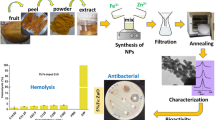
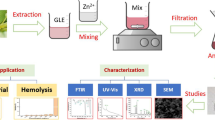
Abstract
The aim of this work was to synthesize 0.02 and 0.06 Mg-doped ZnO nanoparticles (NPs) using the aqueous extract of Plectranthus barbatus leaf. The structural integrity of the hexagonal phase was emphasized by X-ray diffraction analysis. The average crystallite size (D) of 0.02 and 0.06 Mg-doped ZnO NPs was found to be 23.83 and 26.95 nm, respectively. The scanning electron microscope images revealed a surface morphology of irregular nano-shapes of about 83 nm diameter with an elongated one-dimensional structure. The hemolysis activity demonstrated the safe nature of the synthesized materials at low doses. Antibacterial activity against S. aureus and E. coli, which assessed using the disc diffusion method, indicated that the prepared NPs could inhibit S. aureus but not E. coli. These findings suggest that the synthesized NPs could be explored for potential applications in biotechnology and medicine.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Demissie MG, Sabir FK, Edossa GD, Gonfa BA (2020) Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Lippia adoensis (Koseret) and evaluation of its antibacterial activity. J Chem 2020:1–9
Shabaani M, Rahaiee S, Zare M, Jafari SM (2020) Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using loquat seed extract; Biological functions and photocatalytic degradation properties. Lwt 134(14):110133
Chen H, Qu Y, Sun L, Peng J, Ding J (2019) Band structures and optical properties of Ag and Al co-doped ZnO by experimental and theoretic calculation. Physica E 114:113602
Rohith NM, Kathirvel P, Saravanakumar S, Mohan L (2018) Influence of Ag doping on the structural, optical, morphological and conductivity characteristics of ZnO nanorods. Optik Int J Light Electron Opt 172:940–952
Alharthi MN, Ismail I, Bellucci S, Jaremko M, Abo-Aba SEM, Salam MA (2023) Biosynthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ziziphus jujube plant extract assisted by ultrasonic irradiation and their biological applications. Separations 10:78
Suresh S et al (2022) Antibacterial activity and photocatalytic oxidative performance of zinc oxide nanorods biosynthesized using Aerva lanata leaf extract. Inorg Chem Commun 139:109398
Dobrucka R, Dugaszewska J (2016) Biosynthesis and antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticles using Trifolium pratense flower extract. J Biol Sci 23:517–523
Gawade VV, Gavade NL, Shinde HM, Babar SB, Kadam AN, Garadkar KM (2017) Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by using Calotropis procera leaves for the photodegradation of methyl orange. Mater Sci Mater Electron 28:14033–14039
Rajeswari R, Pitchai T, Thangamuthu R, Sridhar S, Alagan V (2017) Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Carica papaya leaf extracts for photocatalytic and photovoltaic applications. Mater Sci Mater Electron 28(14):10374–10381
Ba-Abbad M, Takriff MS, Benamor A, Mahmoudi E, Mohammad AW (2017) Arabic gum as green agent for ZnO nanoparticles synthesis: properties, mechanism and antibacterial activity. Mater Sci Mater Electron 28(16):12100–12107
Rahman A, Harunsani MH, Tan AL, Khan MM (2021) Zinc oxide and zinc oxide-based nanostructures: biogenic and phytogenic synthesis, properties and applications. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 44:1333–1372
Lin M-H et al (2021) Hybrid ZnO/chitosan antimicrobial coatings with enhanced mechanical and bioactive properties for titanium implants. Carbohyd Polym 257:117639
Puspasari V, Ridhova A, Hermawan A, Amal MI, Khan MM (2022) ZnO-based antimicrobial coatings for biomedical applications. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 45(9):1421–1445
Ye L et al (2023) The CuO and AgO co-modified ZnO nanocomposites for promoting wound healing in Staphylococcus aureus infection. Mater Today Bio 18:100552
