Abstract
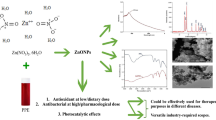
A considerable amount of fruit waste is being produced every day worldwide. The green synthesis of metal nanoparticles from fruit peel waste can be an innovative, cost-effective, and eco-friendly alternative to traditional methods. Copper nanoparticles (CuNPs) were synthesized by a green method using the pineapple peels extract (PLX) and copper sulfate pentahydrate. The formation of CuNPs was visually identified and detected by UV–Visible spectroscopy. The CuNPs were characterized by Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, particle size analyzer, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The antioxidant and reducing power of CuNPs were conducted by %DPPH scavenging and electron transfer-based ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) assay, respectively. The antibacterial properties of CuNPs were determined in gram-positive, and gram-negative bacteria. The results showed that the CuNPs were spherical in shape with mean particle size 290.5 nm. The zeta potential of the nanoparticles was found to be − 12.3 mV indicating the instability in the colloidal state. The FTIR study confirmed the peaks of phytochemicals present in the PLX and the nanoparticles supporting the use of pineapple peels as stabilizing, reducing and capping agents. Both the DPPH and reducing power assay depicted that the synthesized CuNPs had significant antioxidant activity. However, the synthesized CuNPs had strong inhibitory capacity against both gram-positive and gram-negative test organisms. Thus, the CuNPS could be used for its viable antibacterial potential to preserve fruits, flowers, and vegetables from bacterial contamination.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings in this study are presented within the paper. The data are also available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Anjum S, Ishaque S, Fatima H, Farooq W, Hano C, Abbasi BH, Anjum I (2021) Emerging Applications of Nanotechnology in Healthcare Systems: grand challenges and perspectives. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 14:707
Milewska S, Niemirowicz-Laskowska K, Siemiaszko G, Nowicki P, Wilczewska AZ, Car H (2021) Current trends and challenges in pharmacoeconomic aspects of nanocarriers as drug delivery systems for cancer treatment. Int J Nanomedicine 16:6593–6644
Rahman MM, Islam MR, Akash S, Harun-Or-Rashid M, Ray TK, Rahaman MS, Islam M, Anika F, Hosain MK, Aovi FI (2022) Recent advancements of nanoparticles application in cancer and neurodegenerative disorders: at a glance. Biomed Pharmacother 153:113305
Mazayen ZM, Ghoneim AM, Elbatanony RS, Basalious EB, Bendas ER (2022) Pharmaceutical nanotechnology: from the bench to the market. Fut J Pharmaceut Sci 8:12
Jeevanandam J, Barhoum A, Chan YS, Dufresne A, Danquah MK (2018) Review on nanoparticles and nanostructured materials: history, sources, toxicity and regulations. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 9:1050–1074
Joudeh N, Linke D (2022) Nanoparticle classification, physicochemical properties, characterization, and applications: a comprehensive review for biologists. J Nanobiotechnol 20:262
Mondal A, Paul P, Banerjee S (2022) Applications of metal oxide nanoparticles in cancer therapy. In: Patra JK (ed) Advances in nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems. Elsevier, pp 471–515
Rahman A, Harunsani MH, Tan AL, Khan MM (2021) Zinc oxide and zinc oxide-based nanostructures: biogenic and phytogenic synthesis, properties and applications. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 44:1333–1372
Ijaz I, Gilani E, Nazir A, Bukhari A (2020) Detail review on chemical, physical and green synthesis, classification, characterizations and applications of nanoparticles. Green Chem Lett Rev 13:223–245
Ying S, Guan Z, Ofoegbu PC, Clubb P, Rico C, He F, Hong J (2022) Green synthesis of nanoparticles: current developments and limitations. Environ Technol Innov 26:102336
Harish V, Ansari MM, Tewari D, Gaur M, Yadav AB, García-Betancourt M-L, Abdel-Haleem FM, Bechelany M, Barhoum A (2022) Nanoparticle and nanostructure synthesis and controlled growth methods. Nanomaterials 12:3226
Amjad R, Mubeen B, Ali SS, Imam SS, Alshehri S, Ghoneim MM, Alzarea SI, Rasool R, Ullah I, Nadeem MS, Kazmi I (2021) Green Synthesis and Characterization of Copper Nanoparticles Using Fortunella margarita Leaves. Polymers (Basel) 13:4364
