401 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiB3sfltlE%3D Occurrence Handle9121321
GH McCullough JC Rosenbek J Robbins JL Coyle J Wood (1998) ArticleTitleOrdinality and intervality of a penetration–aspiration scale. J Med Speech Lang Pathol 6 65–72
N Colodny (2002) ArticleTitleInterjudge and intrajudge reliability in fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing (FEES) using the penetration–aspiration scale: a replication study. Dysphagia 17 308–315 Occurrence Handle12355146
G Gill J Hind J Robbins (2001) ArticleTitleProtocol 201: A NIDCD funded multisite clinical trial in swallowing—a progress report. ASHA Special Interest Division 13, Swallowing and Swallowing Disorders 10 17–19
C Murphy MM Gilmore CS Seely DP Salmon BR Lasker (1990) ArticleTitleOlfactory thresholds are associated with degree of dementia in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 11 465–469 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BA2c%2Fktl0%3D Occurrence Handle2381506
C Murphy S Nordin S Jinich (1999) ArticleTitleVery early decline in recognition memory for odors in Alzheimer’s disease. Aging Neuropsychol Cognition 6 229–240 Occurrence Handle10.1076/anec.6.3.229.777
S Nordin C Murphy (1996) ArticleTitleImpaired sensory and cognitive olfactory function in questionable Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychology 10 113–119 Occurrence Handle10.1037//0894-4105.10.1.113
Acknowledgements
We thank the nursing home administrators, staff, residents, and families who participated in this study. We are especially grateful to the nurses who assisted in the FEES procedures and to the anonymous reviewers for their helpful suggestions. Thanks also to Alina Prokopchuk for assistance in data collection, Karen Grace–Martin for statistical advice, and Joe Murray, Nancy Colodny, and especially Susan Hiss for their invaluable assistance and suggestions throughout the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pelletier, C.A., Lawless, H.T. Effect of Citric Acid and Citric Acid–Sucrose Mixtures on Swallowing in Neurogenic Oropharyngeal Dysphagia . Dysphagia 18, 231–241 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-003-0013-y
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-003-0013-y