Nadeem MS et al (2021) Hydrothermally derived co, Ni co-doped ZnO nanorods; structural, optical, and morphological study. Opt Mater 111:110606
Ahmad W, Kalra D (2020) Green synthesis, characterization and anti microbial activities of ZnO nanoparticles using Euphorbia hirta leaf extract. J King Saud Univy-Sci 32(4):2358–2364
Nadeem MS, Munawar T, Mukhtar F, Rahman MNu, Riaz M, Iqbal F (2021) Enhancement in the photocatalytic and antimicrobial properties of ZnO nanoparticles by structural variations and energy bandgap tuning through Fe and Co co-doping. Ceram Int 47(8):11109–11121
Khan MM, Harunsani MH, Tan AL, Hojamberdiev M, Poi YA, Ahmad N (2020) Antibacterial studies of ZnO and Cu-doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized using aqueous leaf extractof Stachytarpheta jamaicensis. BioNanoScience 10(4):1037–1048
Slathia S, Gupta T, Chauhan RP (2021) Green synthesis of Ag–ZnO nanocomposite using Azadirachta indica leaf extract exhibiting excellent optical and electrical properties. Phys Condens Matter 621:413287
Badhusha MSM, Joel C, Khan RI, Vijayakumar N (2021) Green synthesis and characterization of Fe doped ZnO nanoparticles and their interaction with bovine serum albumin. J Indian Chem Soc 98:100197
Noukelag SK, Razanamahandry LC, Ntwampe SKO, Arendse CJ, Maaza M (2021) Industrial dye removal using bio-synthesized Ag-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 16:100463
Khan MM, Matussin SN, Rahman A (2022) Recent progress of phytogenic synthesis of ZnO, SnO2, and CeO2 nanomaterials. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 45(4):619–645
Saravanadevi K, Kavitha M, Karpagavinayagam P, Saminathan K, Vedhi C (2022) Biosynthesis of ZnO and Ag doped ZnO nanoparticles from Vitis vinifera leaf for antibacterial, photocatalytic application. Mater Today Proc 48:352–356
Rahman A, Harunsani MH, Tan AL, Ahmad N, Min B-K, Khan MM (2021) Influence of Mg and Cu dual-doping on phytogenic synthesized ZnO for light induced antibacterial and radical scavenging activities. Mater Sci Semicond Process 128:105761
Munawar T et al (2020) Zn0.9Ce0.05MO (M = Er, Y, V) nanocrystals: structural and energy bandgap engineering of ZnO for enhancing photocatalytic and antibacterial activity. Ceram Int 46(10):14369–14383
Sivaselvan S, Muthukumaran S (2016) Microstructure, tuning of band gap, enhanced green band emission and antibacterial studies of Cu, Cr dual doped ZnO nanoparticles by annealing temperature. J Inorganic Organomet Polym Mater 26(5):950–961
Arunpandian M et al (2021) Fabrication of Cu/ZnO system: A dual performer as photocatalyst and luminescent material. Inorg Chem Commun 134:109022
Chen H, Qu Y, Sun L, Peng J, Ding J (2019) Band structures and optical properties of Ag and Al co-doped ZnO by experimental and theoretic calculation. PhysE Low-Dimens Syst Nanostruct 114:113602
Geetha A, Sakthivel R, Mallika J (2017) Characterization of Mg DOPED ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by a novel green route using Azadirachta indica gum and its antibacterial activity. World J Pharm Pharm Sci 6(8):1189–1201
Rahman A, Harunsani MH, Tan AL, Ahmad N, Hojamberdiev M, Khan MM (2021) Effect of Mg doping ZnO fabricated using aqueous leaf extract of Ziziphus mauritiana Lam. for antioxidant and antibacterial studies. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 44:875–889
Almeida WAd et al (2021) Effects of Plectranthus barbatus leaf extract on survival, digestive proteases, midgut morphophysiology and gut microbiota homeostasis of Aedes aegypti larvae. S Afr J Bot 141:116–125
Cordeiro M et al (2021) Phytochemical characterization and biological activities of Plectranthus barbatus Andrews. Brazil J Biol 82:e236297
Ezeonwumelu JO et al (2019) Phytochemical screening, toxicity, analgesic and anti-pyretic studies of aqueous leaf extract of Plectranthus barbatus [Andrews. Engl.] in rats. Pharmacol Pharm 10(4):205–221
Valdes L, Mislankar S, Paul A (1987) Coleus barbatus (C. forskohlii) (Lamiaceae) and the potential new drug forskolin (Coleonol). Econ Bot 41:474–483