Thandapani G, John J, Sekar V (2023) Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Spinacia oleracea leaf extract and evaluation of biological applications: Antioxidant, antibacterial, larvicidal and biosafety assay. Mater Today Commun 34:105248
Keskin C, Ölçekçi A, Baran A, Baran MF, Eftekhari A, Omarova S, Khalilov R, Aliyev E, Sufianov A, Beilerli A, Gareev I (2023) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles mediated Diospyros kaki L. (Persimmon): determination of chemical composition and evaluation of their antimicrobials and anticancer activities. Front Chem 11:1187808
Adewale Akintelu S, Kolawole Oyebamiji A, Charles Olugbeko S, Felix Latona D (2021) Green chemistry approach towards the synthesis of copper nanoparticles and its potential applications as therapeutic agents and environmental control. Curr Res Green Sustain Chem 4:100176
Khan MM, Matussin SN, Rahman A (2022) Recent progress of phytogenic synthesis of ZnO, SnO2, and CeO2 nanomaterials. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 45:619–645
Rahman A, Harunsani MH, Tan AL, Ahmad N, Hojamberdiev M, Khan MM (2021) Effect of Mg doping on ZnO fabricated using aqueous leaf extract of Ziziphus mauritiana Lam. for antioxidant and antibacterial studies. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 44:875–889
Bhagat M, Anand R, Sharma P, Rajput P, Sharma N, Singh K (2021) Multifunctional copper nanoparticles: synthesis and applications. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 10:063011
Nazar N, Bibi I, Kamal S, Iqbal M, Nouren S, Jilani K, Umair M, Ata S (2018) Cu nanoparticles synthesis using biological molecule of P. granatum seeds extract as reducing and capping agent: growth mechanism and photo-catalytic activity. Int J Biol Macromol 106:1203–1210
Naidi SN, Khan F, Harunsani MH, Tan AL, Kim Y-M, Khan MM (2022) Effect of Zr doping on photoantioxidant and antibiofilm properties of CeO2 NPs fabricated using aqueous leaf extract of Pometia pinnata. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 45:279–295
Khan MM, Harunsani MH, Tan AL, Hojamberdiev M, Azamay S, Ahmad N (2020) Antibacterial activities of zinc oxide and Mn-doped zinc oxide synthesized using Melastoma malabathricum (L.) leaf extract. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 43:1499–1508
Letchumanan D, Sok SP, Ibrahim S, Nagoor NH, Arshad NM (2021) Plant-based biosynthesis of copper/copper oxide nanoparticles: an update on their applications in biomedicine, mechanisms, and toxicity. Biomolecules 11:564
Mohamed EA (2020) Green synthesis of copper & copper oxide nanoparticles using the extract of seedless dates. Heliyon 6:e03123
Chandrakala V, Aruna V, Angajala G (2022) Review on metal nanoparticles as nanocarriers: current challenges and perspectives in drug delivery systems. Emergent Materials 5:1593–1615
Sardoiwala MN, Kaundal B, Roy Choudhury S (2018) Development of engineered nanoparticles expediting diagnostic and therapeutic applications across blood-brain barrier. In: Mustansar Hussain C, (ed) Handbook of nanomaterials for industrial applications. Elsevier, 696–709.
Mody VV, Siwale R, Singh A, Mody HR (2010) Introduction to metallic nanoparticles. J Pharm Bioallied Sci 2:282–289
El-Saadony MT, Abd El-Hack ME, Taha AE, Fouda MMG, Ajarem JS, S NM, Allam AA, Elshaer N, (2020) Ecofriendly synthesis and insecticidal application of copper nanoparticles against the storage pest tribolium castaneum. Nanomater (Basel) 10:587
Rai M, Ingle AP, Pandit R, Paralikar P, Shende S, Gupta I, Biswas JK, Silva SSd (2018) Copper and copper nanoparticles: role in management of insect-pests and pathogenic microbes. Nanotechnol Rev 7:303–315
Majumdar TD, Singh M, Thapa M, Dutta M, Mukherjee A, Ghosh CK (2019) Size-dependent antibacterial activity of copper nanoparticles against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae: a synthetic and mechanistic approach. Coll Inter Sci Commun 32:100190
Li T, Shen P, Liu W, Liu C, Liang R, Yan N, Chen J (2014) Major polyphenolics in pineapple peels and their antioxidant interactions. Int J Food Prop 17:1805–1817
Rivera AMP, Toro CR, Londoño L, Bolivar G, Ascacio JA, Aguilar CN (2023) Bioprocessing of pineapple waste biomass for sustainable production of bioactive compounds with high antioxidant activity. J Food Meas Charact 17:586–606
Tang PL, Hassan O (2020) Bioconversion of ferulic acid attained from pineapple peels and pineapple crown leaves into vanillic acid and vanillin by Aspergillus niger I-1472. BMC Chemist 14:7
Zhou W, Ye C, Geng L, Chen G, Wang X, Chen W, Sa R, Zhang J, Zhang X (2021) Purification and characterization of bromelain from pineapple (Ananas comosus L.) peel waste. J Food Sci 86:385–393
Varilla C, Marcone M, Paiva L, Baptista J (2021) Bromelain, a group of pineapple proteolytic complex enzymes (Ananas comosus) and their possible therapeutic and clinical effects. A Summary Foods 10:2249
Lourenço SC, Campos DA, Gómez-García R, Pintado M, Oliveira MC, Santos DI, Corrêa-Filho LC, Moldão-Martins M, Alves VD (2021) Optimization of natural antioxidants extraction from pineapple peel and their stabilization by spray drying. Foods 10:1255
Ghidan AY, Al-Antary TM, Awwad AM (2016) Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Punica granatum peels extract: Effect on green peach Aphid. Environ Nanotechnol Monitor Manage 6:95–98
Amaliyah S, Pangesti DP, Masruri M, Sabarudin A, Sumitro SB (2020) Green synthesis and characterization of copper nanoparticles using Piper retrofractum Vahl extract as bioreductor and capping agent. Heliyon 6:e04636
Vanathi P, Rajiv P, Sivaraj R (2016) Synthesis and characterization of Eichhornia-mediated copper oxide nanoparticles and assessing their antifungal activity against plant pathogens. Bull Mater Sci 39:1165–1170
Hajizadeh YS, Harzandi N, Babapour E, Yazdanian M, Ranjbar R (2022) Green synthesize and characterization of copper nanoparticles using Iranian propolis extracts. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2022:8100440
Mallick A, Sahu R, Nandi G, Dua TK, Shaw TK, Dhar A, Kanu A, Paul P (2023) Development of liposomal formulation for controlled delivery of valacyclovir: an in vitro study. J Pharm Innov 18:1020–1029
Dua TK, Giri S, Nandi G, Sahu R, Shaw TK, Paul P (2023) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Eupatorium adenophorum leaf extract: characterizations, antioxidant, antibacterial and photocatalytic activities. Chem Pap 77:297–2956
Arun SB, Karthik BM, Yatish KV, Prashanth KN, Balakrishna GR (2023) Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using the Bombax ceiba plant: biodiesel production and nano-additive to investigate diesel engine performance-emission characteristics. Energy 274:127345
Baruah K, Konthoujam I, Lyndem S, Aguan K, Singha Roy A (2023) Complexation of turmeric and curcumin mediated silver nanoparticles with human serum albumin: further investigation into the protein-corona formation, anti-bacterial effects and cell cytotoxicity studies. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 294:122540
Das PJ, Paul P, Mukherjee B, Mazumder B, Mondal L, Baishya R, Debnath MC, Dey KS (2015) Pulmonary delivery of voriconazole loaded nanoparticles providing a prolonged drug level in lungs: a promise for treating fungal infection. Mol Pharm 12:2651–2664
Kaningini AG, Motlhalamme T, More GK, Mohale KC, Maaza M (2023) Antimicrobial, antioxidant, and cytotoxic properties of biosynthesized copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO-NPs) using Athrixia phylicoides DC. Heliyon 9:e15265
Oyaizu M (1986) Studies on products of browning reaction prepared from glucose amine products derived from bees. J Pharm Biomed Anal 41:1220–1234
Niknam R, Ghanbarzadeh B, Ayaseh A, Rezagholi F (2020) Barhang (Plantago major L.) seed gum: ultrasound-assisted extraction optimization, characterization, and biological activities. J Food Process Preservat 44:e14750
Haydar MS, Das D, Ghosh S, Mandal P (2022) Implementation of mature tea leaves extract in bioinspired synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles: preparation, process optimization, characterization, and assessment of therapeutic potential. Chem Pap 76:491–514
Ameen F, Amirul Islam M, Dhanker R (2022) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from vegetable waste of pea Pisum sativum and bottle gourd Lagenaria siceraria: characterization and antibacterial properties. Front Environ Sci 10:941554
Nagar N, Devra V (2018) Green synthesis and characterization of copper nanoparticles using Azadirachta indica leaves. Mater Chem Phys 213:44–51
Nzilu DM, Madivoli ES, Makhanu DS, Wanakai SI, Kiprono GK, Kareru PG (2023) Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles and its efficiency in degradation of rifampicin antibiotic. Sci Rep 13:14030
Anna Thomas A, Varghese RM, Rajeshkumar S (2022) Antimicrobial effects of copper nanoparticles with green tea and neem formulation. Bioinformation 18:284–288