Abdel-Mogib M, Albar H, Batterjee S (2002) Chemistry of the genus Plectranthus. Molecules 7(2):271–301
Al-Hammadi A, Alnehia A, Al-Sharabi A, Al-Odayni A-B, Abdu NA, Saeed WS (2023) Plectranthus barbatus leaf extract-mediated synthesis of ZnS and Mg-doped ZnS NPs: structural, optical, morphological, and antibacterial studies. Nanomater Nanotechnol 2023:1399904
Saif MMS, Alodeni RM, Alghamdi AA, Al-Odayni A-B (2022) Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, thermal analysis and in vitro bioactivity studies of the N-(cinnamylidene) tryptophan Schiff base. J King Saud Univ-Sci 34(4):101988
Alnehia A et al (2023) Garlic extract-mediated synthesis of ZnS nanoparticles: structural, optical, antibacterial, and hemolysis studies. J Nanomater 2023:8200912
Alnehia A, Al-Sharabi A, Al-Hammadi AH, Al-Odayni A-B, Alramadhan SA, Alodeni RM (2023) Phyto-mediated synthesis of silver-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles from Plectranthus barbatus leaf extract: optical, morphological, and antibacterial properties. Biomass Convers Biorefin. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-023-03907-5
Al-Sharabi A, Alnehia A, Al-Hammadi AH, Alhumaidha KA, AL-Osta A (2022) The effect of Nigella sativa seed extract concentration on crystal structure, band gap and antibacterial activity of ZnS-NPs prepared by green route. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 33:20812–20822
Alnahari H, Al-Hammadi AH, Al-Sharabi A, Alnehia A, Al-Odayni A-B (2023) Structural, morphological, optical, and antibacterial properties of CuO–Fe2O3–MgO–CuFe2O4nanocomposite synthesized via auto-combustion route. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 34:682
Kumar KC, Rao NM, Kaleemulla S, Rao GV (2017) Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Sn Doped ZnS nano powders prepared by solid state. Phys Condens Matter 522:75–80
Saleem S et al (2022) Modification in structural, optical, morphological, and electrical properties of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles (NPs) by metal (Ni, Co) dopants for electronic device applications. Arab J Chem 15(1):103518
Rafique S, Kasi AK, Kasi JK, Aminullah MB, Shakoor Z (2020) Fabrication of silver-doped zinc oxide nanorods piezoelectric nanogenerator on cotton fabric to utilize and optimize the charging system. Nanomater Nanotechnol 10:1847980419895741
Ramesan M, Greeshma K, Parvathi K, Anilkumar T (2020) Structural, electrical, thermal, and gas sensing properties of new conductive blend nanocomposites based on polypyrrole/phenothiazine/silver-doped zinc oxide. J Vinyl Add Tech 26(2):187–195
Tayel AA et al (2011) Antibacterial action of zinc oxide nanoparticles against foodborne pathogens. J Food Saf 31(2):211–218
Lallo da Silva B et al (2019) Relationship between structure and antimicrobial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles: an overview. Int J Nanomed 14:9395–9410
Alnehia A, Al-Odayni A-B, Al-Sharabi A, Al-Hammadi AH, Saeed WS (2022) Pomegranate peel extract–mediated green synthesis of ZnO-NPs: extract concentration-dependent structure, optical, and antibacterial activity. J Chem 2022:9647793
Wali Muhammad NU, Haroon M, Abbasi BH (2019) Optical, morphological and biological analysis of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) using Papaver somniferum L. RSC Adv 9:29541–29548
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deputyship for Research & Innovation, Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia for funding this research (IFKSURC-1-1909).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Odayni, AB., Alnehia, A., Al-Sharabi, A. et al. Biofabrication of Mg-doped ZnO nanostructures for hemolysis and antibacterial properties. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 46, 1817–1824 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-023-02937-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-023-02937-7