Polanía AM, Ramírez C, Londoño L, Bolívar G, Aguilar CN (2023) Encapsulation of pineapple peel extracts by ionotropic gelation using corn starch, Weissella confusa exopolysaccharide, and sodium alginate as wall materials. Foods 12:2943
Mali SC, Dhaka A, Githala CK, Trivedi R (2020) Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles using Celastrus paniculatus Wild. leaf extract and their photocatalytic and antifungal properties. Biotechnol Rep 27:e00518
Clayton KN, Salameh JW, Wereley ST, Kinzer-Ursem TL (2016) Physical characterization of nanoparticle size and surface modification using particle scattering diffusometry. Biomicrofluidics 10:054107
Varadavenkatesan T, Selvaraj R, Vinayagam R (2016) Phyto-synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Mussaenda erythrophylla leaf extract and their application in catalytic degradation of methyl orange dye. J Mol Liq 221:1063–1070
Keabadile OP, Aremu AO, Elugoke SE, Fayemi OE (2020) Green and traditional synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles—comparative study. Nanomaterials 10:2502
Keskin C, Baran A, Baran MF, Hatipoğlu A, Adican MT, Atalar MN, Huseynova I, Khalilov R, Ahmadian E, Yavuz Ö (2022) Green synthesis, characterization of gold nanomaterials using Gundelia tournefortii leaf extract, and determination of their nanomedicinal (antibacterial, antifungal, and cytotoxic) potential. J Nanomater 2022:1–10
Nasrollahzadeh M, Sajadi SM, Maham M (2015) Tamarix gallica leaf extract mediated novel route for green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles and their application for N-arylation of nitrogen-containing heterocycles under ligand-free conditions. RSC Adv 5:40628–40635
Iliger KS, Sofi TA, Bhat NA, Ahanger FA, Sekhar JC, Elhendi AZ, Al-Huqail AA, Khan F (2021) Copper nanoparticles: Green synthesis and managing fruit rot disease of chilli caused by Colletotrichum capsici. Saudi J Biol Sci 28:1477–1486
Alahdal FAM, Qashqoosh MTA, Manea YK, Mohammed RKA, Naqvi S (2023) Green synthesis and characterization of copper nanoparticles using Phragmanthera austro arabica extract and their biological/environmental applications. Sustain Mater Technol 35:e00540
Rajesh K, Ajitha B, Reddy YAK, Suneetha Y, Reddy PS (2018) Assisted green synthesis of copper nanoparticles using Syzygium aromaticum bud extract: physical, optical and antimicrobial properties. Optik 154:593–600
Rajeshkumar S, Rinitha G (2018) Nanostructural characterization of antimicrobial and antioxidant copper nanoparticles synthesized using novel Persea americana seeds. OpenNano 3:18–27
Shanmugapriya J, Reshma CA, Srinidhi V, Harithpriya K, Ramkumar KM, Umpathy D, Gunasekaran K, Subashini R (2022) Green Synthesis of copper nanoparticles using <i>Withania somnifera</i> and its antioxidant and antibacterial activity. J Nanomater 2022:7967294
Baran NA, Atalar MN, Baran MF, Keskin C, Düz MZ, Yavuz Ö, Kandemir SI, Kavak DE (2021) Biosynthesis of black mulberry leaf extract and silver nanoparticles (AgNPs): characterization, antimicrobial and cytotoxic activity applications. MAS J Appl Sci 6:685–700
Raffi M, Mehrwan S, Bhatti TM, Akhter JI, Hameed A, Yawar W, Ul Hasan MM (2010) Investigations into the antibacterial behavior of copper nanoparticles against Escherichia coli. Ann Microbiol 60:75–80
Ma X, Zhou S, Xu X, Du Q (2022) Copper-containing nanoparticles: Mechanism of antimicrobial effect and application in dentistry-a narrative review. Front Surg 9:905892
Acknowledgements
The authors thank to Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, University of North Bengal, Darjeeling, India, for providing necessary infrastructural facility and required chemicals.
Funding
No funding was received for the publication of this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SM, TKD, SE, MSH: investigation, data collection, formal analysis, writing—original draft, visualization. SS, APR, RS, GN, SR: methodology, formal analysis, writing—review and editing. PP: conceptualization, resources, investigation, supervision, writing—review, editing, and manuscript proof reading. All the authors read and approve the current manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mitra, S., Dua, T.K., Easmin, S. et al. Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles by using pineapple peel waste: in vitro characterizations and antibacterial potential. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-024-02982-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-024-02982-w